ActiveJob on SQS & Lambda

Lambdakiq
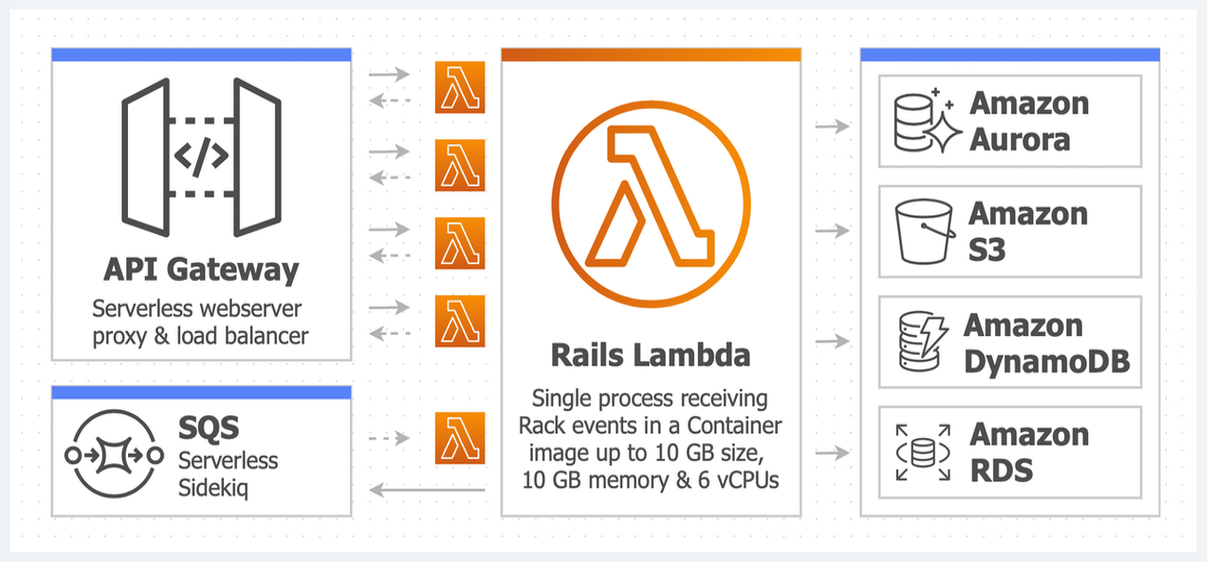
A drop-in replacement for Sidekiq when running Rails in AWS Lambda using the Lamby gem.
Lambdakiq allows you to leverage AWS’ managed infrastructure to the fullest extent. Gone are the days of managing pods and long polling processes. Instead AWS delivers messages directly to your Rails’ job functions and scales it up and down as needed. Observability is built in using AWS CloudWatch Metrics, Dashboards, and Alarms. Learn more about Using AWS Lambda with Amazon SQS or get started now.
Key Features
- Distinct web & jobs Lambda functions.
- AWS fully managed polling. Event-driven.
- Maximum 12 retries. Per job configurable.
- Mirror Sidekiq’s retry backoff timing.
- Last retry is at 11 hours 30 minutes.
- Supports ActiveJob’s wait/delay. Up to 15 minutes.
- Dead messages are stored for up to 14 days.
Project Setup
This gem assumes your Rails application is on AWS Lambda, ideally with our Lamby gem. It could be using Lambda’s traditional zip package type or the newer container format. If Rails on Lambda is new to you, consider following our quick start guide to get your first application up and running. From there, to use Lambdakiq, here are steps to setup your project
Bundle & Config
Add the Lambdakiq gem to your Gemfile.
gem 'lambdakiq'
Open config/environments/production.rb and set Lambdakiq as your ActiveJob queue adapter.
config.active_job.queue_adapter = :lambdakiq
Open app/jobs/application_job.rb and add our worker module. The queue name will be set by an environment using CloudFormation further down.
class ApplicationJob < ActiveJob::Base
include Lambdakiq::Worker
queue_as ENV['JOBS_QUEUE_NAME']
end
Using ActionMailer’s built-in deliver job with ActiveJob? Make sure to include the Lambdakiq worker and set the queue name depending on your Rails version. You can do this in a newly created config/initializers//action_mailer.rb or another initializer of your choice.
