Tool for parsing of logs collected by sosreport and foreman-debug
Grok’n’Gelf
Tool for parsing logs collected by foreman-debug and sosreport tools
and import them to a centralized log manager.
How do I use it
Log server is not part of this tool. You can use service of your choice.
The only requirement is it has to accept log data in GELF format.
The tool was tested with Graylog server
Install the tool:
git clone https://github.com/mbacovsky/grokngelf
cd grokngelf
bundle install
bundle exec bin/grokngelf -h
Lets assume you have your Graylog server running at graylog.example.com
and accepting GELF input on port 12201 via TCP. Also assume you have your
sosreport extracted in /tmp/sosreport-sample. To import the logs run:
$ grokngelf sosreport -t graylog.example.com --host testhost.example.com --import-id 1 /tmp/sosreport-sample
Importing sosreport from [/tmp/sosreport-sample]...
Importing yum log [/tmp/sosreport-sample/var/log/yum.log].....................................................................|
Importing syslog [/tmp/sosreport-sample/var/log/messages]..........................................|
Done
If you sosreport is a tarball the tool can extract it for you:
$ grokngelf sosreport -t graylog.example.com --host testhost.example.com --import-id 1 /tmp/sosreport-sample.tar.xz
For more help see:
$ grokngelf -h
Usage:
grokngelf [OPTIONS] SUBCOMMAND [ARG] ...
Parameters:
SUBCOMMAND subcommand
[ARG] ... subcommand arguments
Subcommands:
yum process yum log
syslog process system log
sosreport process sos report
dynflow-tasks process CSV export of dynflow tasks
Options:
-h, --help print help
$ grokngelf sosreport -h
Usage:
grokngelf sosreport [OPTIONS] SOSREPORT
Parameters:
SOSREPORT sosreport tarball or directory with extracted logs
Options:
-h, --help print help
--target, -t TARGET machine where we can send the processed logs
--port, -p PORT port where we can send the processed logs (default: "12201")
--protocol PROTOCOL protocol to use to send the data (default: "TCP")
--host HOST hostname of the machine the logs originates from (a.k.a facilty) (default: "default")
--import-id IMPORT_ID unique identification of the import (default: 1)
How does it work
For sosreport all applicable importers are called for the relevant logs from collection.
Importer reads the log line by line and tries to match the line
to GROK patterns
from its library. From the matched line structured event is created and send in
GELF format to the log manager.
For more complex logs such as syslog we need to parse the content in multiple runs
and every pass pick data just for specific pattern. Lines that were not matched are imported with program: 'unmatched' and can be filtered and revieved later.
Each event has mandatory attributes regardless of importer it originates from:
{
'version' => '1.1', # GELF version, *internal*
'import_id' => '', # id of the import as set on CLI
'source' => '', # hostname of importer machine, *internal*
'short_message' => '', # log entry without timestamps, pids, etc.
