💫 Ngrok FRP Alternative • ⚡ Fast • 🪶 Lightweight • 0️⃣ Dependency • 🔌 Pluggable • 😈 TLS interception • 🔒 DNS-over-HTTPS • 🔥 Poor Man's VPN • ⏪ Reverse & ⏩ Forward • 👮🏿 "Proxy Server" framework • 🌐 "Web Server" framework • ➵ ➶ ➷ ➠ "PubSub" framework • 👷 "Work" acceptor & executor framework
Table of Contents
- Features
- Install
- Start proxy.py
- Plugin Examples
- HTTP Proxy Plugins
- ShortLink Plugin
- Modify Post Data Plugin
- Mock Api Plugin
- Redirect To Custom Server Plugin
- Filter By Upstream Host Plugin
- Cache Responses Plugin
- Cache By Response Type
- Man-In-The-Middle Plugin
- Proxy Pool Plugin
- Filter By Client IP Plugin
- Modify Chunk Response Plugin
- Modify Request Header Plugin
- Cloudflare DNS Resolver Plugin
- Custom DNS Resolver Plugin
- Custom Network Interface
- Program Name Plugin
- HTTP Web Server Plugins
- Reverse Proxy Plugins
- Plugin Ordering
- HTTP Proxy Plugins
- End-to-End Encryption
- TLS Interception
- GROUT (NGROK Alternative)
- Proxy Over SSH Tunnel
- Embed proxy.py
- Unit testing with proxy.py
- Utilities
- Run Dashboard
- Chrome DevTools Protocol
- Prometheus Metrics
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Deploying proxy.py in production
- Stable vs Develop
- Threads vs Threadless
- Threadless Remote vs Local Execution Mode
- SyntaxError: invalid syntax
- Unable to load plugins
- Unable to connect with proxy.py from remote host
- Basic auth not working with a browser
- Docker image not working on MacOS
ValueError: filedescriptor out of range in select- None:None in access logs
- OSError when wrapping client for TLS Interception
- Plugin Developer and Contributor Guide
- Projects Using Proxy.Py
- Benchmarks
- Flags
- Changelog
Features
-
Fast & Scalable
-
Scale up by using all available cores on the system
-
Threadless executions using asyncio
-
Made to handle
tens-of-thousandsconnections / sec# On Macbook Pro M2 2022 ❯ python --version Python 3.11.8 ❯ oha --version oha 1.4.3 ❯ ./benchmark/compare.sh CONCURRENCY: 100 workers, DURATION: 1m, TIMEOUT: 1sec ============================= Benchmarking Proxy.Py Server (pid:75969) running Summary: Success rate: 100.00% Total: 60.0006 secs Slowest: 0.2525 secs Fastest: 0.0002 secs Average: 0.0019 secs Requests/sec: 51667.3774 Total data: 56.17 MiB Size/request: 19 B Size/sec: 958.64 KiB Response time histogram: 0.000 [1] | 0.025 [3073746] |■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■ 0.051 [10559] | 0.076 [4980] | 0.101 [2029] | 0.126 [5896] | 0.152 [2466] | 0.177 [116] | 0.202 [40] | 0.227 [52] | 0.253 [87] | Response time distribution: 10.00% in 0.0005 secs 25.00% in 0.0007 secs 50.00% in 0.0009 secs 75.00% in 0.0014 secs 90.00% in 0.0021 secs 95.00% in 0.0035 secs 99.00% in 0.0198 secs 99.90% in 0.1262 secs 99.99% in 0.1479 secs Details (average, fastest, slowest): DNS+dialup: 0.0018 secs, 0.0004 secs, 0.0031 secs DNS-lookup: 0.0000 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0002 secs Status code distribution: [200] 3099972 responses Error distribution: [100] aborted due to deadline =============================Consult Threads vs Threadless and Threadless Remote vs Local Execution Mode to control number of CPU cores utilized.
