Fake Craigslist is a fully functional ASP.NET web application using MVC 5 that provides an implements of a popular website – Craigslist (www.craigslist.org). The entire solution is layered in 5 C# libraries: user interface, Entity Framework data model, business logic, database design, and unit test.
Fake Craigslist
Developed By
- Xuebo Lai
- Jiaqi Liu
- Chenyu Liu
Introduction
Fake Craigslist is a fully functional ASP.NET web application using MVC 5 that provides an implements of a popular website – Craigslist (www.craigslist.org). The entire solution is layered in 5 C# libraries: user interface, Entity Framework data model, business logic, database design, and unit test.
Craigslist (www.craigslist.org) is a web site that allows users to post items and services for sale. It is particularly notable for its simplistic user interface. This Fake Craigslist Application is created in the same spirit as Craigslist.
Website Demo
https://fakecraigslistfinalproject.azurewebsites.net/
Admin Account
Username: [email protected]
Password: QQPassword123!
Solution Details
User Roles
There are three main user roles: admin, user, and anonymous.
The first two roles require an account on the system.
Anonymous users are those who use the web site without logging in.
The user role allows one to create, modify, and delete posts, read other people’s posts, and respond to posts. The anonymous role can read posts, but cannot create or respond to them.
The admin role is is for web site administrators to set up and configure the web site, but can also access most of the same functions as the user role.
The first user on the system is automatically generated as soon as the App finished compiling, and the account will be placed into the admin role by default.
Post
A post is a single listing for an item or service which can be posted by anyone in the admin or user roles. To facilitate data modeling, a post has a unique identifier, timestamp, expiration, owner, title, body, location, and category information.
By default, the expiration time of a post is 5 days after the time of the post creation or last edit.
Views
The list posts screen allows a logged in user to see a list of their own unexpired and expired posts separately. The posts on the screen are always paginated, and sorted by their timestamp.
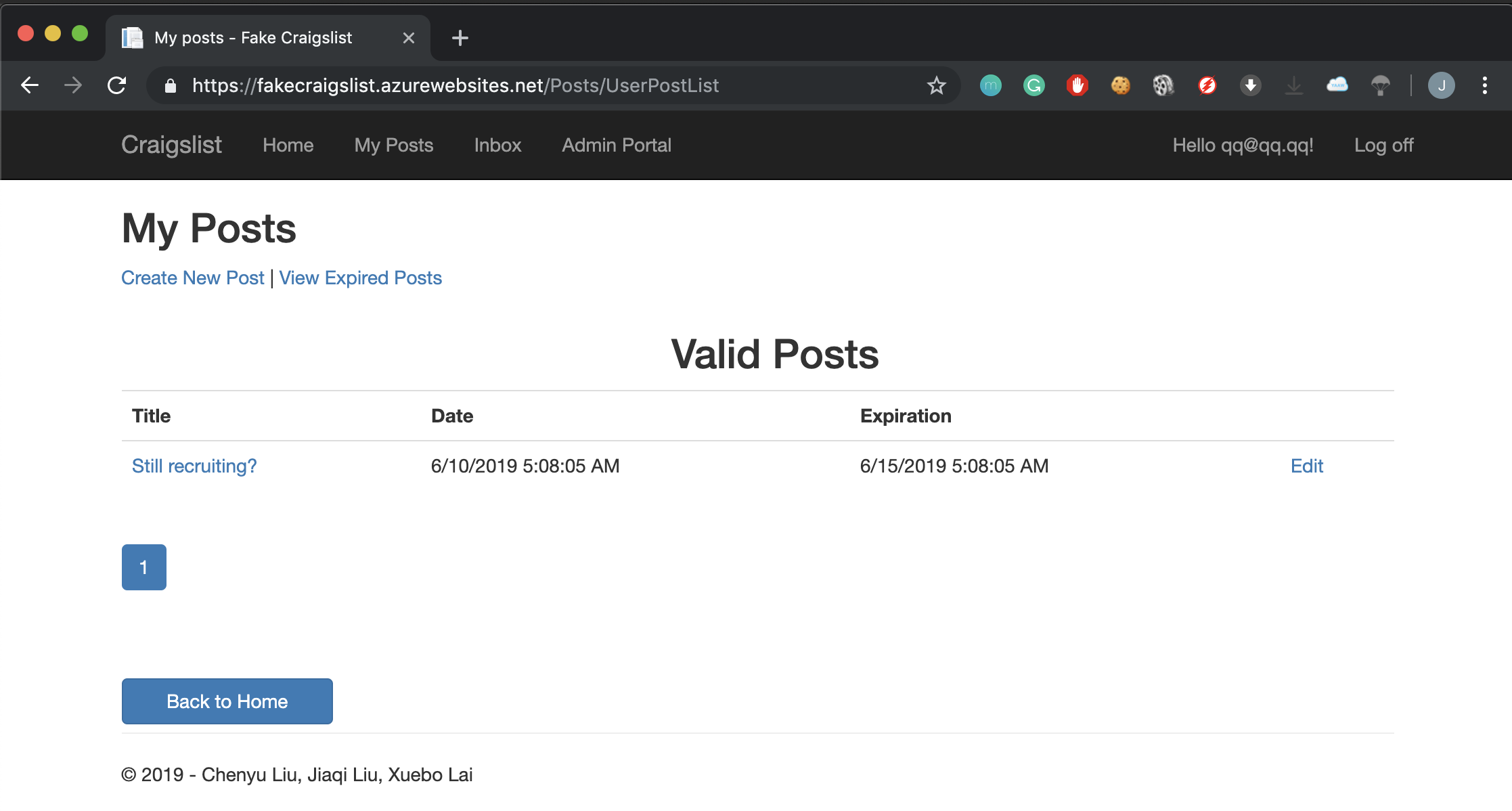
The create post screen allows admin or user to create a new post.