'original_line' => '', # full original log entry
'timestamp' => 1485359137, # log event timestamp
'level' => 1, # log level number
'level_hr' => 'DEBUG', # log level in human readable format
'facility' => '', # source (hostname) of the log entry, set on CLI
'file' => 'N/A', # file the notify was called from *internal*
'line' => 'N/A', # line the notify was called from *internal*
'log_file' => '', # file that was parsed to produce this entry
}
How can I improve it
Any contribution is highly appreciated. I welcome any kind of help
- report issues
- send feature your requests and ideas
- improve documentation
- send PRs with fixes
- develop new importers
What logs are supported
var/log/yum.log
- Importer:
Yum - Status: Complete
- Example:
{
"original_line" => "Jan 25 15:45:37 Installed: rh-ruby22-ruby-2.2.2-16.el7.x86_64",
"timestamp" => 1485359137,
"level" => 1,
"level_hr" => "INFO",
"program" => "yum",
"short_message" => "Installed: rh-ruby22-ruby-2.2.2-16.el7.x86_64",
"package_name" => "rh-ruby22-ruby",
"action" => "Installed",
"package_nevra" => "rh-ruby22-ruby-2.2.2-16.el7.x86_64",
"package_epoch" => 0,
"package_version" => "2.2.2",
"package_version_major" => 2,
"package_version_minor" => 2,
"package_release" => "16.el7",
"package_architecture" => "x86_64"
}
var/log/messages
- Importer:
Syslog - Status: WIP
- Pulp messages
- Generic syslog messages
tmp/export
- Importer:
DynflowTasks - Status: Complete
- Execution plans (+ data from dynflow actions and foreman tasks)
- Execution steps
- Example of Execution plan:
{
"timestamp"=>1485035640,
"level"=>1,
"level_hr"=>"INFO",
"importer"=>"GrokNGelf::Importers::DynflowTasks",
'program' => 'dynflow',
'short_message' => "Execution plan 3926bad1-7b7d-4a49-9e86-e31e4f431483 started",
'dynflow_object' => 'execution_plan',
'dynflow_plan_id' => '3926bad1-7b7d-4a49-9e86-e31e4f431483',
'dynflow_class' => 'Actions::RemoteExecution::RunHostsJob',
'dynflow_input' => {"job_invocation"=>{"id"=>2, "name"=>"Commands", "description"=>"Run echo hello"}},
'dynflow_output' => {"total_count"=>1, "failed_count"=>0, "success_count"=>1, "pending_count"=>0},
'dynflow_event_type' => 'start',
'dynflow_state' => 'stopped',
'dynflow_result' => 'success',
'dynflow_started_at' => '2017-01-21 21:54:00',
'dynflow_ended_at' => '2017-01-21 21:54:03',
'dynflow_real_time' => 3.601317757,
'dynflow_real_time_hr' => '3 s',
'dynflow_execution_time' => 0.440313698,
'foreman_task_start_at' => '2017-01-21 21:54:00.053138',
'foreman_task_start_before' => '2017-01-21 21:54:00.053138',
'foreman_task_id' => 'd8a0ec75-b056-4102-be4d-f211dc8734be',
'foreman_task_type' => 'ForemanTasks::Task::DynflowTask',
'foreman_task_label' => 'Actions::RemoteExecution::RunHostsJob',
'log_file' => fixture_log('dynflow_tasks_success/dynflow_execution_plans.csv')
}
- Example of Execution step:
{
'timestamp' => 1485035641,
'level' => 1,
'level_hr' => 'INFO',
'program' => 'dynflow',
'short_message' => "Execution step started",
'dynflow_object' => 'step',
'dynflow_plan_id' => '3926bad1-7b7d-4a49-9e86-e31e4f431483',
'dynflow_event_type' => 'start',
'dynflow_class' => 'Actions::RemoteExecution::RunHostsJob',
'dynflow_step_class' => 'Dynflow::ExecutionPlan::Steps::RunStep',
'dynflow_input' => {"job_invocation"=>{"id"=>2, "name"=>"Commands", "description"=>"Run echo hello"}},
'dynflow_output' => {"total_count"=>1, "failed_count"=>0, "success_count"=>1, "pending_count"=>0},
'dynflow_error' => nil,
'dynflow_step_id' => 2,
'dynflow_result' => 'success',
'dynflow_started_at' => '2017-01-21 21:54:01',
'dynflow_ended_at' => '2017-01-21 21:54:03',
'dynflow_real_time' => 2.376708706,
'dynflow_real_time_hr' => '2 s',
'dynflow_execution_time' => 0.394046164,
'dynflow_progress_done' => 1.0,
'dynflow_progress_weight' => 1.0,
'log_file' => fixture_log('dynflow_tasks_success/dynflow_steps.csv')
}
How do I install Graylog
There is plenty of ways to install Graylog.
Most easy is probably to use Graylog’s VM appliances. I have good experience with their ansible playbook
that I extended to create GELF TCP input and to open the port.
