MyLayout is a powerful iOS UI framework implemented by Objective-C. It integrates the functions with Android Layout,iOS AutoLayout,SizeClass, HTML CSS float and flexbox and bootstrap. So you can use LinearLayout,RelativeLayout,FrameLayout,TableLayout,FlowLayout,FloatLayout,PathLayout,GridLayout,LayoutSizeClass to build your App 自动布局 UIView UITableView UICollectionView RTL

MyLayout
MyLayout is a simple and easy objective-c framework for iOS view layout. MyLayout provides some simple functions to build a variety of complex interface. It integrates the functions including: Autolayout and SizeClass of iOS, five layout classes of Android, float and flex-box and bootstrap of HTML/CSS. The MyLayout’s Swift version are named: TangramKit
 Chinese (Simplified): 中文说明
Chinese (Simplified): 中文说明
Usage
- There is a container view S which width is 100 and height is wrap to all subviews height. there are four subviews A,B,C,D arranged from top to bottom.
- Subview A’s left margin is 20% width of S, right margin is 30% width of S, height is equal to width of A.
- Subview B’s left margin is 40, width is filled in to residual width of S,height is 40.
- Subview C’s width is filled in to S, height is 40.
- Subview D’s right margin is 20, width is 50% width of S, height is 40
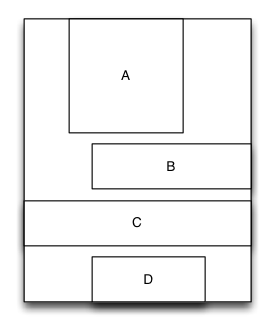
MyLinearLayout *S = [MyLinearLayout linearLayoutWithOrientation:MyOrientation_Vert];
S.subviewSpace = 10;
S.widthSize.equalTo(@100);
UIView *A = UIView.new;
A.leftPos.equalTo(@0.2);
A.rightPos.equalTo(@0.3);
A.heightSize.equalTo(A.widthSize);
[S addSubview:A];
UIView *B = UIView.new;
B.leftPos.equalTo(@40);
B.widthSize.equalTo(@60);
B.heightSize.equalTo(@40);
[S addSubview:B];
UIView *C = UIView.new;
C.leftPos.equalTo(@0);
C.rightPos.equalTo(@0);
C.heightSize.equalTo(@40);
[S addSubview:C];