See Benchmark for more details and for how to run benchmarks locally.
-
-
Lightweight
- Uses only
~5-20 MBRAM- No memory leaks
- Start once and forget, no restarts required
- Compressed containers size is only
~25 MB - No external dependency other than standard Python library
- Uses only
-
Programmable
- Customize proxy behavior using Proxy Server Plugins. Example:
--plugins proxy.plugin.ProxyPoolPlugin
- Enable builtin Web Server. Example:
--enable-web-server --plugins proxy.plugin.WebServerPlugin
- Enable builtin Reverse Proxy Server. Example:
--enable-reverse-proxy --plugins proxy.plugin.ReverseProxyPlugin
- Plugin API is currently in development phase. Expect breaking changes. See Deploying proxy.py in production on how to ensure reliability across code changes.
- Customize proxy behavior using Proxy Server Plugins. Example:
-
Can listen on multiple addresses and ports
- Use
--hostnamesflag to provide additional addresses - Use
--portsflag to provide additional ports - Optionally, use
--portflag to override default port8899 - Capable of serving multiple protocols over the same port
- Use
-
Real-time Dashboard
- Optionally, enable proxy.py dashboard.
- Use
--enable-dashboard - Then, visit
http://localhost:8899/dashboard
- Use
- Inspect, Monitor, Control and Configure
proxy.pyat runtime - Chrome DevTools Protocol support
- Extend dashboard frontend using
typescriptbased plugins - Dashboard is currently in development phase Expect breaking changes.
- Optionally, enable proxy.py dashboard.
-
Secure
- Enable end-to-end encryption between clients and
proxy.py - See End-to-End Encryption
- Enable end-to-end encryption between clients and
-
Private
- Protection against DNS based traffic blockers
- Browse with malware and adult content protection enabled
- See DNS-over-HTTPS
-
Man-In-The-Middle
- Can decrypt TLS traffic between clients and upstream servers
- See TLS Interception
-
Supported http protocols for proxy requests
http(s)http1http1.1with pipeline
http2websockets
-
Support for
HAProxy Protocol- See
--enable-proxy-protocolflag
- See
-
Static file server support
- See
--enable-static-serverand--static-server-dirflags
- See
-
Optimized for large file uploads and downloads
- See
--client-recvbuf-size,--server-recvbuf-size,--max-sendbuf-sizeflags
- See
-
IPv4andIPv6support- See
--hostnameflag
- See
-
Unix domain socket support
- See
--unix-socket-pathflag
- See
-
Basic authentication support
- See
--basic-authflag
- See
-
PAC (Proxy Auto-configuration) support
- See
--pac-fileand--pac-file-url-pathflags
- See
Install
Consult Deploying proxy.py in production when deploying production grade applications using proxy.py.
Using PIP
Stable Version with PIP
Install from PyPi
❯ pip install --upgrade proxy.py
or from GitHub master branch
❯ pip install git+https://github.com/abhinavsingh/proxy.py.git@master
Development Version with PIP
❯ pip install git+https://github.com/abhinavsingh/proxy.py.git@develop
Using Docker
Multi-platform containers are available via:
- Docker Hub
latesttag points to laststablereleasedocker pull abhinavsingh/proxy.py:latest
- GitHub container registry (GHCR)
latesttag points to lastdevelopreleasedocker pull ghcr.io/abhinavsingh/proxy.py:latest
Stable version container releases are available for following platforms:
linux/386linux/amd64linux/arm/v6linux/arm/v7linux/arm64/v8linux/ppc64lelinux/s390x
Stable Version from Docker Hub
Run proxy.py latest container:
❯ docker run -it -p 8899:8899 --rm abhinavsingh/proxy.py:latest
Docker daemon will automatically pull the matching platform image.