- name: Create graylog global GELF input for receiving logs
uri:
url: http://127.0.0.1:9000/api/system/inputs
method: POST
user: "admin"
password: "admin"
body: '{"title":"GELFTCPInput","type":"org.graylog2.inputs.gelf.udp.GELFTCPInput","configuration":{"bind_address":"0.0.0.0","port":12201,"recv_buffer_size":1048576,"override_source":null,"decompress_size_limit":8388608},"global":true}'
force_basic_auth: yes
status_code: 201
body_format: json
- name: Open port 12201 in firewall
firewalld:
port: 12201/tcp
permanent: true
state: enabled
Regardless of the type of installation you use make sure the GELF Input is Up and running.
In Graylog UI select System > Input
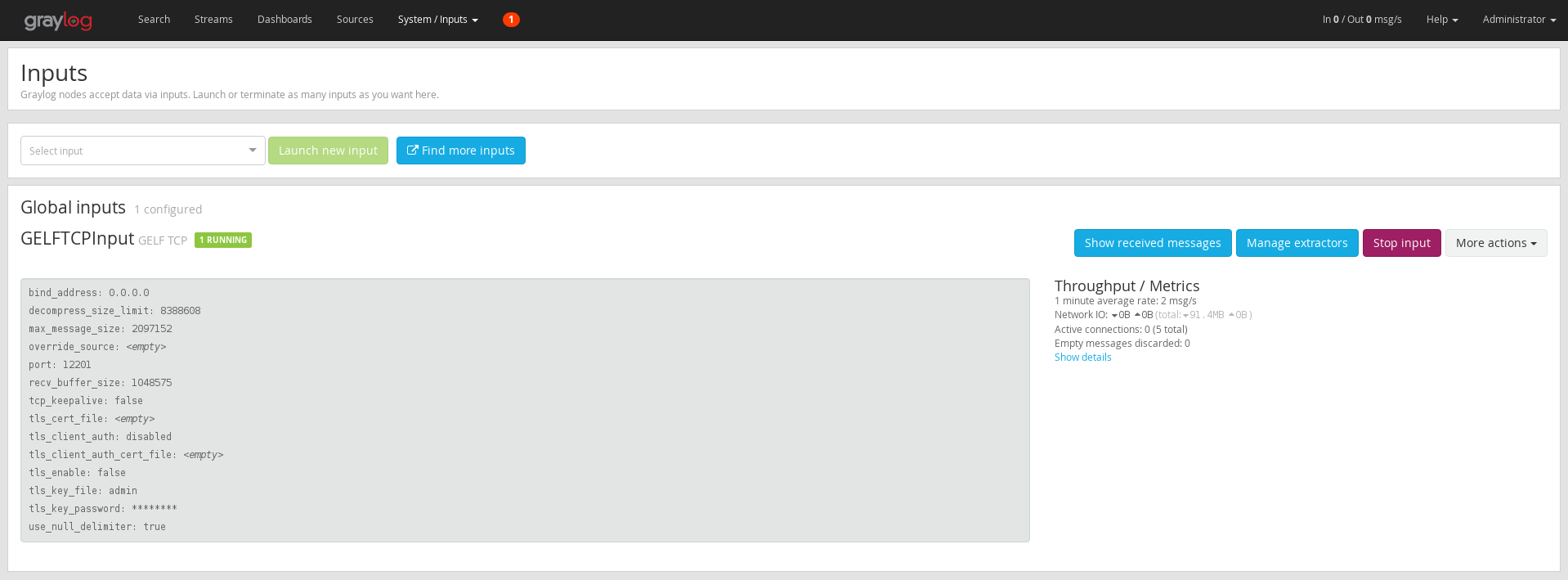
Also open the port in the firewall if necessary with e.g.
$ firewall-cmd --add-port="12201/tcp"
How do I search the logs in Graylog
Import some data to the Graylog e.g. with
$ grokngelf yum -t graylog.example.com --host testhost.example.com --import-id 1 /tmp/sosreport-sample
In the Graylog UI go to Search and select Search in all messages at the top in the time range selector.