UIView *D = UIView.new;
D.rightPos.equalTo(@20);
D.widthSize.equalTo(S.widthSize).multiply(0.5);
D.heightSize.equalTo(@40);
[S addSubview:D];
Performance comparison
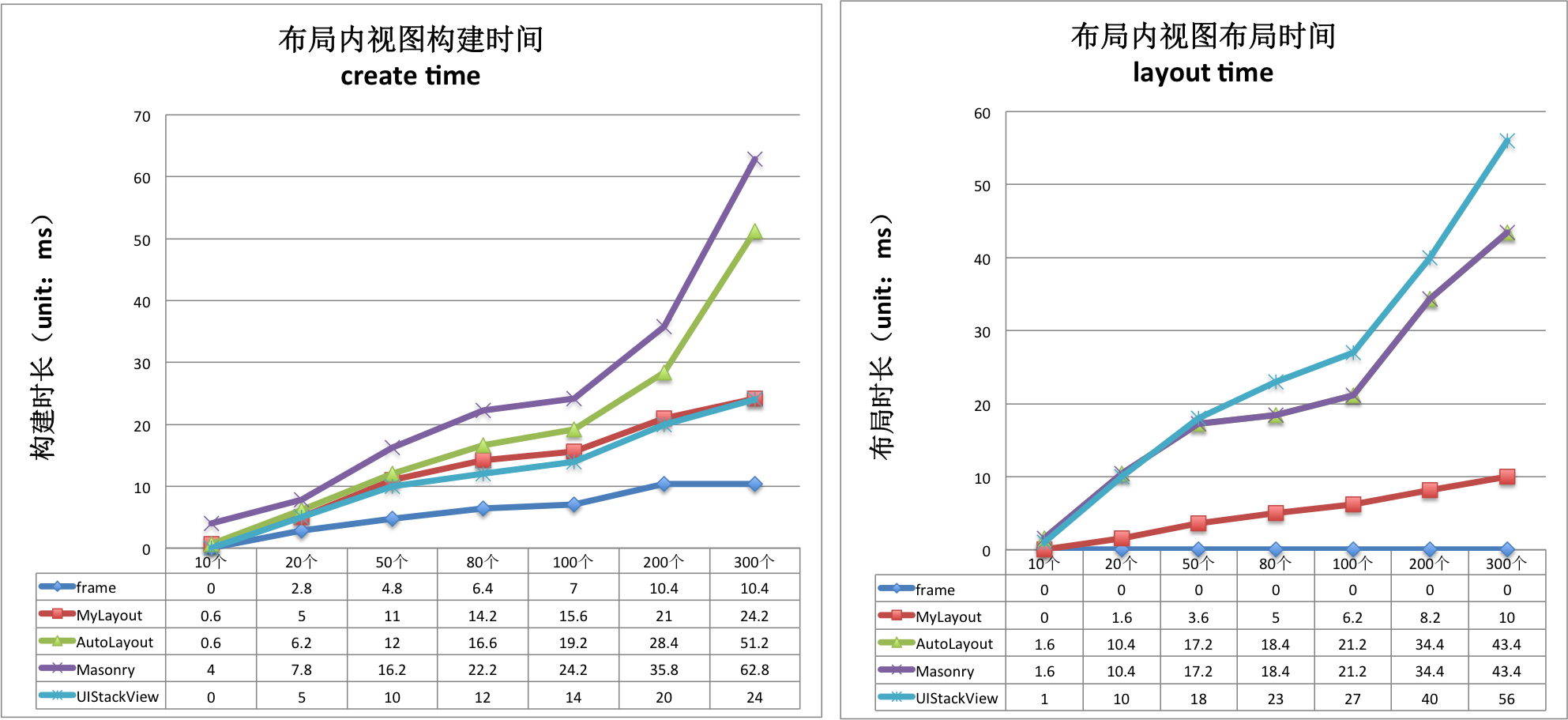
| create time(ms)/per subview | Frame | MyLayout | AutoLayout | Masonry | UIStackView |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MyLinearLayout | 0.08 | 0.164 | 0.219 | 0.304 | 0.131 |
| MyFrameLayout | 0.05 | 0.149 | 0.209 | 0.273 | 0.131 |
| MyRelativeLayout | 0.079 | 0.182 | 0.116 | 0.359 | 0.131 |
| MyFlowLayout | 0.08 | 0.107 | 0.198 | 0.258 | 0.131 |
| MyFloatLayout | 0.044 | 0.148 | 0.203 | 0.250 | 0.131 |
| layout time(ms)/per subview | Frame | MyLayout | AutoLayout | Masonry | UIStackView |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MyLinearLayout | 0 | 0.049 | 0.269 | 0.269 | 0.272 |
| MyFrameLayout | 0 | 0.042 | 0.243 | 0.243 | 0.272 |
| MyRelativeLayout | 0 | 0.068 | 0.274 | 0.274 | 0.272 |
| MyFlowLayout | 0 | 0.036 | 0.279 | 0.279 | 0.272 |
| MyFloatLayout | 0 | 0.055 | 0.208 | 0.208 | 0.272 |
Architecture
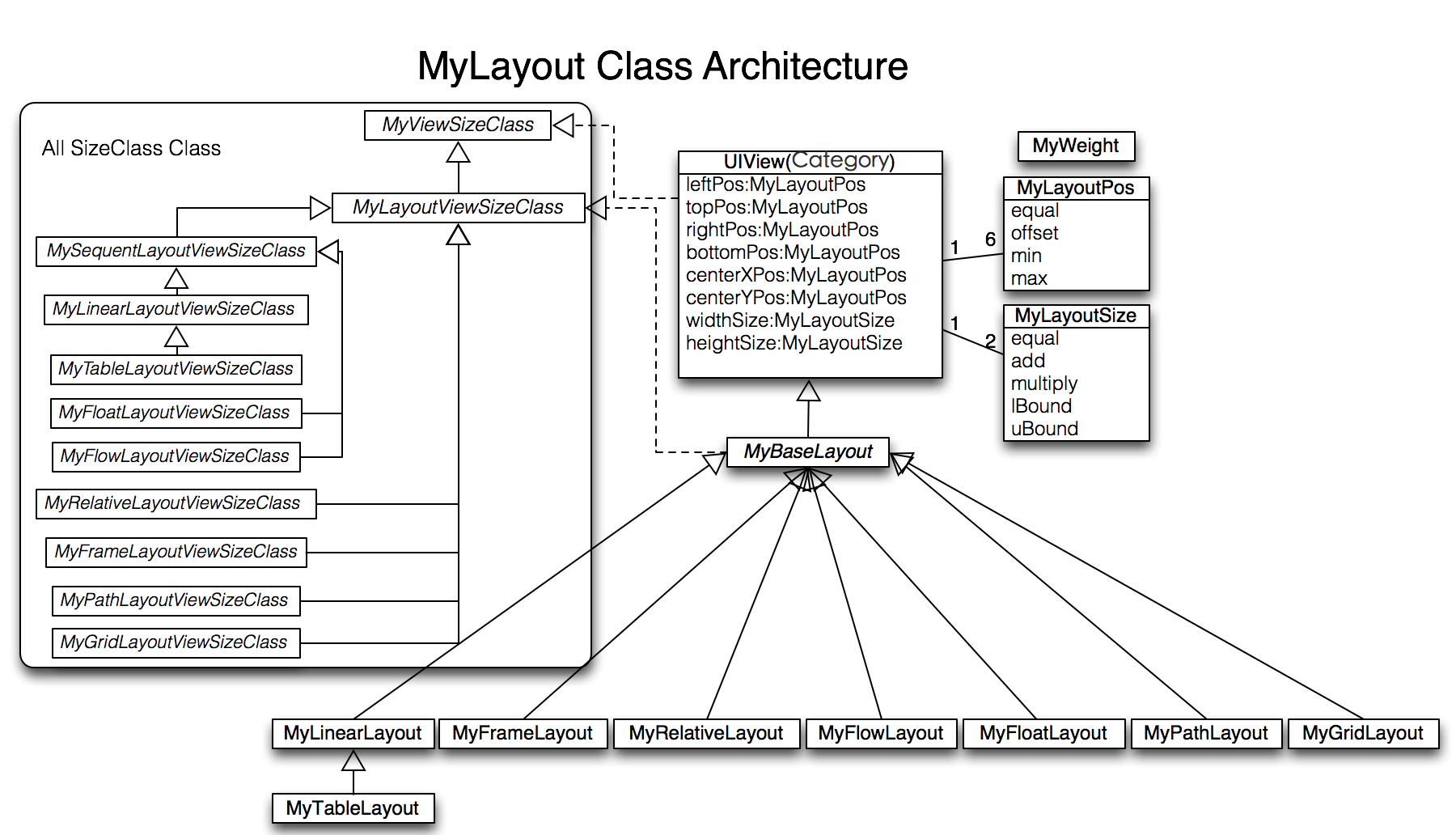
MyLayoutPos
MyLayoutPos is represent to the position of a view. UIView provides six extension variables:leftPos, topPos, bottomPos, rightPos, centerXPos, centerYPos to set view’s margin or space distance between self and others. You can use equalTo method to set NSNumber or MyLayoutPos or NSArray<MyLayoutPos*> value. there are six simple variables:myLeft,myTop,myBottom,myRight,myCenterX,myCenterY use to set NSNumber value. eg. A.leftPos.equalTo(@10); <==> A.myLeft = 10;
MyLayoutSize
MyLayoutSize is represent to the size of a view. UIView provides two extension variables:widthSize,heightSize to set view’s width and height dimension. You can use equalTo method to set NSNumber or MyLayoutSize or NSArray<MyLayoutSize*> value. there are two simple variables: myWidth, myHeight use to set NSNumber value. eg. A.widthSize.equalTo(@10); <==> A.myWidth = 10;
