Play RTSP stream from IP camera in browser in this HTML5 player without plugins
Overview
All modern browsers don’t natively support playback of RTSP (Real Time Streaming Protocol) streams,
which is a common format for many popular IP cameras.
So for a long time if you wanted to display your RTSP IP camera stream on the web page,
you had to use intermediate transcoding servers, which would receive RTSP stream,
decode it and convert into format accepted by browser like HLS, MPEG-DASH or MP4.
This solution gets the job done, but it may suffer from big latency and poor performance due to the need to transcode and convert video with often compromised output video quality as the result.
This custom HTML5 player, that works directly on top of a standard HTML5 <video> element,
was developed to implement different philosophy. Instead of decoding RTSP stream on the intermediate server
it shifts this heavy task to the end user browser, where task of decoding of a single stream is insignificant.
This means that your intermediate server no longer have to pull all the load,
you can share it between everyone watching your RTSP stream. As an additional advantage,
end user browser will always receive full quality unaltered picture from your IP camera.
Streamedian is a Javascript library which implements RTSP client for watching live streams in your browser.
It requires support of HTML5 Video with Media Sources Extensions for playback. Also player relies on server-side websocket
proxy for retransmitting RTSP streams to browser.
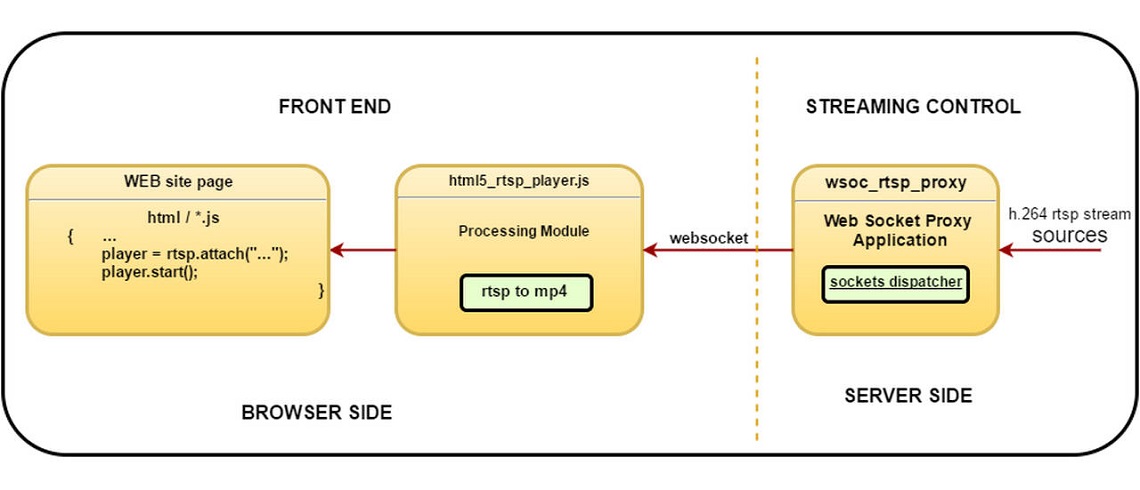
It works by muxing RTP H264 and AAC payload into ISO BMFF (MP4) fragments.
Streamedian is written using ECMAScript 2015 standard.
Live test stream
Demo is available on https://streamedian.com
Browser support (ES5 transpiled version):
- Firefox v.42+
- Chrome v.23+
- OSX Safari v.8+
- MS Edge v.13+
- Opera v.15+
- Android browser v.5.0+
- IE Mobile v.11+
Not supported in iOS Safari and Internet Explorer
Install
npm install git://github.com/Streamedian/html5_rtsp_player.git
Usage
Browser side
Attach HTML Video with RTSP URL
<video id="test_video" controls autoplay src="rtsp://your_rtsp_stream/url"></video>
or
<video id="test_video" controls autoplay>
<source src="rtsp://your_rtsp_stream/url">
</video>
You can ignore source by passing data-ignore=“true”:
<video id="test_video" controls autoplay>
<source src="natively_supported_video_url" data-ignore="true">
<source src="rtsp://your_rtsp_stream/url">
</video>
If browser can play that source, player will not be initialized for this element.