-
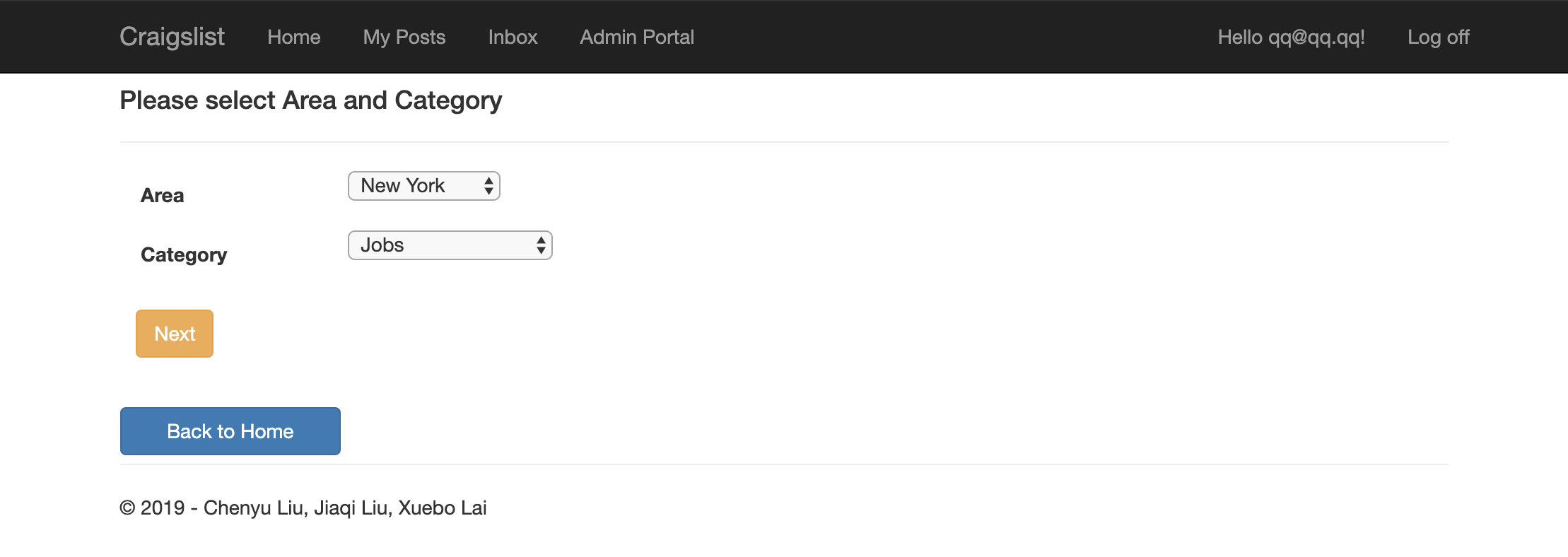
To avoid malicious input and solve unmatched input problems such as (Miami ?= miami), we have implemented a two-step post creation screen.
-
The first screen will prompt the user to select post location and category.
- The second screen will prompt the user to enter post title, post body, post locale and subcategory.