MyLinearLayout
Is equivalent to: UIStackView of iOS and LinearLayout of Android.
Linear layout is a single line layout view that the subviews are arranged in sequence according to the added order(from top to bottom or from left to right). So the subviews’ origin&size constraints are established by the added order. Subviews arranged in top-to-bottom order is called vertical linear layout view, and
the subviews arranged in left-to-right order is called horizontal linear layout.
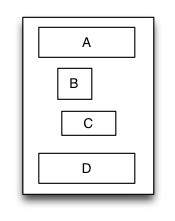
Sample code:
-(void)loadView {
[super loadView];
MyLinearLayout *S = [MyLinearLayout linearLayoutWithOrientation:MyOrientation_Vert];
S.myWidth = 120;
S.subviewSpace = 10;
UIView *A = [UIView new];
A.myHorzMargin = 5;
A.myHeight = 40;
[S addSubview:A];
UIView *B = [UIView new];
B.myLeft = 20;
B.mySize = CGSizeMake(40,40);
[S addSubview:B];
UIView *C = [UIView new];
C.myRight = 40;
C.mySize = CGSizeMake(50,40);
[S addSubview:C];
UIView *D = [UIView new];
D.myHorzMargin = 10;
D.myHeight = 40;
[S addSubview:D];
[self.view addSubview:S];
S.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
A.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
B.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
C.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
D.backgroundColor = [UIColor cyanColor];
}
MyRelativeLayout
Is equivalent to: AutoLayout of iOS and RelativeLayout of Android.
Relative layout is a layout view that the subviews layout and position through mutual constraints.The subviews in the relative layout are not depended to the adding order but layout and position by setting the subviews’ constraints.