Setup player in your js:
import * as streamedian from 'streamedian/player.js';
// import WebsocketTransport from 'wsp/transport/websocket';
// import RTSPClient from 'wsp/client/rtsp/client';
let mediaElement = rtsp.attach(document.getElementById('test_video'));
let player = new streamedian.WSPlayer(mediaElement, {
// url: `${STREAM_URL}`, // overrides mediaElement's sources
modules: [
{
// client module constructor. Should be subclass or BaseClient. RTSPClient by default
// client: RTSPClient,
transport: {
// client module constructor. Should be subclass or BaseTransport. WebsocketTransport by default
// constructor: WebsocketTransport,
options: {
// address of websocket proxy described below. ws${location.protocol=='https:'?'s':''}://${location.host}/ws/ by default
socket: "ws://websocket_proxy_address/ws",
// function called player exceptions
errorHandler (e) {
alert(`Failed to start player: ${e.message}`);
},
// function to get credentials for protected streams
queryCredentials() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
let c = prompt('input credentials in format user:password');
if (c) {
this.setCredentials.apply(this, c.split(':'));
resolve();
} else {
reject();
}
});
}
}
}
},
]
});
ES6 Modules support is required. You can use rollup to build this script:
rollup.config.js
import buble from 'rollup-plugin-buble';
import alias from 'rollup-plugin-alias';
const path = require('path');
export default {
entry: path.join(__dirname, 'example.js'),
targets: [
{dest: path.join(__dirname, 'example/streamedian.js'), format: 'es'}
],
sourceMap: true,
plugins: [
// uncomment if you want to transpile into es5
//buble({
//exclude: 'node_modules/**'
//}),
alias({
bp_logger: path.join(__dirname,'node_modules/bp_logger/logger'),
bp_event: path.join(__dirname,'node_modules/bp_event/event'),
bp_statemachine: path.join(__dirname,'node_modules/bp_statemachine/statemachine'),
//jsencrypt: path.join(__dirname,'node_modules/jsencrypt/src/jsencrypt.js'),
streamedian: path.join(__dirname,'src')
})
]
}
> npm install bp_event bp_logger bp_statemachine
> rollup -c
Include compiled script into your HTML:
<script src="streamedian.js"></script>
RTSP Authentication
Streamedian player support both basic and digest authentication. Authentication type is detected automatically
when you connect to the stream.
You can directly specify user/password in rtsp url in form rtsp://username@password:stream.url/resource/
or pass queryCredentials() function to streamedian.WSPlayer. This function in order
should return promise that call this.setCredentials(user, password).
Server side
-
Install websocket proxy
Sign up and install websocket proxy from http://streamedian.com
Register domain you want to use this player
Download license file to your server
Note that this package depends on systemd and gcc5+ runtime so it can be installed
only on recent distribution versions. -
Configure port and license file path in /etc/ws_rtsp.ini
This port should be open in your firewall. Also you can pass request to this port from your proxy. (for example: http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/websocket.html)
-
Run it
> service ws_rtsp start
Player architecture
Player comprises three main modules: transport, client and remuxer.
Transport responsible for data delivery and data queuing. It should fire connected, disconnected and data events.
As soon data received, transport should push it into dataQueue and fire data event. Base class for transports can be found in core/base_transport.
As a default, WebsocketTransport that relies on websocket proxy is implemented.
Client listens for data events, parse it into elementary stream packets and enqueue parsed data into it’s own queue. Client can
pass queued buffer to remuxer with samples event. To identify stream track client should fire tracks event. When ready, flush
event can be used to construct media fragment and pass it to video presenter. Base class for transports can be found in core/base_client.
Default client is RTSP client over websocket transport.
Remuxer prepares media fragment for video presenter and push it. There is only video presenter at the moment, based on media source extensions.
Remuxer collects data into mp4 media fragments (moof+mdat) and pass it into source buffer.