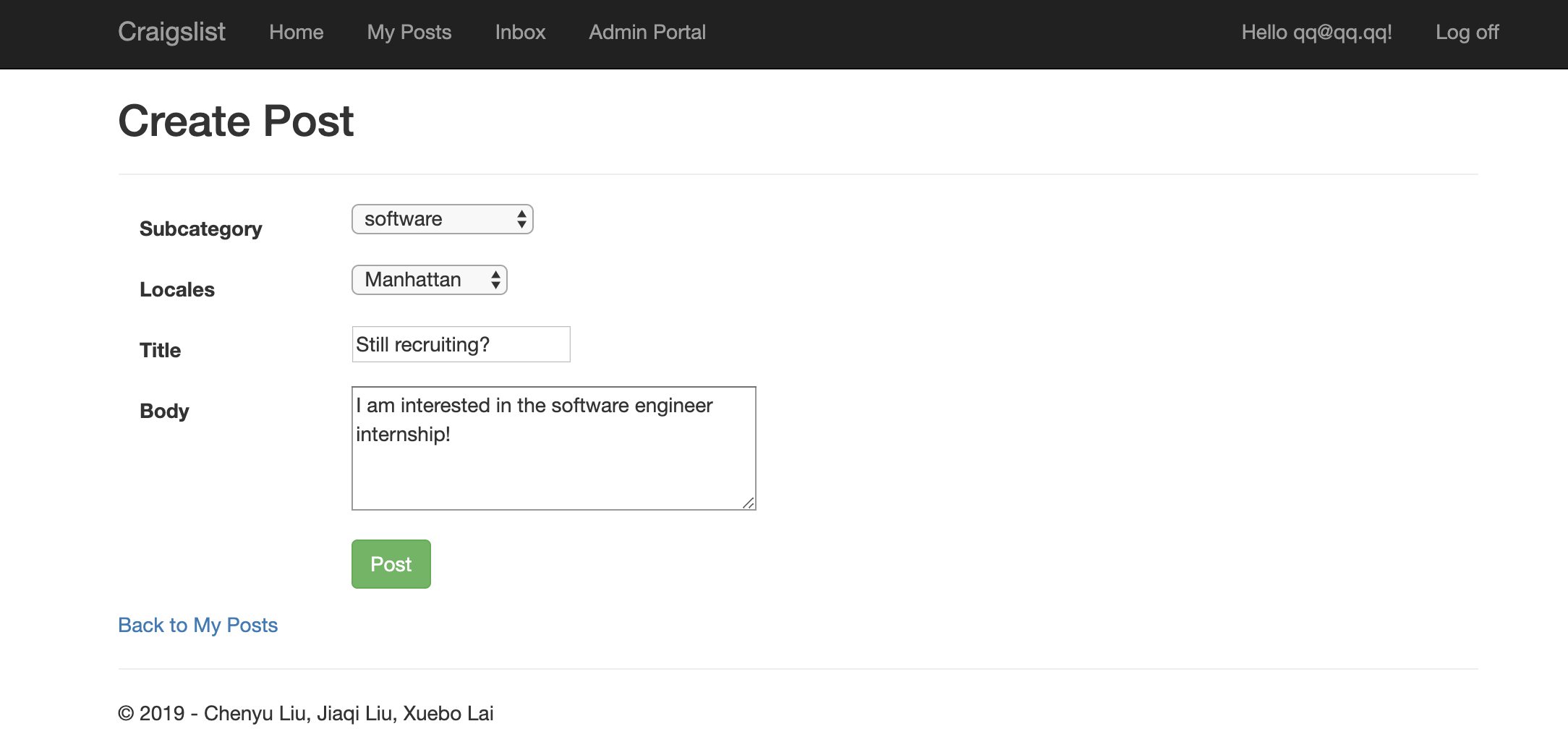
- Other fields such as the date/time and unique identifier will be computed internally.
The modify post screen is similar to the second step of create post, except that the user can edit an existing post. As the user modifies the post, the time stamp will be updated to reflect the time of the modification.