To run specific target platform container on multi-platform supported servers:
❯ docker run -it -p 8899:8899 --rm --platform linux/arm64/v8 abhinavsingh/proxy.py:latest
Development Version from GHCR
Run proxy.py container from cutting edge code in the develop branch:
❯ docker run -it -p 8899:8899 --rm ghcr.io/abhinavsingh/proxy.py:latest
Build Development Version Locally
❯ git clone https://github.com/abhinavsingh/proxy.py.git
❯ cd proxy.py && make container
❯ docker run -it -p 8899:8899 --rm abhinavsingh/proxy.py:latest
docker image is currently broken on macOS due to incompatibility with vpnkit.
Using HomeBrew
Updated formulae for HomeBrew are maintained in develop branch under the helper/homebrew directory.
stableformulae installs the package frommasterbranch.developformulae installs the package fromdevelopbranch.
Stable Version with HomeBrew
❯ brew install https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abhinavsingh/proxy.py/develop/helper/homebrew/stable/proxy.rb
Development Version with HomeBrew
❯ brew install https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abhinavsingh/proxy.py/develop/helper/homebrew/develop/proxy.rb
Start proxy.py
From command line when installed using PIP
When proxy.py is installed using pip,
an executable named proxy is placed under your $PATH.
Run it
Simply type proxy on command line to start with default configuration.
❯ proxy
...[redacted]... - Loaded plugin proxy.http.proxy.HttpProxyPlugin
...[redacted]... - Started 8 threadless workers
...[redacted]... - Started 8 acceptors
...[redacted]... - Listening on 127.0.0.1:8899
Understanding logs
Things to notice from above logs:
-
Loaded pluginproxy.pywill loadproxy.http.proxy.HttpProxyPluginby default- As name suggests, this core plugin adds
http(s)proxy server capabilities toproxy.pyinstance
-
Started N threadless workers- By default,
proxy.pywill start as many worker processes as there are CPU cores on the machine - Use
--num-workersflag to customize number of worker processes - See Threads vs Threadless to understand how to control execution mode
- By default,
-
Started N acceptors- By default,
proxy.pywill start as many acceptor processes as there are CPU cores on the machine - Use
--num-acceptorsflag to customize number of acceptor processes - See High Level Architecture to understand relationship between acceptors and workers
- By default,
-
Started server on ::1:8899- By default,
proxy.pylistens on IPv6::1, which is equivalent of IPv4127.0.0.1 - If you want to access
proxy.pyfrom external host, use--hostname ::or--hostname 0.0.0.0or bind to any other interface available on your machine. - See CustomNetworkInterface for how to customize
proxy.pypublic IP seen by upstream servers.
- By default,
-
Port 8899- Use
--portflag to customize default TCP port.
- Use
Enable DEBUG logging
All the logs above are INFO level logs, default --log-level for proxy.py
Lets start proxy.py with DEBUG level logging:
❯ proxy --log-level d
...[redacted]... - Open file descriptor soft limit set to 1024
...[redacted]... - Loaded plugin proxy.http_proxy.HttpProxyPlugin
...[redacted]... - Started 8 workers
...[redacted]... - Started server on ::1:8899
You can use single letter to customize log level. Example:
d = DEBUGi = INFOw = WARNINGe = ERRORc = CRITICAL
As we can see from the above logs, before starting up:
proxy.pytried to set open file limitulimiton the system- Default value for
--open-file-limitused is1024 --open-file-limitflag is a no-op onWindowsoperating systems
See flags for full list of available configuration options.
From command line using repo source
If you are trying to run proxy.py from source code,
there is no binary file named proxy in the source code.
To start proxy.py from source code follow these instructions:
-
Clone repo
❯ git clone https://github.com/abhinavsingh/proxy.py.git ❯ cd proxy.py -
Create a Python 3 virtual env
❯ python3 -m venv venv ❯ source venv/bin/activate -
Install deps
❯ make lib-dep -
Generate
proxy/common/_scm_version.pyNOTE: Following step is not necessary for editable installs.