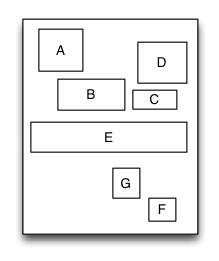
Sample code:
-(void)loadView {
[super loadView];
MyRelativeLayout *S = [MyRelativeLayout new];
S.widthSize.equalTo(@170);
S.heightSize.equalTo(@280);
UIView *A = [UIView new];
A.leftPos.equalTo(@20);
A.topPos.equalTo(@20);
A.widthSize.equalTo(@40);
A.heightSize.equalTo(A.widthSize);
[S addSubview:A];
UIView *B = [UIView new];
B.leftPos.equalTo(A.centerXPos);
B.topPos.equalTo(A.bottomPos).offset(10);
B.widthSize.equalTo(@60);
B.heightSize.equalTo(A.heightSize);
[S addSubview:B];
UIView *C = [UIView new];
C.leftPos.equalTo(B.rightPos).offset(10);
C.bottomPos.equalTo(B.bottomPos);
C.widthSize.equalTo(@40);
C.heightSize.equalTo(B.heightSize).multiply(0.5);
[S addSubview:C];
UIView *D = [UIView new];
D.bottomPos.equalTo(C.topPos).offset(10);
D.rightPos.equalTo(@15);
D.heightSize.equalTo(A.heightSize);
D.widthSize.equalTo(D.heightSize);
[S addSubview:D];
UIView *E = [UIView new];
E.centerYPos.equalTo(@0);
E.centerXPos.equalTo(@0);
E.heightSize.equalTo(@40);
E.widthSize.equalTo(S.widthSize).add(-20);
[S addSubview:E];
//.. F, G
[self.view addSubview:S];
S.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
A.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
B.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
C.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
D.backgroundColor = [UIColor cyanColor];
E.backgroundColor = [UIColor magentaColor];
}
MyFrameLayout
Is equivalent to: FrameLayout of Android.
Frame layout is a layout view that the subviews can be overlapped and gravity in a special location of the superview.The subviews’ layout position&size is not depended to the adding order and establish dependency constraint with the superview. Frame layout devided the vertical orientation to top,vertical center and bottom, while horizontal orientation is devided to left,horizontal center and right. Any of the subviews is just gravity in either vertical orientation or horizontal orientation.
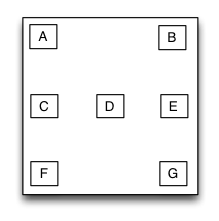
Sample code:
-(void)loadView {
[super loadView];
MyFrameLayout *S = [MyFrameLayout new];
S.mySize = CGSizeMake(320,500);
UIView *A = [UIView new];
A.mySize = CGSizeMake(40,40);
[S addSubview:A];
UIView *B = [UIView new];
B.mySize = CGSizeMake(40,40);
B.myRight = 0;
[S addSubview:B];
UIView *C = [UIView new];
C.mySize = CGSizeMake(40,40);
C.myCenterY = 0;
[S addSubview:C];
UIView *D = [UIView new];
D.mySize = CGSizeMake(40,40);
D.myCenter = CGPointZero;
[S addSubview:D];
//..E,F,G
[self.view addSubview:S];
S.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
A.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
B.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
C.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
D.backgroundColor = [UIColor cyanColor];
}
MyTableLayout
Is equivalent to: TableLayout of Android and table of HTML.
Table layout is a layout view that the subviews are multi-row&col arranged like a table. First you must create a rowview and add it to the table layout, then add the subview to the rowview. If the rowviews arranged in top-to-bottom order,the tableview is caled vertical table layout,in which the subviews are arranged from left to right; If the rowviews arranged in in left-to-right order,the tableview is caled horizontal table layout,in which the subviews are arranged from top to bottom.
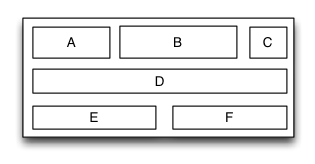
Sample code:
-(void)loadView {
[super loadView];
MyTableLayout *S = [MyTableLayout tableLayoutWithOrientation:MyOrientation_Vert];
S.myWidth = MyLayoutSize.wrap;
S.subviewHSpace = 10;
S.subviewVSpace = 10;
[S addRow:MyLayoutSize.wrap colSize:MyLayoutSize.wrap];
UIView *A = [UIView new];
A.mySize = CGSizeMake(50,40);
[S addSubview:A];
UIView *B = [UIView new];
B.mySize = CGSizeMake(100,40);
[S addSubview:B];
UIView *C = [UIView new];
C.mySize = CGSizeMake(30,40);
[S addSubview:C];
[S addRow:MyLayoutSize.wrap colSize:MyLayoutSize.wrap];
UIView *D = [UIView new];
D.mySize = CGSizeMake(200,40);
[S addSubview:D];
//...E,F
[self.view addSubview:S];
S.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
A.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
B.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
C.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
D.backgroundColor = [UIColor cyanColor];
}
MyFlowLayout
Is equivalent to: flexbox of CSS3.
Flow layout is a layout view presents in multi-line that the subviews are arranged in sequence according to the added order, and when meeting with a arranging constraint it will start a new line and rearrange. The constrains mentioned here includes count constraints and size constraints. The orientation of the new line would be vertical and horizontal, so the flow layout is divided into: count constraints vertical flow layout, size constraints vertical flow layout, count constraints horizontal flow layout, size constraints horizontal flow layout. Flow layout often used in the scenes that the subviews is arranged regularly, it can be substitutive of UICollectionView to some extent. the MyFlowLayout is almost implement the flex-box function of the HTML/CSS.