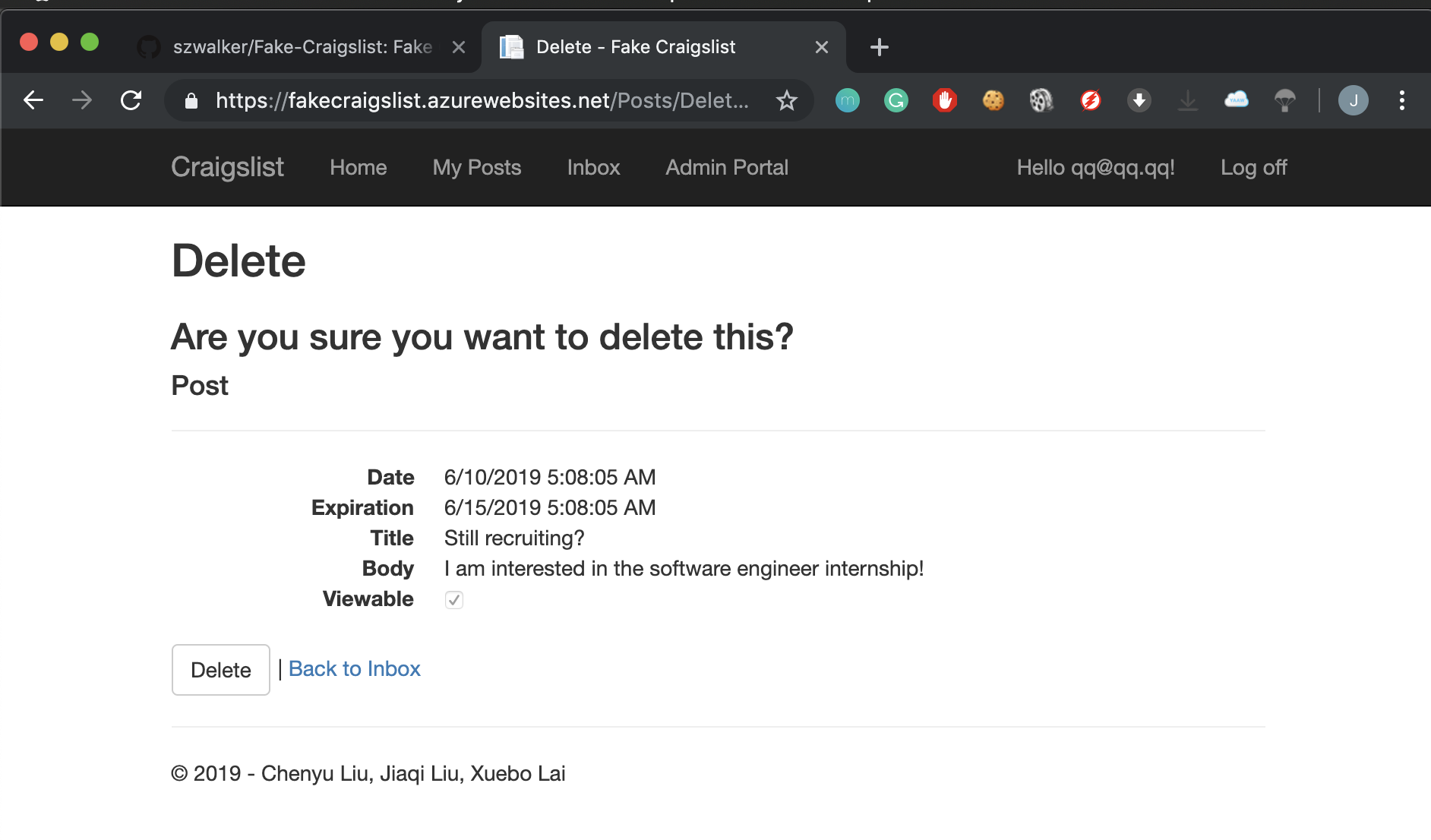
The delete post screen allows a admin user to delete an existing post. After the deletion, the post remains in the database but will be hidden from the user.
