Python package for the evaluation of odometry and SLAM
evo
Python package for the evaluation of odometry and SLAM
| Linux / macOS / Windows / ROS / ROS2 |
|---|
This package provides executables and a small library for handling, evaluating and comparing the trajectory output of odometry and SLAM algorithms.
Supported trajectory formats:
- ‘TUM’ trajectory files
- ‘KITTI’ pose files
- ‘EuRoC MAV’ (.csv groundtruth and TUM trajectory file)
- ROS and ROS2 bagfile with
geometry_msgs/PoseStamped,geometry_msgs/TransformStamped,geometry_msgs/PoseWithCovarianceStamped,geometry_msgs/PointStampedornav_msgs/Odometrytopics or TF messages
See here for more infos about the formats.
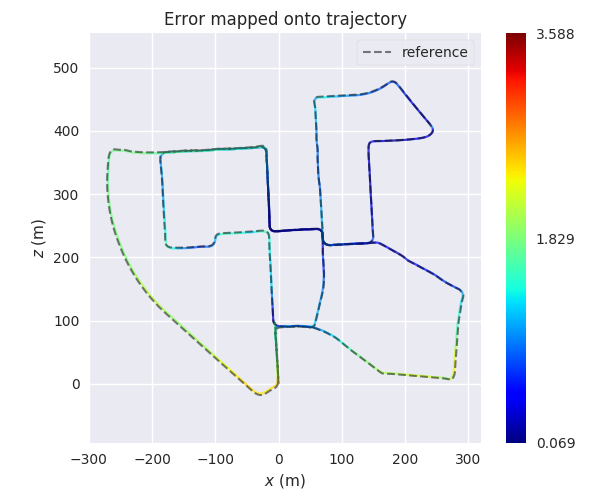
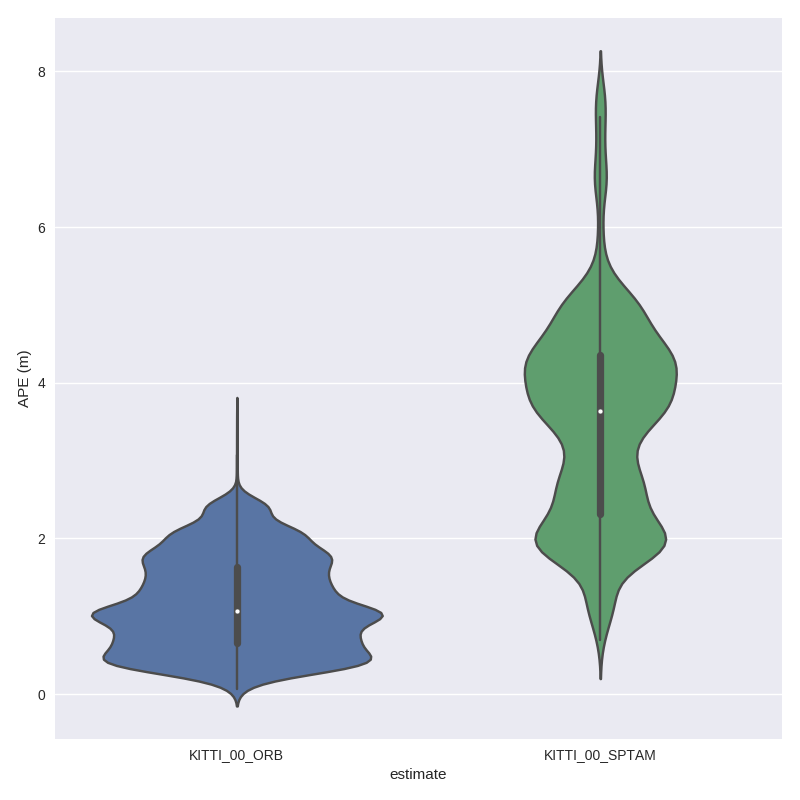
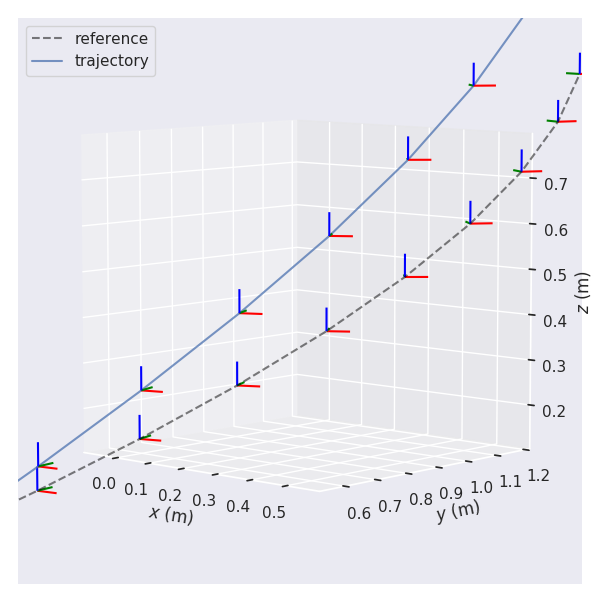
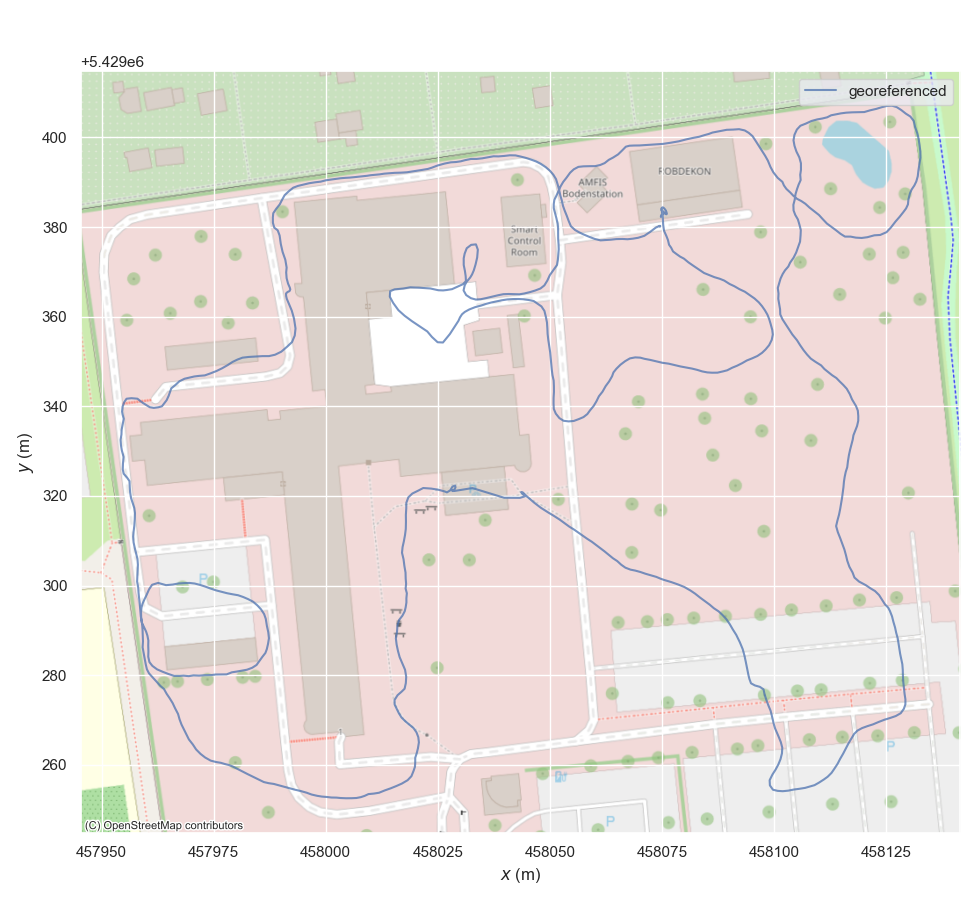
Why?
evo has several advantages over other public benchmarking tools:
- common tools for different formats
- algorithmic options for association, alignment, scale adjustment for monocular SLAM etc.