This file writes SCM detected version to
proxy/common/_scm_version.pyfile.❯ ./write-scm-version.sh -
Optionally, run tests
❯ make -
Run
proxy.py❯ python -m proxy
See Plugin Developer and Contributor Guide
if you plan to work with proxy.py source code.
Docker image
Customize startup flags
By default docker binary is started with IPv4 networking flags:
--hostname 0.0.0.0 --port 8899
You can override flag from command line when starting the docker container. For example, to check proxy.py version within the docker container, run:
❯ docker run -it \
-p 8899:8899 \
--rm abhinavsingh/proxy.py:latest \
-v
Plugin Examples
- See plugin module for full code.
- All the bundled plugin examples also works with
httpstraffic- Require additional flags and certificate generation
- See TLS Interception.
- Plugin examples are also bundled with Docker image.
- See Customize startup flags to try plugins with Docker image.
HTTP Proxy Plugins
ShortLinkPlugin
Add support for short links in your favorite browsers / applications.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.ShortLinkPlugin
Now you can speed up your daily browsing experience by visiting your
favorite website using single character domain names 😃. This works
across all browsers.
Following short links are enabled by default:
| Short Link | Destination URL |
|---|---|
| a/ | amazon.com |
| i/ | instagram.com |
| l/ | linkedin.com |
| f/ | facebook.com |
| g/ | google.com |
| t/ | twitter.com |
| w/ | web.whatsapp.com |
| y/ | youtube.com |
| proxy/ | localhost:8899 |
ModifyPostDataPlugin
Modifies POST request body before sending request to upstream server.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.ModifyPostDataPlugin
By default plugin replaces POST body content with hard-coded b'{"key": "modified"}'
and enforced Content-Type: application/json.
Verify the same using curl -x localhost:8899 -d '{"key": "value"}' http://httpbin.org/post
{
"args": {},
"data": "{\"key\": \"modified\"}",
"files": {},
"form": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Content-Length": "19",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0"
},
"json": {
"key": "modified"
},
"origin": "1.2.3.4, 5.6.7.8",
"url": "https://httpbin.org/post"
}
Note following from the response above:
- POST data was modified
"data": "{\"key\": \"modified\"}".
Originalcurlcommand data was{"key": "value"}. - Our
curlcommand did not add anyContent-Typeheader,
but our plugin did add one"Content-Type": "application/json".
Same can also be verified by looking atjsonfield in the output above:"json": { "key": "modified" }, - Our plugin also added a
Content-Lengthheader to match length
of modified body.
MockRestApiPlugin
Mock responses for your server REST API.
Use to test and develop client side applications
without need of an actual upstream REST API server.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.ProposedRestApiPlugin
Verify mock API response using curl -x localhost:8899 http://api.example.com/v1/users/
{"count": 2, "next": null, "previous": null, "results": [{"email": "[email protected]", "groups": [], "url": "api.example.com/v1/users/1/", "username": "admin"}, {"email": "[email protected]", "groups": [], "url": "api.example.com/v1/users/2/", "username": "admin"}]}
Verify the same by inspecting proxy.py logs:
... [redacted] ... - access_log:1210 - ::1:64792 - GET None:None/v1/users/ - None None - 0 byte
Access log shows None:None as server ip:port. None simply means that
the server connection was never made, since response was returned by our plugin.
Now modify ProposedRestApiPlugin to returns REST API mock
responses as expected by your clients.
RedirectToCustomServerPlugin
Redirects all incoming http requests to custom web server.
By default, it redirects client requests to inbuilt web server,
also running on 8899 port.
Start proxy.py and enable inbuilt web server:
❯ proxy \
--enable-web-server \
--plugins proxy.plugin.RedirectToCustomServerPlugin
Verify using curl -v -x localhost:8899 http://google.com
... [redacted] ...
< HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND
< Server: proxy.py v1.0.0
< Connection: Close
<
* Closing connection 0
Above 404 response was returned from proxy.py web server.
Verify the same by inspecting the logs for proxy.py.