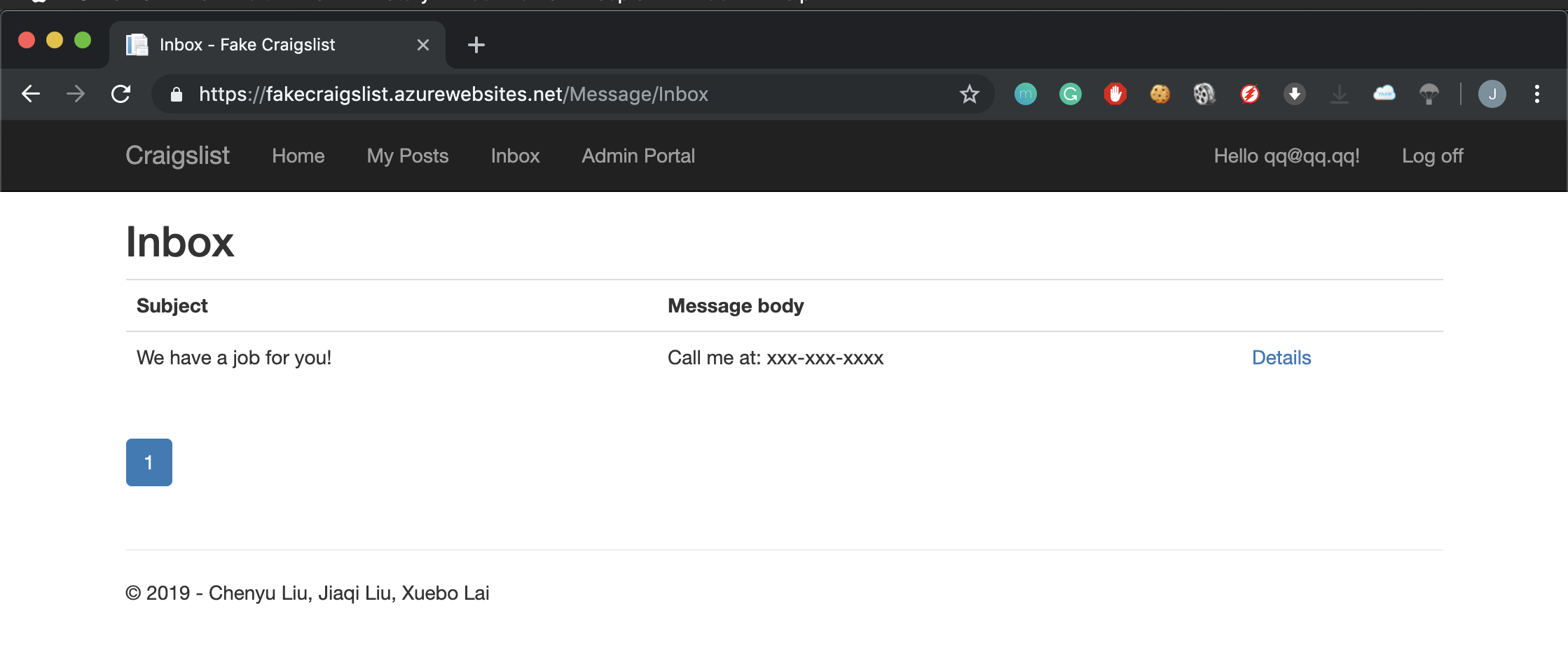
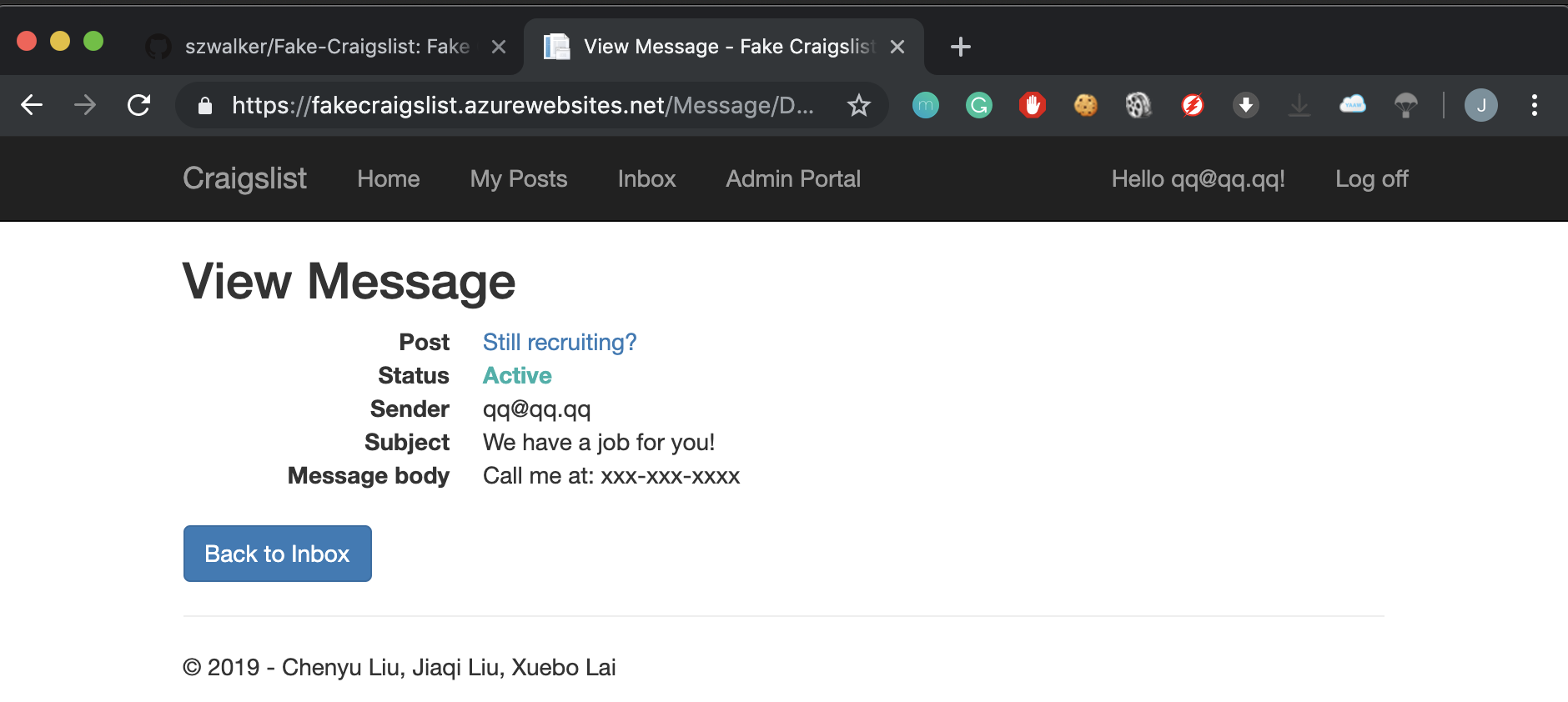
The inbox screen allows a user to see responses to their posts. Responses to posts are private communications between the reader of the post and the originator of the post.