- flexible options for output, plotting or export (e.g. LaTeX plots or Excel tables)
- a powerful, configurable CLI that can cover many use cases
- modular
coreandtoolslibraries for custom extensions - faster than other established Python-based tools (see here)
What it’s not: a 1-to-1 re-implementation of a particular evaluation protocol tailored to a specific dataset.
Installation / Upgrade
Installation is easy-peasy if you’re familiar with this: https://xkcd.com/1987/#
The latest version of evo supports Python 3.10+.
You might also want to use a virtual environment.
From PyPi
If you just want to use the executables of the latest release version, the easiest way is to run:
pip install evo
This will download the package and its dependencies from PyPI and install or upgrade them. If you want, you can subscribe to new releases via https://libraries.io/pypi/evo.
To upgrade to a newer version: pip install --upgrade evo
From Source
Run this in the repository’s base folder:
pip install --editable .
Tab completion
Tab completion is supported via the argcomplete package. Run activate-global-python-argcomplete after the installation to use it.
Dependencies
Python packages
evo has some required dependencies that are automatically resolved during installation with pip.
See the pyproject.toml file for all details.
PyQt5 (optional)
PyQt5 will give you the enhanced GUI for plot figures from the “Qt5Agg” matplotlib backend (otherwise: “TkAgg”). If PyQt5 is already installed when installing this package, it will be used as a default (see evo_config show). To change the plot backend afterwards, run evo_config set plot_backend Qt5Agg.
If you run into issues with installing tkinter, trying PyQt5 is a good idea.
ROS (optional)
Some ROS-related features require a ROS installation, see here. We are testing this package with ROS Kilted.
Reading ROS bag files works also without a ROS installation thanks to the great rosbags package that is installed together with evo. This allows you also to read ROS 1 & 2 bags even if you don’t have one of those ROS distros installed. (except for reading
/tftopics, because there we need the buffer implementation from ROS)
contextily (optional)
contextily is required for adding map tiles to plots of geo-referenced data.
Command Line Interface
After installation with pip, the following executables can be called globally from your command-line:
Metrics:
evo_ape- absolute pose errorevo_rpe- relative pose error
Tools:
evo_traj- tool for analyzing, plotting or exporting one or more trajectoriesevo_res- tool for comparing one or multiple result files fromevo_apeorevo_rpeevo_fig- (experimental) tool for re-opening serialized plots (saved with--serialize_plot)evo_config- tool for global settings and config file manipulation
Call the commands with --help to see the options, e.g. evo_ape --help. Tab-completion of command line parameters is available on UNIX-like systems.
More documentation
Check out the Wiki on GitHub.
Example Workflow
There are some example trajectories in the source folder in test/data.