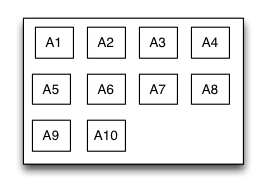
Sample code:
-(void)loadView {
[super loadView];
MyFlowLayout *S = [MyFlowLayout flowLayoutWithOrientation:MyOrientation_Vert arrangedCount:4];
S.myHeight = MyLayoutSize.wrap;
S.myWidth = 300;
S.padding = UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10);
S.gravity = MyGravity_Horz_Fill;
S.subviewSpace = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
UIView *A = [UIView new];
A.heightSize.equalTo(A.widthSize);
[S addSubview:A];
A.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
}
[self.view addSubview:S];
S.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
}
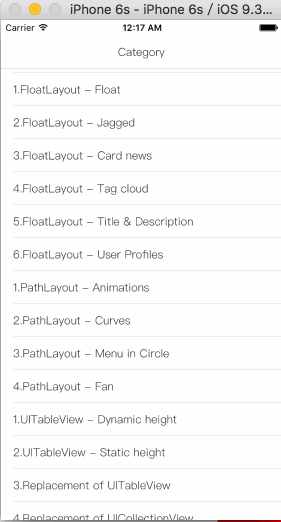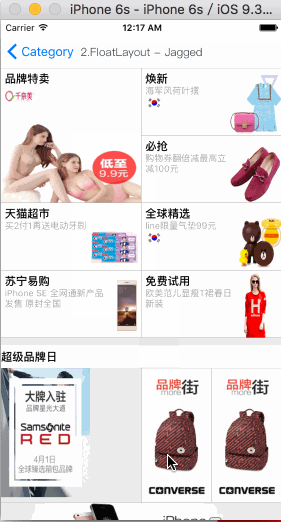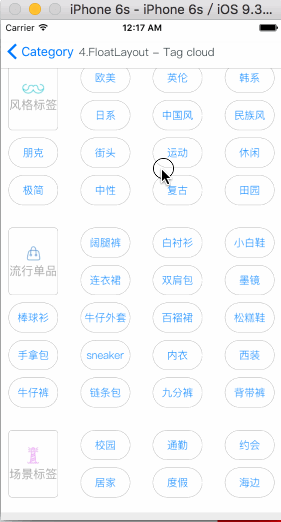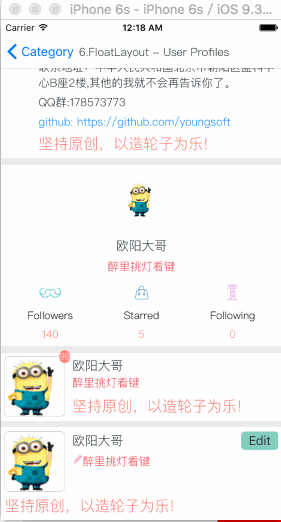
MyFloatLayout
Is equivalent to: float of CSS.
Float layout is a layout view that the subviews are floating gravity in the given orientations, when the size is not enough to be hold, it will automatically find the best location to gravity. float layout’s conception is reference from the HTML/CSS’s floating positioning technology, so the float layout can be designed in implementing irregular layout. According to the different orientation of the floating, float layout can be divided into left-right float layout and up-down float layout.
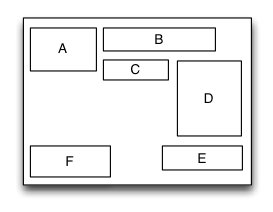
Sample code:
-(void)loadView {
[super loadView];
MyFloatLayout *S = [MyFloatLayout floatLayoutWithOrientation:MyOrientation_Vert];
S.padding = UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10);
S.subviewSpace = 10;
S.myWidth = 300;
S.myHeight = MyLayoutSize.wrap;
UIView *A = [UIView new];
A.mySize = CGSizeMake(80,70);
[S addSubview:A];
UIView *B = [UIView new];
B.mySize = CGSizeMake(150,40);
[S addSubview:B];
UIView *C = [UIView new];
C.mySize = CGSizeMake(70,40);
[S addSubview:C];
UIView *D = [UIView new];
D.mySize = CGSizeMake(100,140);
[S addSubview:D];
UIView *E = [UIView new];
E.mySize = CGSizeMake(150,40);
E.reverseFloat = YES;
[S addSubview:E];
UIView *F = [UIView new];
F.mySize = CGSizeMake(120,60);
[S addSubview:F];
[self.view addSubview:S];
S.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
A.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
B.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
C.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
D.backgroundColor = [UIColor cyanColor];
E.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
F.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
}
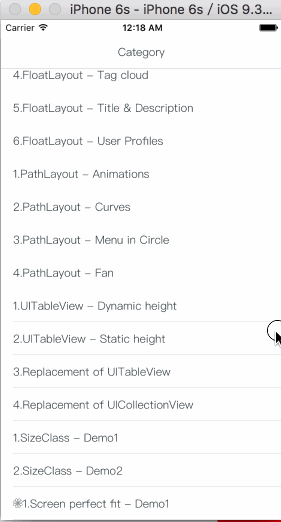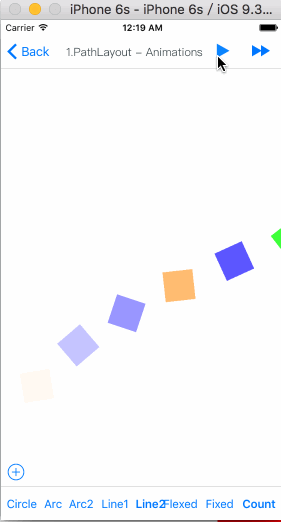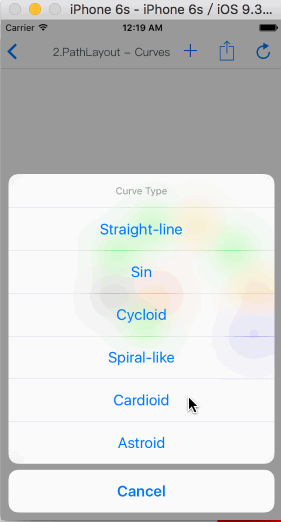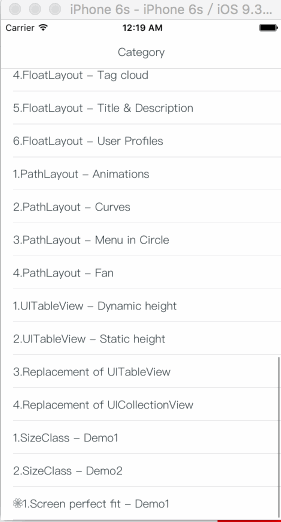
MyPathLayout
Is unique characteristic layout view of iOS.
Path layout is a layout view that the subviews are according to a specified path curve to layout. You must provide a type of Functional equation,a coordinate and a type of distance setting to create a Path Curve than all subview are equidistance layout in the Path layout. path layout usually used to create some irregular and gorgeous UI layout.