# Rails 5.x
ActionMailer::DeliveryJob.include Lambdakiq::Worker
ActionMailer::DeliveryJob.queue_as ENV['JOBS_QUEUE_NAME']
# Rails 6.x
ActionMailer::MailDeliveryJob.include Lambdakiq::Worker
ActionMailer::MailDeliveryJob.queue_as ENV['JOBS_QUEUE_NAME']
The same Docker image will be used for both your web and jobs functions (example setup in following sections). The Lamby gem can automatically can detect if Lambdakiq is present when using the newer Lamby.cmd or older lower Lamby.handler method. That said, please take a look at the JobsLambda in the following section and how ImageConfig is used as the golden path for sharing containers.
SQS Resources
Open up your project’s SAM template.yaml file and make the following additions and changes. First, we need to create your SQS queues under the Resources section.
JobsQueue:
Type: AWS::SQS::Queue
Properties:
ReceiveMessageWaitTimeSeconds: 10
RedrivePolicy:
deadLetterTargetArn: !GetAtt JobsDLQueue.Arn
maxReceiveCount: 13
VisibilityTimeout: 301
JobsDLQueue:
Type: AWS::SQS::Queue
Properties:
MessageRetentionPeriod: 1209600
In this example above we are also creating a queue to automatically handle our redrives and storage for any dead messages. We use long polling to receive messages for lower costs. In most cases your message is consumed almost immediately. Sidekiq polling is around 10s too.
The max receive count is 13 which means you get 12 retries. This is done so we can mimic Sidekiq’s automatic retry and backoff. The dead letter queue retains messages for the maximum of 14 days. This can be changed as needed. We also make no assumptions on how you want to handle dead jobs.
Queue Name Environment Variable
We need to pass the newly created queue’s name as an environment variable to your soon to be created jobs function. Since it is common for your Rails web and jobs functions to share these, we can leverage SAM’s Globals section.
Globals:
Function:
Environment:
Variables:
RAILS_ENV: !Ref RailsEnv
JOBS_QUEUE_NAME: !GetAtt JobsQueue.QueueName
We can remove the Environment section from our web function and all functions in this stack will now use the globals. Here we are using an intrinsic function to pass the queue’s name as the JOBS_QUEUE_NAME environment variable.
IAM Permissions
Both functions will need capabilities to access the SQS jobs queue. We can add or extend the SAM Policies section of our RailsLambda web function so it (and our soon to be created jobs function) have full capabilities to this new queue.
Policies:
- Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- sqs:*
Resource:
- !Sub arn:aws:sqs:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:${JobsQueue.QueueName}
Overview
Now we can duplicate our RailsLambda resource YAML (except for the Events property) to a new JobsLambda one. This gives us a distinct Lambda function to process jobs whose events, memory, timeout, and more can be independently tuned. However, both the web and jobs functions will use the same ECR container image!
JobsLambda:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Metadata:
DockerContext: ./.lamby/RailsLambda
Dockerfile: Dockerfile
DockerTag: jobs
Properties:
Events:
SQSJobs:
Type: SQS
Properties:
Queue: !GetAtt JobsQueue.Arn
BatchSize: 1
FunctionResponseTypes:
- ReportBatchItemFailures
ImageConfig:
Command: ["config/environment.Lambdakiq.cmd"]
MemorySize: 1792
PackageType: Image
Policies:
- Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- sqs:*
Resource:
- !Sub arn:aws:sqs:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:${JobsQueue.QueueName}
Timeout: 300
Here are some key aspects of our JobsLambda resource above:
- We use the
ImageConfig.Commandto load your Rails env and invoke theLambdakiq.cmdwhich calls theLambdakiq.handleron your behalf. - The
Eventsproperty uses the SQS Type. - The BatchSize can be any number you like. Less means more Lambda concurrency, more means some jobs could take longer. The jobs function
Timeoutmust be lower than theJobsQueue’sVisibilityTimeoutproperty. When the batch size is one, the queue’s visibility is generally one second more. - You must use
ReportBatchItemFailuresresponse types. Lambdakiq assumes we are reporting batch item failures. This is a new feature of SQS introduced in November 2021. - The
Metadata’s Docker properties must be the same as our web function except for theDockerTag. This is needed for the image to be shared. This works around a known SAM issue vs using theImageConfigproperty.
🎉 Deploy your application and have fun with ActiveJob on SQS & Lambda.
Configuration
Most general Lambdakiq configuration options are exposed via the Rails standard configuration method.
Rails Configs
config.lambdakiq
max_retries=- Retries for all jobs. Default is the Lambdakiq maximum of12.metrics_namespace=- The CloudWatch Embedded Metrics namespace. Default isLambdakiq.metrics_logger=- Set to the Rails logger which is STDOUT via Lamby/Lambda.