In the search box filter the data you’ve just imported with facility:testhost.example.com AND import_id:1
and click the search button. Note that the host (a.k.a facility in Graylog) and import_id fields are there just for
filtering of the logs so you can use whatever data there that work for you e.g. bug number, hostname, customer name, etc.
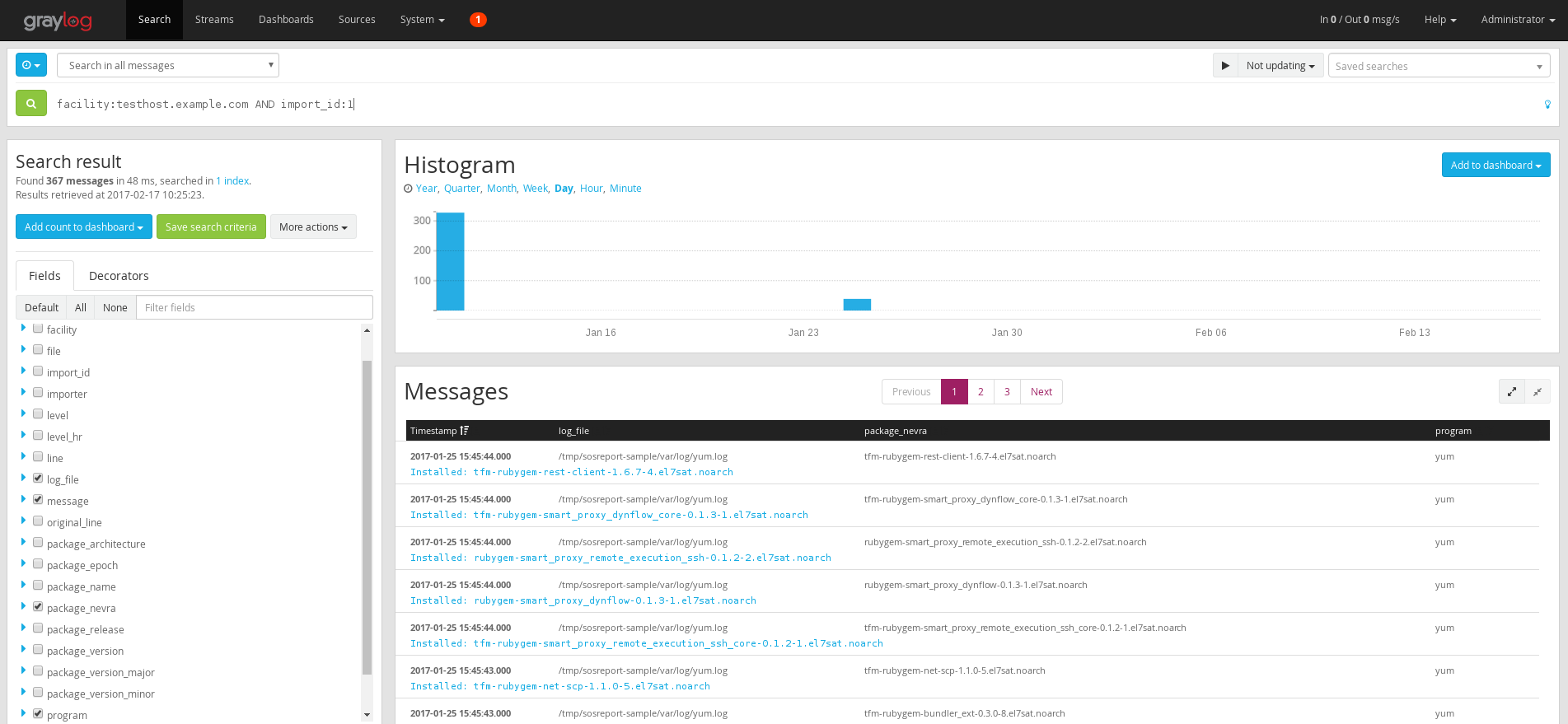
More on filtering possibilities, query language, exports, statistics and analysis in Graylog check the docs.
License
This project is licensed under the GPLv3+.