1.) Plot multiple trajectories
Here, we plot two KITTI pose files and the ground truth using evo_traj:
cd test/data
evo_traj kitti KITTI_00_ORB.txt KITTI_00_SPTAM.txt --ref=KITTI_00_gt.txt -p --plot_mode=xz
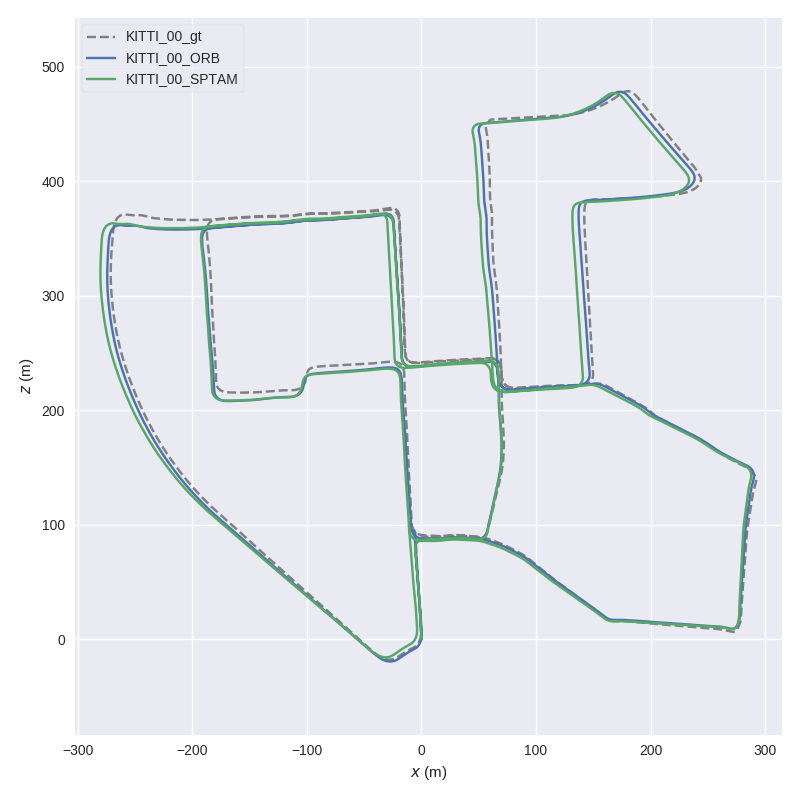
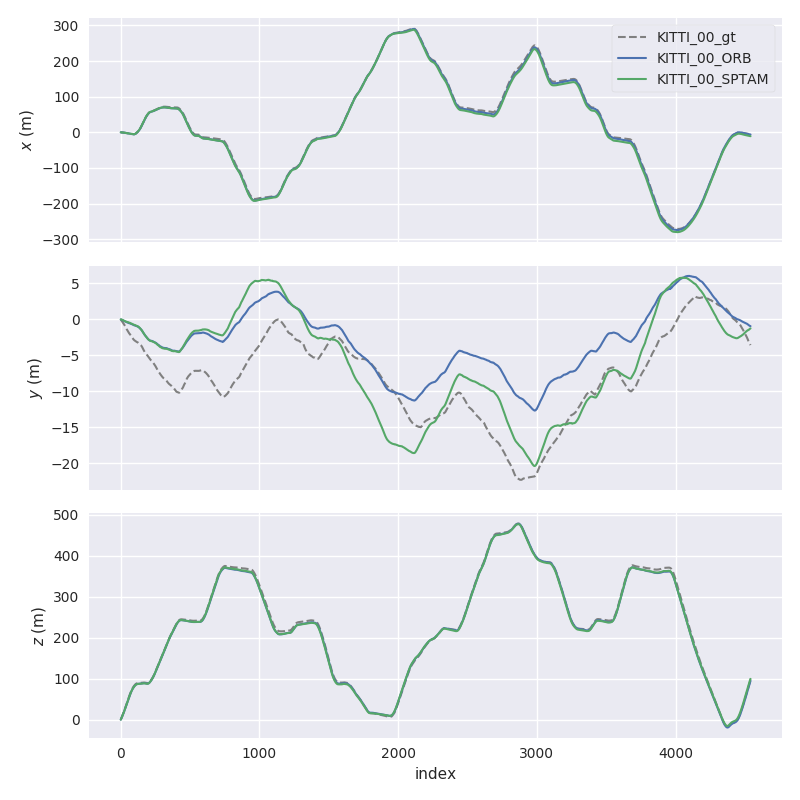
2.) Run a metric on trajectories
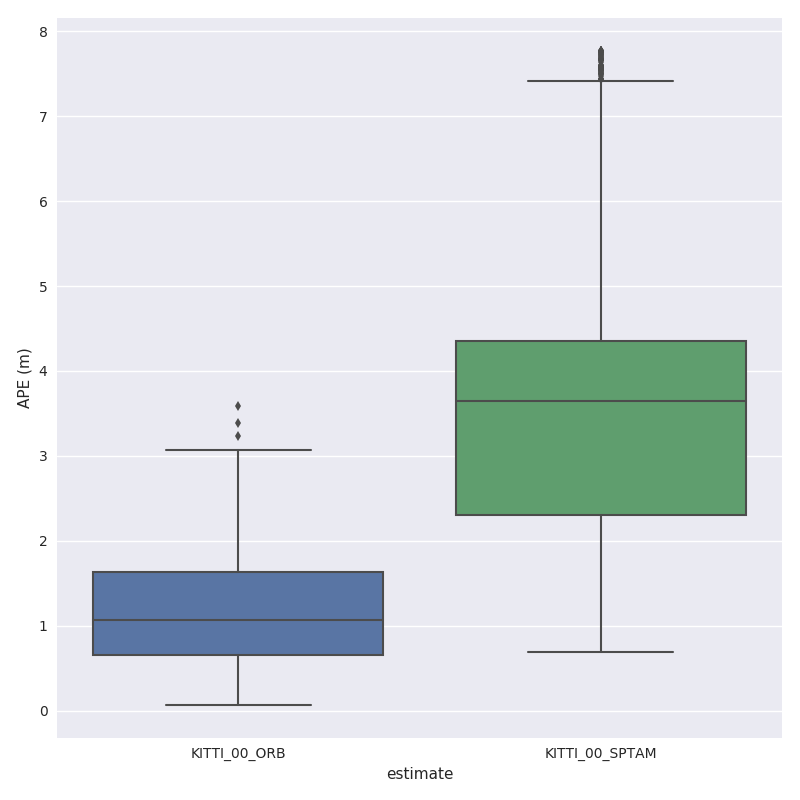
For example, here we calculate the absolute pose error for two trajectories from ORB-SLAM and S-PTAM using evo_ape (KITTI_00_gt.txt is the reference (ground truth)) and plot and save the individual results to .zip files for evo_res:
First trajectory (ORB Stereo):
mkdir results