ActiveJob Configs
You can also set configuration options on a per job basis using the lambdakiq_options method.
class OrderProcessorJob < ApplicationJob
lambdakiq_options retry: 2
end
retry- Overrides the default Lambdakiqmax_retriesfor this one job.
Observability with CloudWatch
Get ready to gain way more insights into your ActiveJobs using AWS’ CloudWatch service. Every AWS service, including SQS & Lambda, publishes detailed CloudWatch Metrics. This gem leverages CloudWatch Embedded Metrics to add detailed ActiveJob metrics to that system. You can mix and match these data points to build your own CloudWatch Dashboards. If needed, any combination can be used to trigger CloudWatch Alarms. Much like Sumo Logic, you can search & query for data using CloudWatch Logs Insights.

Metrics are published under the Lambdakiq namespace. This is configurable using config.lambdakiq.metrics_namespace but should not be needed since all metrics are published using these three dimensions which allow you to easily segment metrics/dashboards to a specific application.
Metric Dimensions
AppName- This is the name of your Rails application. Ex:MyAppJobEvent- Name of the ActiveSupport Notification. Ex:*.active_job.JobName- The class name of the ActiveSupport job. Ex:NotificationJob
ActiveJob Event Names
For reference, here are the JobEvent names published by ActiveSupport. A few of these are instrumented by Lambdakiq since we use custom retry logic like Sidekiq. These event/metrics are found in the Rails application CloudWatch logs because they publish/enqueue jobs.
enqueue.active_jobenqueue_at.active_job
While these event/metrics can be found in the jobs function’s log.
perform_start.active_jobperform.active_jobenqueue_retry.active_jobretry_stopped.active_job
Metric Properties
These are the properties published with each metric. Remember, properties can not be used as metric data in charts but can be searched using CloudWatch Logs Insights.
JobId- ActiveJob Unique ID. Ex:9f3b6977-6afc-4769-aed6-bab1ad9a0df5QueueName- SQS Queue Name. Ex:myapp-JobsQueue-14F18LG6XFUW5.fifoMessageId- SQS Message ID. Ex:5653246d-dc5e-4c95-9583-b6b83ec78602ExceptionName- Class name of error raised. Present in perform and retry events.EnqueuedAt- When ActiveJob enqueued the message. Ex:2021-01-14T01:43:38ZExecutions- The number of current executions. Counts from1and up.JobArg#{n}- Enumerated serialized arguments.
Metric Data
And finally, here are the metrics which each dimension can chart using CloudWatch Metrics & Dashboards.
Duration- Of the job event in milliseconds.Count- Of the event.ExceptionCount- Of the event. Useful withExceptionName.
CloudWatch Dashboard Examples
Please share how you are using CloudWatch to monitor and/or alert on your ActiveJobs with Lambdakiq!
💬 https://github.com/rails-lambda/lambdakiq/discussions/3
Common Questions
Are Scheduled Jobs Supported? - No. If you need a scheduled job please use the SAM Schedule event source which invokes your function with an Eventbridege AWS::Events::Rule.
Are FIFO Queues Supported? - Yes. When you create your AWS::SQS::Queue resources you can set the FifoQueue property to true. Remember that both your jobs queue and the redrive queue must be the same. When using FIFO we:
- Simulate
delay_secondsfor ActiveJob’s wait by using visibility timeouts under the hood. We still cap it to non-FIFO’s 15 minutes. - Set both the messages
message_group_idandmessage_deduplication_idto the unique job id provided by ActiveJob.
Can I Use Multiple Queues? - Yes. Nothing is stopping you from creating any number of queues and/or functions to process them. Your subclasses can use ActiveJob’s queue_as method as needed. This is an easy way to handle job priorities too.
class SomeLowPriorityJob < ApplicationJob
queue_as ENV['BULK_QUEUE_NAME']
end
What Is The Max Message Size? - 256KB. ActiveJob messages should be small however since Rails uses the GlobalID gem to avoid marshaling large data structures to jobs.
Contributing
After checking out the repo, run:
$ ./bin/bootstrap
$ ./bin/setup
$ ./bin/test
Bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub at https://github.com/rails-lambda/lambdakiq. This project is intended to be a safe, welcoming space for collaboration, and contributors are expected to adhere to the Contributor Covenant code of conduct.
Code of Conduct
Everyone interacting in the Lambdakiq project’s codebases, issue trackers, chat rooms and mailing lists is expected to follow the code of conduct.