Along with the proxy request log, you must also see a http web server request log.
... [redacted] ... - access_log:1241 - ::1:49525 - GET /
... [redacted] ... - access_log:1157 - ::1:49524 - GET localhost:8899/ - 404 NOT FOUND - 70 bytes
FilterByUpstreamHostPlugin
Drops traffic by inspecting upstream host.
By default, plugin drops traffic for facebook.com and www.facebok.com.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.FilterByUpstreamHostPlugin
Verify using curl -v -x localhost:8899 http://facebook.com:
... [redacted] ...
< HTTP/1.1 418 I'm a tea pot
< Proxy-agent: proxy.py v1.0.0
* no chunk, no close, no size. Assume close to signal end
<
* Closing connection 0
Above 418 I'm a tea pot is sent by our plugin.
Verify the same by inspecting logs for proxy.py:
... [redacted] ... - handle_readables:1347 - HttpProtocolException type raised
Traceback (most recent call last):
... [redacted] ...
... [redacted] ... - access_log:1157 - ::1:49911 - GET None:None/ - None None - 0 bytes
CacheResponsesPlugin
Caches Upstream Server Responses.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.CacheResponsesPlugin
You may also use the --cache-requests flag to enable request packet caching for inspection.
Verify using curl -v -x localhost:8899 http://httpbin.org/get:
... [redacted] ...
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
< Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
< Content-Type: application/json
< Date: Wed, 25 Sep 2019 02:24:25 GMT
< Referrer-Policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade
< Server: nginx
< X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
< X-Frame-Options: DENY
< X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
< Content-Length: 202
< Connection: keep-alive
<
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0"
},
"origin": "1.2.3.4, 5.6.7.8",
"url": "https://httpbin.org/get"
}
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
Get path to the cache file from proxy.py logs:
... [redacted] ... - GET httpbin.org:80/get - 200 OK - 556 bytes
... [redacted] ... - Cached response at /var/folders/k9/x93q0_xn1ls9zy76m2mf2k_00000gn/T/httpbin.org-1569378301.407512.txt
Verify contents of the cache file cat /path/to/your/cache/httpbin.org.txt
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
Content-Type: application/json
Date: Wed, 25 Sep 2019 02:24:25 GMT
Referrer-Policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade
Server: nginx
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
X-Frame-Options: DENY
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
Content-Length: 202
Connection: keep-alive
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0"
},
"origin": "1.2.3.4, 5.6.7.8",
"url": "https://httpbin.org/get"
}
CacheByResponseType
CacheResponsesPlugin plugin can also automatically cache responses by content-type.
To try this, you must be running under TLS Interception mode
and then pass --cache-by-content-type flag. Example:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.CacheResponsesPlugin \
--cache-by-content-type \
--ca-key-file ca-key.pem \
--ca-cert-file ca-cert.pem \
--ca-signing-key ca-signing-key.pem
Make a few requests to the proxy server and you shall see data under ~/.proxy/cache directory.
You should see 2 folders:
content: Contains parsedjpg,css,js,html,pdfetc by content typeresponses: Contains raw responses as received (of-course decrypted because of interception)
ManInTheMiddlePlugin
Modifies upstream server responses.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.ManInTheMiddlePlugin
Verify using curl -v -x localhost:8899 http://google.com:
... [redacted] ...
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Length: 28
<
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
Hello from man in the middle
Response body Hello from man in the middle is sent by our plugin.
ProxyPoolPlugin
Forward incoming proxy requests to a set of upstream proxy servers.
Let’s start 2 upstream proxies first. To simulate upstream proxies,
start proxy.py on port 9000 and 9001
❯ proxy --port 9000
❯ proxy --port 9001
Now, start proxy.py with ProxyPoolPlugin (on default 8899 port),
pointing to our upstream proxies at 9000 and 9001 port.
