Label images and video for Computer Vision applications
OpenLabeling: open-source image and video labeler
Image labeling in multiple annotation formats:
- PASCAL VOC (= darkflow)
- YOLO darknet
- ask for more (create a new issue)…

Citation
This project was developed for the following paper, please consider citing it:
@INPROCEEDINGS{8594067,
author={J. {Cartucho} and R. {Ventura} and M. {Veloso}},
booktitle={2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)},
title={Robust Object Recognition Through Symbiotic Deep Learning In Mobile Robots},
year={2018},
pages={2336-2341},
}
Latest Features
- Jun 2019: Deep Learning Object Detection Model
- May 2019: [ECCV2018] Distractor-aware Siamese Networks for Visual Object Tracking
- Jan 2019: easy and quick bounding-boxe’s resizing!
- Jan 2019: video object tracking with OpenCV trackers!
- TODO: Label photos via Google drive to allow “team online labeling”.
New Features Discussion
Table of contents
Quick start
To start using the YOLO Bounding Box Tool you need to download the latest release or clone the repo:
git clone --recurse-submodules [email protected]:Cartucho/OpenLabeling.git
Prerequisites
You need to install:
- Python
- OpenCV version >= 3.0
python -mpip install -U pippython -mpip install -U opencv-pythonpython -mpip install -U opencv-contrib-python
- numpy, tqdm and lxml:
python -mpip install -U numpypython -mpip install -U tqdmpython -mpip install -U lxml
Alternatively, you can install everything at once by simply running:
python -mpip install -U pip
python -mpip install -U -r requirements.txt
- PyTorch
Visit the link for a configurator for your setup.
Run project
Step by step:
-
Open the
main/directory -
Insert the input images and videos in the folder input/
-
Insert the classes in the file class_list.txt (one class name per line)
-
Run the code:
-
You can find the annotations in the folder output/
python main.py [-h] [-i] [-o] [-t] [--tracker TRACKER_TYPE] [-n N_FRAMES] optional arguments: -h, --help Show this help message and exit -i, --input Path to images and videos input folder | Default: input/ -o, --output Path to output folder (if using the PASCAL VOC format it's important to set this path correctly) | Default: output/ -t, --thickness Bounding box and cross line thickness (int) | Default: -t 1 --tracker tracker_type tracker_type being used: ['CSRT', 'KCF','MOSSE', 'MIL', 'BOOSTING', 'MEDIANFLOW', 'TLD', 'GOTURN', 'DASIAMRPN'] -n N_FRAMES number of frames to track object for
To use DASIAMRPN Tracker:
- Install the DaSiamRPN submodule and download the model (VOT) from google drive
- copy it into ‘DaSiamRPN/code/’
- set default tracker in main.py or run it with --tracker DASIAMRPN
How to use the deep learning feature
- Download one or some deep learning models from https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/object_detection/g3doc/detection_model_zoo.md
and put it intoobject_detection/modelsdirectory (you need to create themodelsfolder by yourself). The outline ofobject_detectionlooks like that:tf_object_detection.pyutils.pymodels/ssdlite_mobilenet_v2_coco_2018_05_09
Download the pre-trained model by clicking this link http://download.tensorflow.org/models/object_detection/ssdlite_mobilenet_v2_coco_2018_05_09.tar.gz and put it into object_detection/models. Create the models folder if necessary. Make sure to extract the model.
Note: Default model used in main_auto.py is ssdlite_mobilenet_v2_coco_2018_05_09. We can
set graph_model_path in file main_auto.py to change the pretrain model
-
Using
main_auto.pyto automatically label data firstTODO: explain how the user can
GUI usage
Keyboard, press:

| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| a/d | previous/next image |
| s/w | previous/next class |
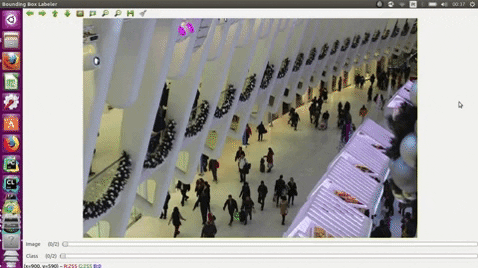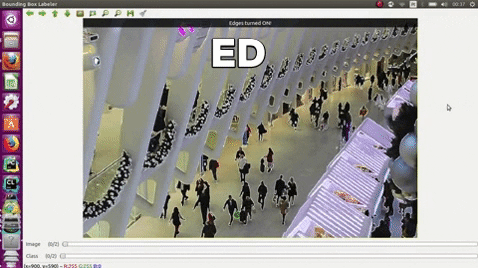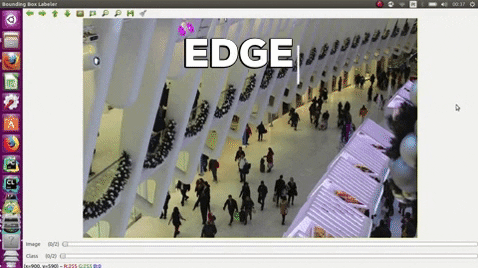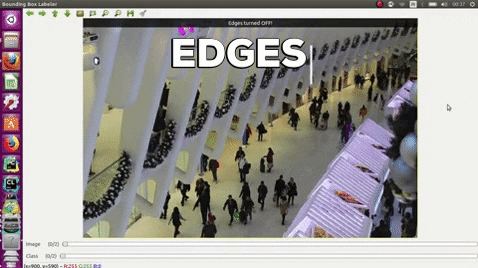
| e | edges |
| h | help |
| q | quit |
Video:
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| p | predict the next frames’ labels |
Mouse:
- Use two separate left clicks to do each bounding box
- Right-click -> quick delete!
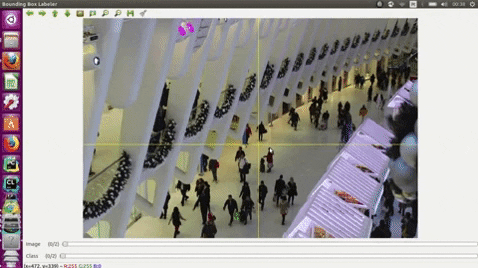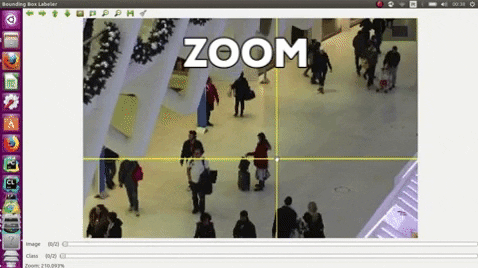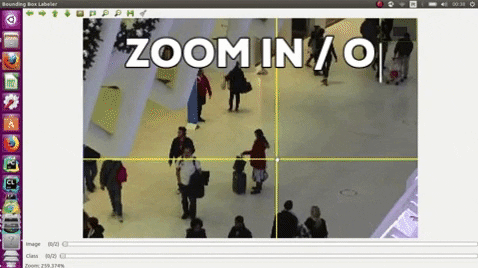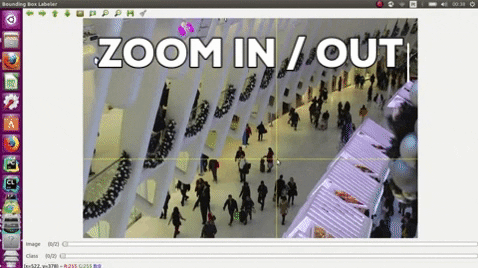
- Use the middle mouse to zoom in and out
- Use double click to select a bounding box

