SwiftUI sample app using Clean Architecture. Examples of working with SwiftData persistence, networking, dependency injection, unit testing, and more.
Articles related to this project
- Clean Architecture for SwiftUI
- Programmatic navigation in SwiftUI project
- Separation of Concerns in Software Design
Clean Architecture for SwiftUI + Combine
A demo project showcasing the setup of the SwiftUI app with Clean Architecture.
The app uses the restcountries.com REST API to show the list of countries and details about them.
Check out mvvm branch for the MVVM revision of the same app.
For the example of handling the authentication state in the app, you can refer to my other tiny project that harnesses the locks and keys principle for solving this problem.

Key features
- End of 2024 update: the project was fully revamped to use modern iOS stack technologies
- Decoupled Presentation, Business Logic, and Data Access layers
- Programmatic navigation. Push notifications with deep link
- Redux-like centralized
AppStateas the single source of truth - Native SwiftUI dependency injection
- Handling of the system events (such as
didBecomeActive,willResignActive) - Full test coverage, including the UI (thanks to the ViewInspector)
- Simple yet flexible networking layer built on async - await
- UI - vanilla SwiftUI + Combine
- Data persistence with SwiftData
Architecture overview
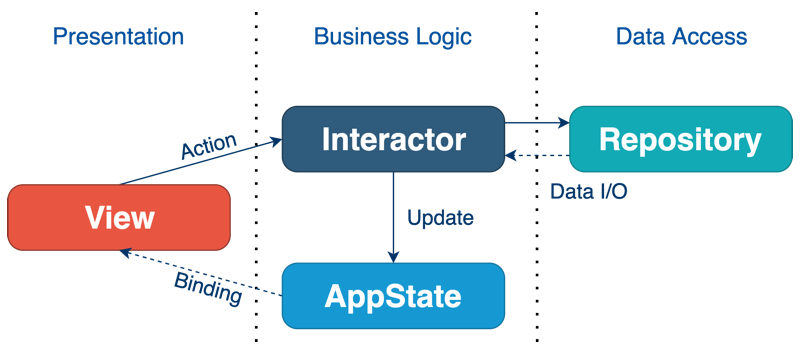
Presentation Layer
SwiftUI views that contain no business logic and are a function of the state.
Side effects are triggered by the user’s actions (such as a tap on a button) or view lifecycle event onAppear and are forwarded to the Interactors.
State and business logic layer (AppState + Interactors) are natively injected into the view hierarchy with @Environment.
Business Logic Layer
Business Logic Layer is represented by Interactors.
Interactors receive requests to perform work, such as obtaining data from an external source or making computations, but they never return data back directly.
Instead, they forward the result to the AppState or to a Binding. The latter is used when the result of work (the data) is used locally by one View and does not belong to the AppState.
Previously, this app did not use CoreData for persistence, and all loaded data were stored in the AppState.
With the persistence layer in place we have a choice - either to load the DB content onto the AppState, or serve the data from Interactors on an on-demand basis through Binding.
The first option suits best when you don’t have a lot of data, for example, when you just store the last used login email in the UserDefaults. Then, the corresponding string value can just be loaded onto the AppState at launch and updated by the Interactor when the user changes the input.
The second option is better when you have massive amounts of data and introduce a fully-fledged database for storing it locally.
Data Access Layer
Data Access Layer is represented by Repositories.
Repositories provide asynchronous API (Publisher from Combine) for making CRUD operations on the backend or a local database. They don’t contain business logic, neither do they mutate the AppState. Repositories are accessible and used only by the Interactors.