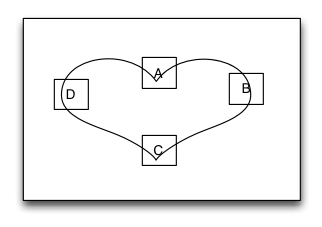
Sample code:
-(void)loadView {
[super loadView];
MyPathLayout *S = [MyPathLayout new];
S.mySize = CGSizeMake(320,320);
S.coordinateSetting.isReverse = YES;
S.coordinateSetting.origin = CGPointMake(0.5, 0.2);
S.polarEquation = ^(CGFloat angle) {
return 80 * (1 + cos(angle));
};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
UIView *A = [UIView new];
A.mySize = CGSizeMake(40,40);
[S addSubview:A];
A.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
}
[self.view addSubview:S];
S.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
}
MyGridLayout
Is unique characteristic layout view of iOS.
Grid layout is a view to a rectangular area according to the row or column divided into multiple sub areas, sub area according to the requirements of layout can continue recursive partitioning, grid layout inside the child view will be in accordance with the sequence to add to the corresponding leaf area filling in the layout of the mechanism. Grid layout through a system of the layout of the custom to the position and size, added to the inside of the grid layout child view will no longer need to specify the location and size but by grid layout of the grid to complete, so can be very convenient to adjust the layout structure, so as to realize the ability of dynamic layout.
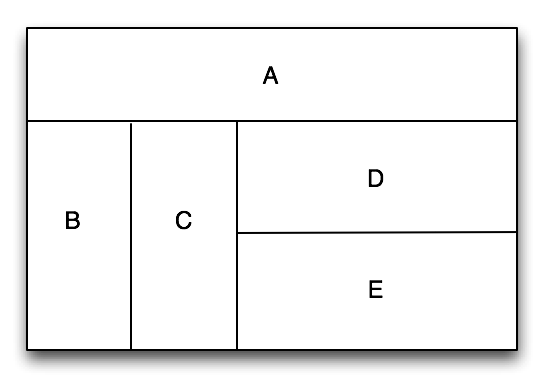
Sample code:
-(void)loadView {
[super loadView];
MyGridLayout *S = [MyGridLayout new];
S.mySize = CGSizeMake(320,320);
S.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
[self.view addSubview:S];
//add grids
[S addRow:50];
id<MyGrid> g2 = [S addRow:MyLayoutSize.fill];
[g2 addCol:0.2];
[g2 addCol:0.2];
id<MyGrid> g23 = [g2 addCol:0.6];
[g23 addRow:0.5];
[g23 addRow:0.5];
//add subviews
UIView *A = [UIView new];
A.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
[S addSubview:A];
UIView *B = [UIView new];
B.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
[S addSubview:B];
UIView *C = [UIView new];
C.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
[S addSubview:C];
UIView *D = [UIView new];
D.backgroundColor = [UIColor cyanColor];
[S addSubview:D];
UIView *E = [UIView new];
E.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
[S addSubview:E];
}
MyFlexLayout
Flex is a layout defined in the W3C specification. This layout allows simple, fast, responsive implementation of various layout pages, and is intended to replace “position+display+float”. MyFlexLayout implements a subset of the flex specification while extending some of the capabilities in the flex specification. Since MyFlowLayout also provides similar elastic layout capabilities, but the syntax is not compatible with the flex specification, MyFlexLayout provides a new layout writing syntax derived from MyFlowLayout. Syntax candy allows you to use the syntax defined by the flex specification to implement the layout of the code.