evo_ape kitti KITTI_00_gt.txt KITTI_00_ORB.txt -va --plot --plot_mode xz --save_results results/ORB.zip
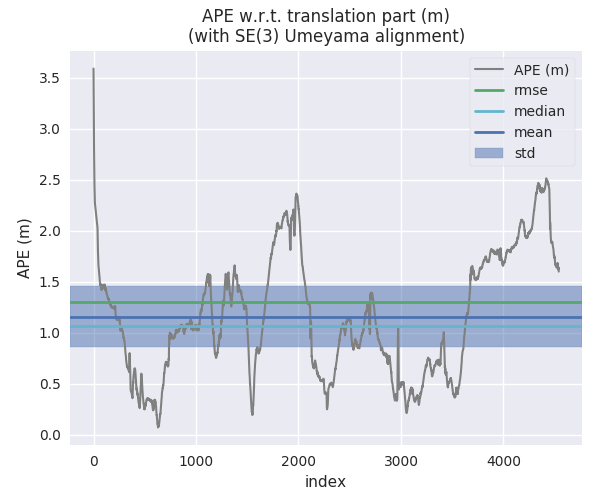

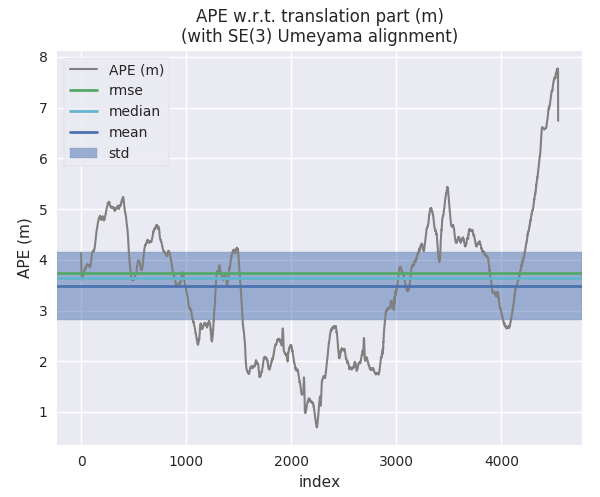
Second trajectory (S-PTAM):
evo_ape kitti KITTI_00_gt.txt KITTI_00_SPTAM.txt -va --plot --plot_mode xz --save_results results/SPTAM.zip
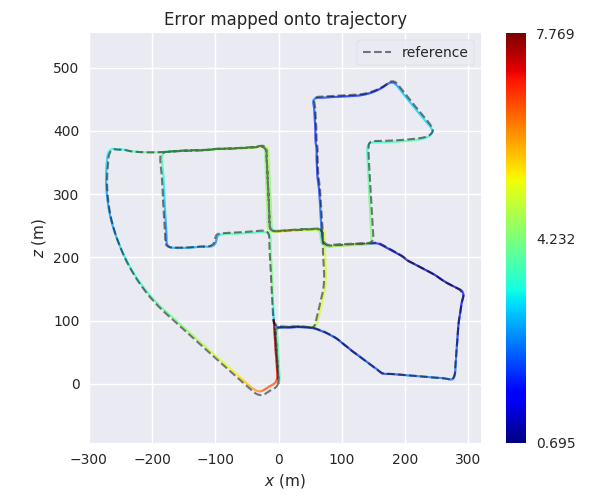
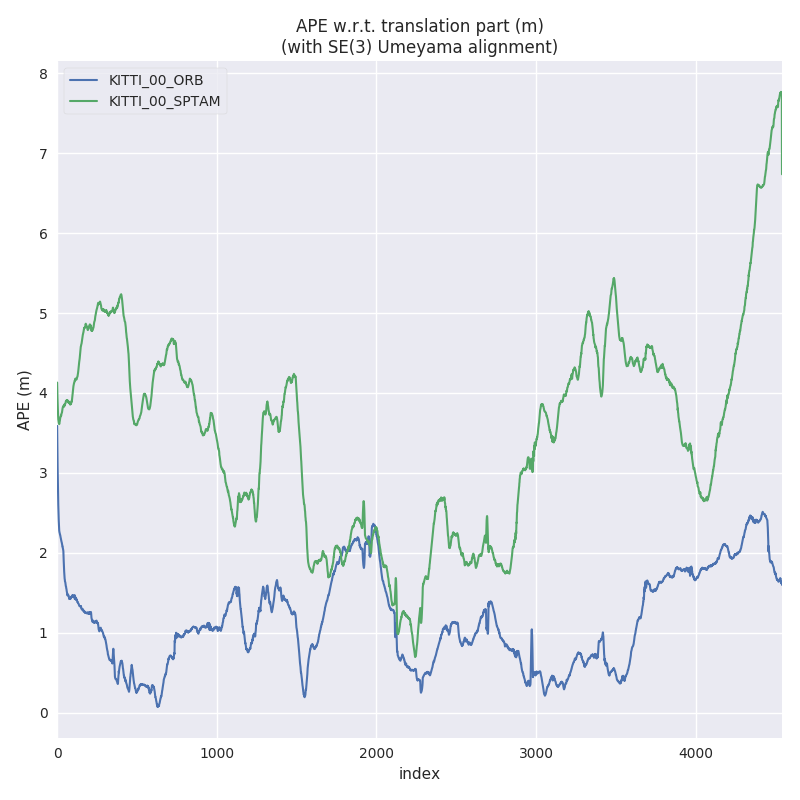
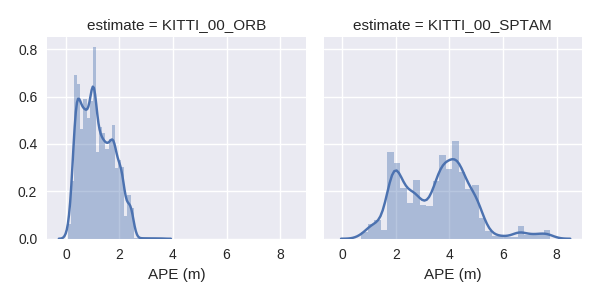
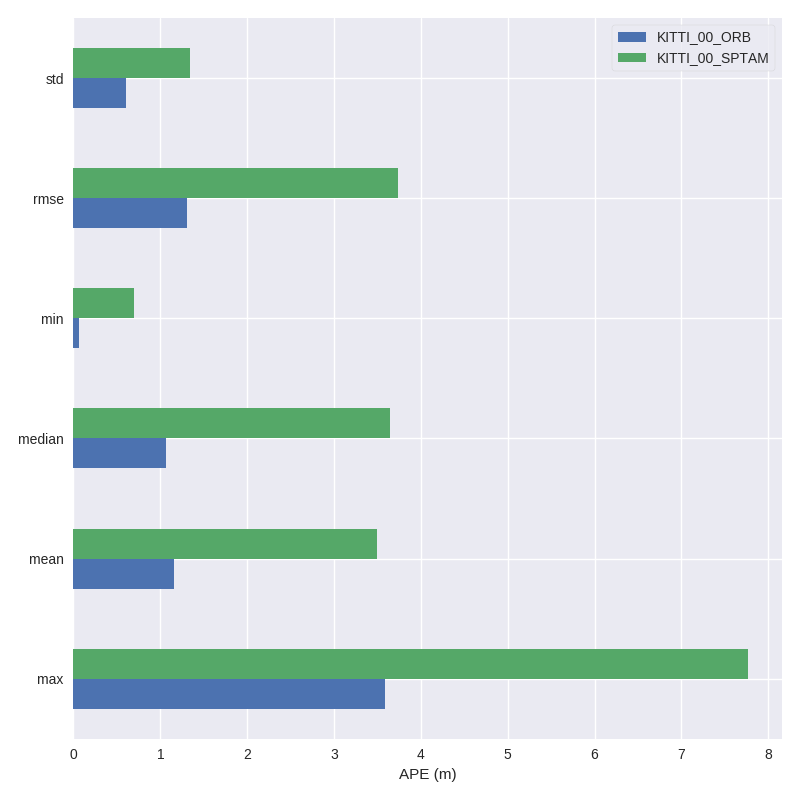
3.) Process multiple results from a metric
evo_res can be used to compare multiple result files from the metrics, i.e.:
- print infos and statistics (default)
- plot the results
- save the statistics in a table
Here, we use the results from above to generate a plot and a table:
evo_res results/*.zip -p --save_table results/table.csv

IPython / Jupyter Resources
For an interactive source code documentation, open the Jupyter notebook metrics_tutorial.ipynb in the notebooks folder of the repository. More infos on Jupyter notebooks: see here
If you have IPython installed, you can launch an IPython shell with a custom evo profile with the command evo_ipython.
Contributing Utilities
A few “inoffical” scripts for special use-cases are collected in the contrib/ directory of the repository. They are inofficial in the sense that they don’t ship with the package distribution and thus aren’t regularly tested in continuous integration.
Trouble
“😱, this piece of 💩 software doesn’t do what I want!!1!1!!”
First aid:
- append
-h/--helpto your command - check the Wiki
- check the previous issues
- open a new issue
Contributing
Patches are welcome, preferably as pull requests.
License
If you use this package for your research, a footnote with the link to this repository is appreciated: github.com/MichaelGrupp/evo.
…or, for citation with BibTeX:
@misc{grupp2017evo,
title={evo: Python package for the evaluation of odometry and SLAM.},
author={Grupp, Michael},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/MichaelGrupp/evo}},
year={2017}
}