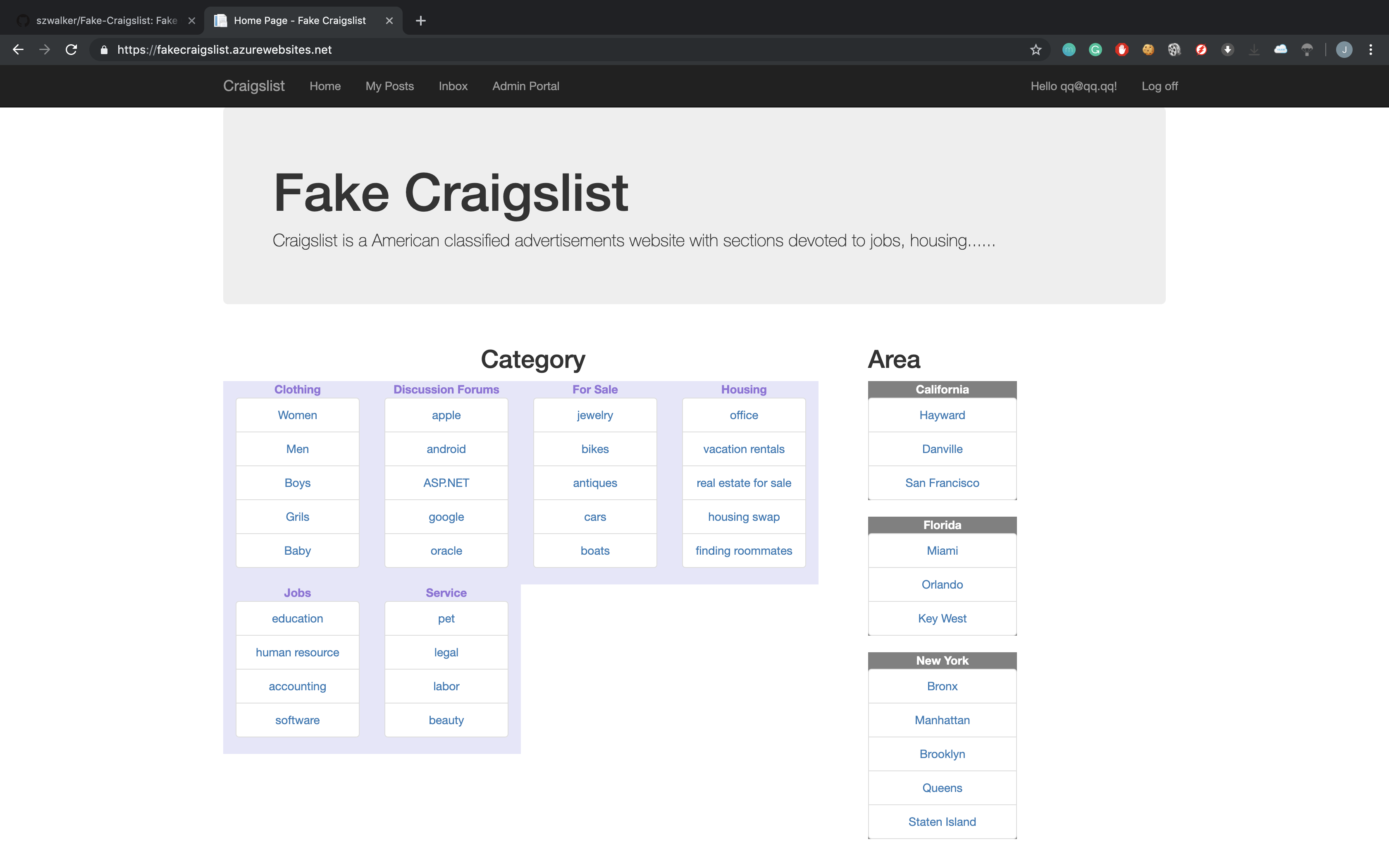
The home screen of the web site is accessible to all user roles and have the following functionality:
- Display all categories and subcategories currently in the system (unless hidden) and display all subcategories within their corresponding category.