Sample code:
-(void)loadView {
[super loadView];
MyFlexLayout *S = MyFlexLayout.new.myFlex
.flex_direction(MyFlexDirection_Row)
.flex_wrap(MyFlexWrap_Wrap)
.vert_space(10)
.horz_space(10)
.padding(UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10))
.width(300)
.height(MyLayoutSize.wrap)
.addTo(self.view);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
UIView *A = UIView.new.myFlex
.width(60)
.height(50)
.addTo(S);
A.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
}
}
MySizeClass
Is equivalent to: Size Classes of iOS.
MyLayout provided support to SizeClass in order to fit the different screen sizes of devices. You can combinate the SizeClass with any of the 6 kinds of layout views mentioned above to perfect fit the UI of all equipments. there are two UIView extension method:
-(instancetype)fetchLayoutSizeClass:(MySizeClass)sizeClass;
-(instancetype)fetchLayoutSizeClass:(MySizeClass)sizeClass copyFrom:(MySizeClass)srcSizeClass;
to set Size Classes Characteristics like below:
//default is all Size Classes
MyLinearLayout *rootLayout = [MyLinearLayout linearLayoutWithOrientation:MyOrientation_Vert];
rootLayout.padding = UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10);
rootLayout.myHeight = MyLayoutSize.empty;
rootLayout.gravity = MyGravity_Horz_Fill;
//MySizeClass_wAny | MySizeClass_hCompact is iPhone landscape orientation.
MyLinearLayout *lsc = [rootLayout fetchLayoutSizeClass:MySizeClass_wAny | MySizeClass_hCompact copyFrom:MySizeClass_wAny | MySizeClass_hAny];
lsc.orientation = MyOrientation_Horz;
lsc.myWidth = MyLayoutSize.empty;
lsc.gravity = MyGravity_Vert_Fill;
Demo sample
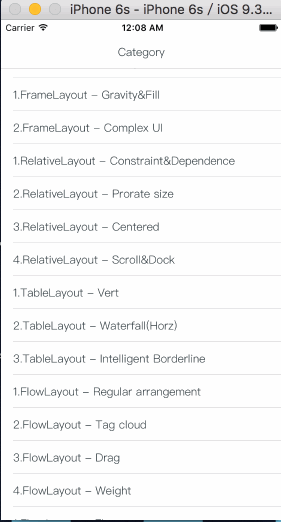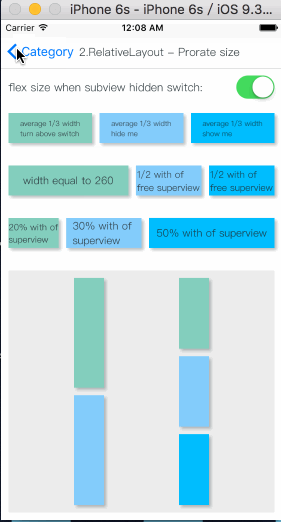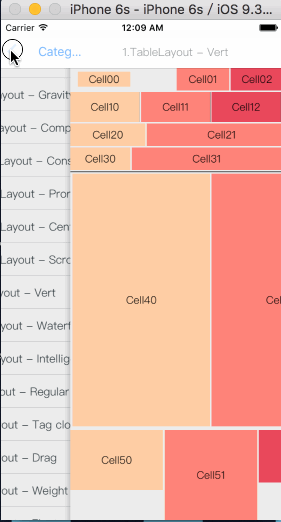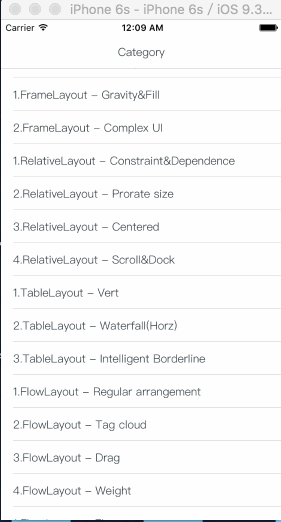

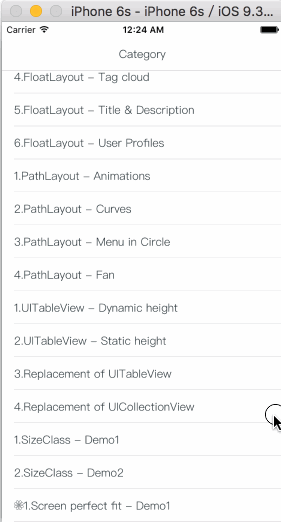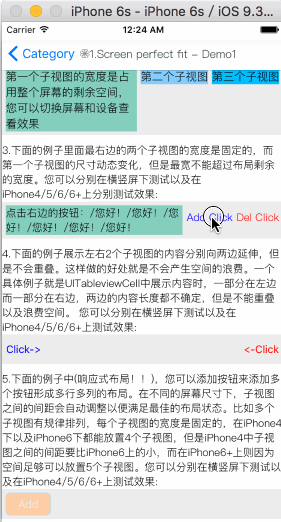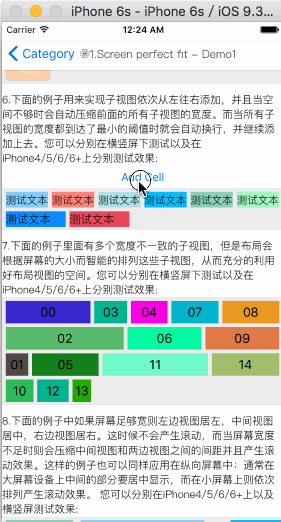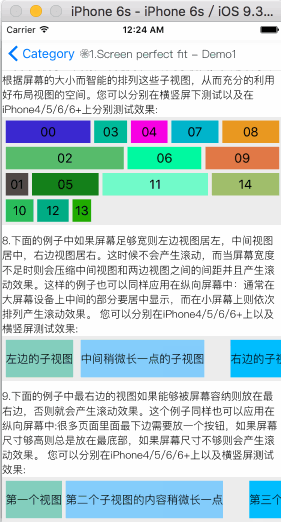

How To Get Started
Download MyLayout and try out the included iPad and iPhone example apps
Read FAQ, or articles below:
http://www.jianshu.com/p/4c1eb0dd676f 布局框架和原理介绍
http://blog.csdn.net/yangtiang/article/details/46483999 线性布局
http://blog.csdn.net/yangtiang/article/details/46795231 相对布局
http://blog.csdn.net/yangtiang/article/details/46492083 框架布局
http://blog.csdn.net/yangtiang/article/details/48011431 表格布局
http://blog.csdn.net/yangtiang/article/details/50652946 流式布局
http://www.jianshu.com/p/0c075f2fdab2 浮动布局
http://www.jianshu.com/p/4ac229057396 路径布局
Because my english is poor so I just only can support chinese articles,and I wish somebody can help me translate to english.