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.ProxyPoolPlugin \
--proxy-pool localhost:9000 \
--proxy-pool localhost:9001
Make a curl request via 8899 proxy:
curl -v -x localhost:8899 http://httpbin.org/get
Verify that 8899 proxy forwards requests to upstream proxies
by checking respective logs.
If an upstream proxy require credentials, pass them as arguments. Example:
--proxy-pool user:[email protected]:port
FilterByClientIpPlugin
Reject traffic from specific IP addresses. By default this
plugin blocks traffic from 127.0.0.1 and ::1.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.FilterByClientIpPlugin
Send a request using curl -v -x localhost:8899 http://google.com:
... [redacted] ...
> Proxy-Connection: Keep-Alive
>
< HTTP/1.1 418 I'm a tea pot
< Connection: close
<
* Closing connection 0
Modify plugin to your taste e.g. Allow specific IP addresses only.
ModifyChunkResponsePlugin
This plugin demonstrate how to modify chunked encoded responses. In able to do so, this plugin uses proxy.py core to parse the chunked encoded response. Then we reconstruct the response using custom hard-coded chunks, ignoring original chunks received from upstream server.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.ModifyChunkResponsePlugin
Verify using curl -v -x localhost:8899 http://httpbin.org/stream/5:
... [redacted] ...
modify
chunk
response
plugin
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
* Closing connection 0
Modify ModifyChunkResponsePlugin to your taste. Example, instead of sending hard-coded chunks, parse and modify the original JSON chunks received from the upstream server.
ModifyRequestHeaderPlugin
This plugin demonstrate how to modify outgoing HTTPS request headers under TLS interception mode.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.ModifyRequestHeaderPlugin \
... [TLS interception flags] ...
Verify using curl -x localhost:8899 --cacert ca-cert.pem https://httpbin.org/get:
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
... [redacted] ...,
"X-Proxy-Py-Version": "2.4.4rc6.dev15+gf533c711"
},
... [redacted] ...
}
CloudflareDnsResolverPlugin
This plugin uses Cloudflare hosted DNS-over-HTTPS API (json).
DoH mandates a HTTP2 compliant client. Unfortunately proxy.py
does not provide that yet, so we use a dependency. Install it:
❯ pip install "httpx[http2]"
Now start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.CloudflareDnsResolverPlugin
By default, CloudflareDnsResolverPlugin runs in security mode and provides malware protection.
Use --cloudflare-dns-mode family to also enable adult content protection too.
CustomDnsResolverPlugin
This plugin demonstrate how to use a custom DNS resolution implementation with proxy.py.
This example plugin currently uses Python’s in-built resolution mechanism. Customize code
to your taste. Example, query your custom DNS server, implement DoH or other mechanisms.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.CustomDnsResolverPlugin
CustomNetworkInterface
HttpProxyBasePlugin.resolve_dns callback can also be used to configure network interface which must be used as the source_address for connection to the upstream server.
See this thread
for more details.
PS: There is no plugin named, but CustomDnsResolverPlugin
can be easily customized according to your needs.
ProgramNamePlugin
Attempts to resolve program (application) name for proxy requests originating from the local machine.
If identified, client IP in the access logs is replaced with program name.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.ProgramNamePlugin
Make a request using curl:
❯ curl -v -x localhost:8899 https://httpbin.org/get
You must see log lines like this:
... [redacted] ... - [I] server.access_log:419 - curl:58096 - CONNECT httpbin.org:443 - 6010 bytes - 1824.62ms
Notice curl in-place of ::1 or 127.0.0.1 as client IP.

ProgramNamePlugin does not work reliably on your operating system, kindly contribute by sending a pull request and/or open an issue. Thank you!!!
HTTP Web Server Plugins
Web Server Route
Demonstrates inbuilt web server routing using plugin.
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy --enable-web-server \
--plugins proxy.plugin.WebServerPlugin
Verify using curl -v localhost:8899/http-route-example, should return:
HTTP route response
Reverse Proxy Plugins
Extends in-built Web Server to add Reverse Proxy capabilities.