- Allow the user to select a location (both area and locale) that corresponds to where they want to search for posts. The web page will demonstrate a url slug of the selected location and this change will also be reflected on the url path.
- If the user have previously selected location and clicks any category or subcategory on the home page (to go to the categories screen), the posts shown on these screens should be restricted to only those posts within the location selected on the home page. Otherwise, all posts, unless expired, falls under the subcategory will be displayed.
The admin portal allows the authenticated admin user to control list of areas, categories, and users.
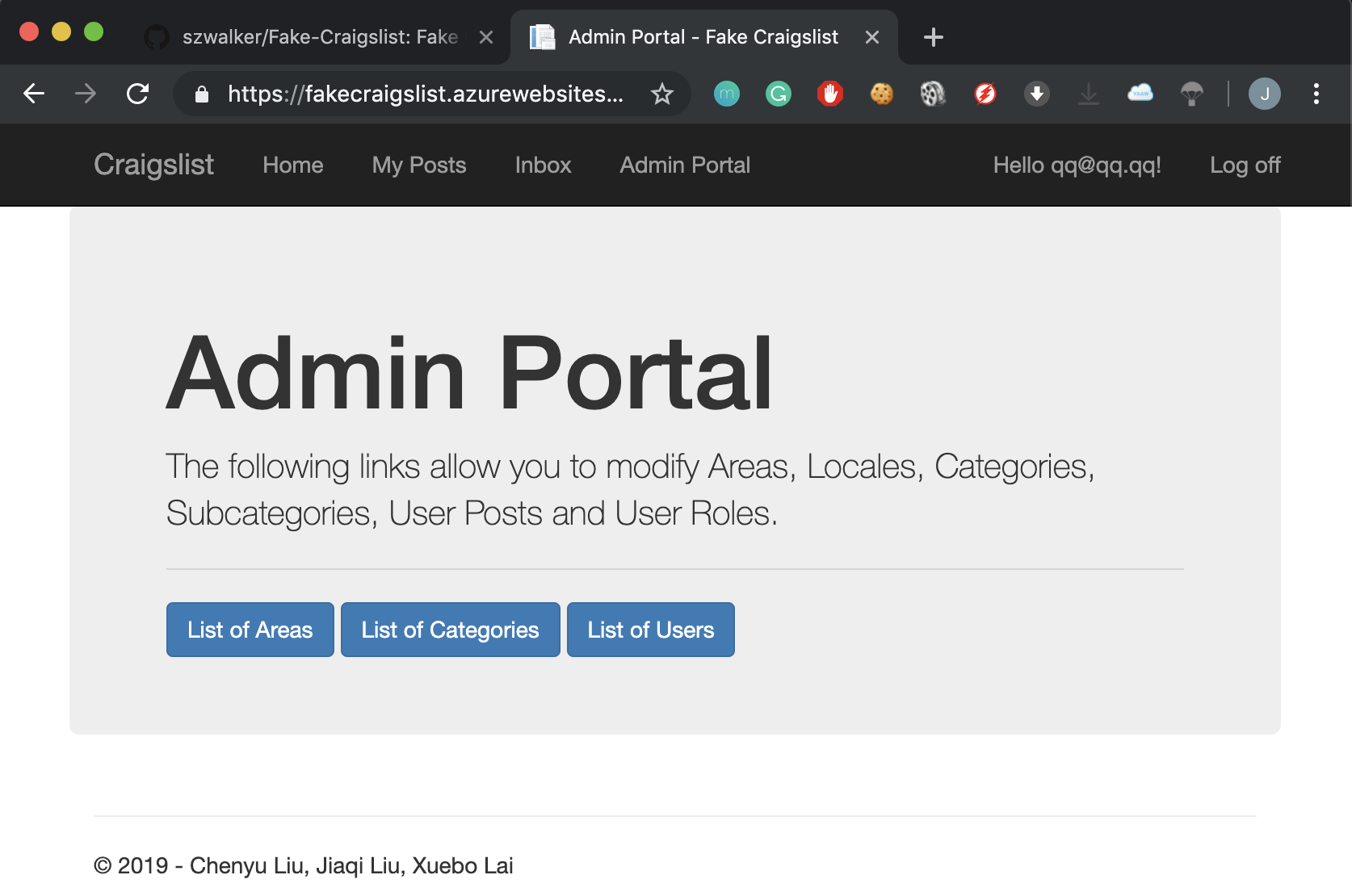
Use Cases
An authenticated user such as admin or regular user may perform the following operations:
- Create a new post - Please see the create post screen above for page details.