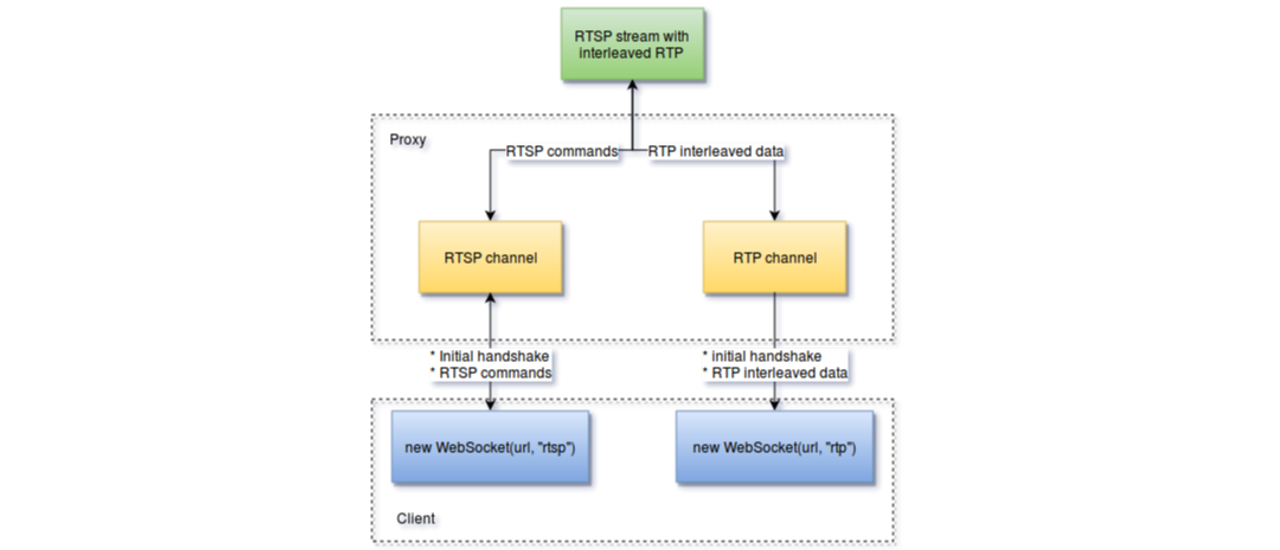
How RTSP proxy works?
RTSP player establish connection with proxy with following protocol:
-
Connect to RTSP channel by connecting websocket with “rtsp” protocol specified and get connection id
c>s: WSP/1.1 INIT\r\n seq: <sequence_id for response tracking> host: <RTSP stream host>\r\n port: <RTSP stream port>\r\n\r\n s>c: WSP/1.1 200 OK\r\n seq: <sequence_id for response tracking> channel: <channel_id>\r\n\r\n Error codes >= 400 means error -
Connect to RTP channel by connecting websocket with “rtp” protocol
c>s: WSP/1.1 JOIN\r\n seq: <sequence_id for response tracking>\r\n channel: <channel_id achieved from RTSP socket initialization>\r\n\r\n s>c: WSP/1.1 200 OK\r\n seq: <sequence_id for response tracking>\r\n\r\n Error codes >= 400 means error -
Send RTSP commands wrapped into WSP protocol:
c>s: WSP/1.1 WRAP\r\n seq: <sequence_id for response tracking>\r\n \r\n <RTSP_PROTOCOL_DATA> s>c: WSP/1.1 200 OK\r\n channel: <channel_id>\r\n \r\n <RTSP_PROTOCOL_RESPONSE> Error codes >= 400 means error -
RTP channel should send interleaved data with 4 byte header ($<channel><size>). Separate RTP is not supported at this moment
Load balancing
RTSP proxy does not support load balancing itself but can be easily integrated with such load balancers like nginx.
You can start multiple instances of proxy on different sockets and configure nginx upstreams.
Have any suggestions to improve our player?
Feel free to leave comments or ideas [email protected]