Communication
- If you need help, use Stack Overflow or Baidu. (Tag ‘mylayout’)
- If you’d like to contact me, use qq:156355113 or weibo:欧阳大哥 or email:[email protected]
- If you found a bug, and can provide steps to reliably reproduce it, open an issue.
- If you have a feature request, open an issue.
- If you want to contribute, submit a pull request.
Installation
MyLayout supports multiple methods for installing the library in a project.
Copy to your project
- Copy
Libfolder from the demo project to your project - Add
#import "MyLayout.h"to your project’s PCH file or the referenced header file。
Installation with CocoaPods
CocoaPods is a dependency manager for Objective-C, which automates and simplifies the process of using 3rd-party libraries like MyLayout in your projects. You can install it with the following command:
$ gem install cocoapods
To integrate MyLayout into your Xcode project using CocoaPods, specify it in your Podfile:
source 'https://github.com/CocoaPods/Specs.git'
platform :ios, '9.0'
pod 'MyLayout'
Then, run the following command:
$ pod install
Use Carthage
-
Create a
Cartfilefile.github "youngsoft/MyLinearLayout" -
Run
carthage update. -
On your application targets’ “General” settings tab, in the “Linked Frameworks and Libraries” section, drag and drop
MyLayoutframework from the Carthage/Build folder on disk. -
On your application targets’ “Build Phases” settings tab, click the “+” icon and choose “New Run Script Phase”. Create a Run Script in which you specify your shell (ex: bin/sh), add the following contents to the script area below the shell:
/usr/local/bin/carthage copy-frameworksand add the path under “Input Files”, e.g.:
$(SRCROOT)/Carthage/Build/iOS/MyLayout.framework
FAQ
- If you use MyLayout runtime cause 100% CPU usage said appeared constraint conflict, please check the subview’s constraint set.
- If you use MyLayout exception crashed in MyBaseLayout willMoveToSuperview method. it does not matter, just remove the exception break setting in CMD+7.
- If you set wrapConentWidth or wrapContentHeight while set widthSize or heightSize in layout view may be constraint conflict。
- If you set the layout view as a UIViewController’s root view. please set wrapContentWidth and wrapContentHeight to NO.
- Just only MyLinearLayout and MyFrameLayout’s subview support relative margin.
- If subview added in layout view, the setFrame method can’t setting the origin but the size.
License
MyLayout is released under the MIT license. See LICENSE for details.