- View existing post - Please see the list post screen above for page details.
- Viewing the inbox - Please see the inbox screen above for page details.
In addition, a user in admin role may perform the following extra operations:
- Change the role of any person in the user role to the admin role.
- List, add, modify, and hide categories and subcategories.
- List, add, modify, and hide areas and locales.
- List, or hide posts for any user on the system.
Security
Security measurements has been taken to prevent XSS and CSRF requests using string encoding and hidden anti-forgery tokens on sensitive pages.
Custom Filter
The default ASP.NET filter worked fine as long as a user has not logged-in the website. The filter would redirect the user to a login page and ask the user to login.
However, we soon realize when a user has logged-in a website, the default filter still displays a login page to the logged-in user, which might confuse the user.
To improve user experience, we created a customized role check filter that performs the following activities:
if a user is not logged-in, and visit any page that requires a user role, then the filter would behave like the default filter: redirect the page to a login screen and ask the user to log in.
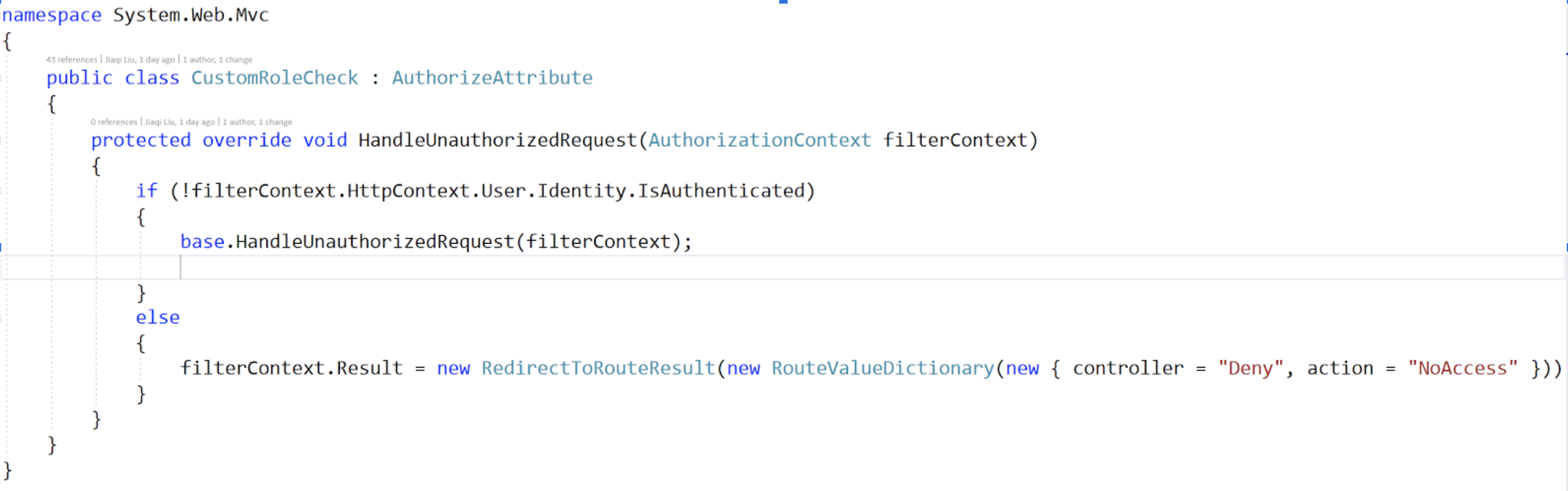
After the user is logged-in, if the user does not have the proper role to visit a page, the filter will be responsible for redirecting the user to a screen that displays an informative information to the user.