Reverse Proxy
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy --enable-reverse-proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.ReverseProxyPlugin
With default configuration, ReverseProxyPlugin plugin is equivalent to
following Nginx config:
location /get {
proxy_pass http://httpbin.org/get;
}
Verify using curl -v localhost:8899/get:
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "localhost",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.64.1"
},
"origin": "1.2.3.4, 5.6.7.8",
"url": "https://localhost/get"
}
Rewrite Host Header
With above example, you may sometimes see:
>
* Empty reply from server
* Closing connection
curl: (52) Empty reply from server
This is happenening because our default reverse proxy plugin ReverseProxyPlugin is configured
with a http and a https upstream server. And, by default ReverseProxyPlugin preserves the
original host header. While this works with https upstreams, this doesn’t work reliably with
http upstreams. To work around this problem use the --rewrite-host-header flags.
Example:
❯ proxy --enable-reverse-proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.ReverseProxyPlugin \
--rewrite-host-header
This will ensure that Host header field is set as httpbin.org and works with both http and
https upstreams.
NOTE: Whether to use
--rewrite-host-headeror not depends upon your use-case.
Plugin Ordering
When using multiple plugins, depending upon plugin functionality,
it might be worth considering the order in which plugins are passed
on the command line.
Plugins are called in the same order as they are passed. Example,
say we are using both FilterByUpstreamHostPlugin and
RedirectToCustomServerPlugin. Idea is to drop all incoming http
requests for facebook.com and www.facebook.com and redirect other
http requests to our inbuilt web server.
Hence, in this scenario it is important to use
FilterByUpstreamHostPlugin before RedirectToCustomServerPlugin.
If we enable RedirectToCustomServerPlugin before FilterByUpstreamHostPlugin,
facebook requests will also get redirected to inbuilt web server,
instead of being dropped.
End-to-End Encryption
By default, proxy.py uses http protocol for communication with clients e.g. curl, browser. For enabling end-to-end encrypting using tls / https first generate certificates. Checkout the repository and run:
make https-certificates
Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--cert-file https-cert.pem \
--key-file https-key.pem
Verify using curl -x https://localhost:8899 --proxy-cacert https-cert.pem https://httpbin.org/get:
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0"
},
"origin": "1.2.3.4, 5.6.7.8",
"url": "https://httpbin.org/get"
}
If you want to avoid passing --proxy-cacert flag, also consider signing generated SSL certificates. Example:
First, generate CA certificates:
make ca-certificates
Then, sign SSL certificate:
make sign-https-certificates
Now restart the server with --cert-file https-signed-cert.pem flag. Note that you must also trust generated ca-cert.pem in your system keychain.
TLS Interception
By default, proxy.py will not decrypt https traffic between client and server.
To enable TLS interception first generate root CA certificates:
❯ make ca-certificates
Lets also enable CacheResponsePlugin so that we can verify decrypted
response from the server. Start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy \
--plugins proxy.plugin.CacheResponsesPlugin \
--ca-key-file ca-key.pem \
--ca-cert-file ca-cert.pem \
--ca-signing-key-file ca-signing-key.pem

--ca-file flag.
Verify TLS interception using curl
❯ curl -v -x localhost:8899 --cacert ca-cert.pem https://httpbin.org/get
* issuer: C=US; ST=CA; L=SanFrancisco; O=proxy.py; OU=CA; CN=Proxy PY CA; [email protected]
* SSL certificate verify ok.
> GET /get HTTP/1.1
... [redacted] ...
< Connection: keep-alive
<
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0"
},
"origin": "1.2.3.4, 5.6.7.8",
"url": "https://httpbin.org/get"
}
The issuer line confirms that response was intercepted.
Also verify the contents of cached response file. Get path to the cache
file from proxy.py logs.
❯ cat /path/to/your/tmp/directory/httpbin.org-1569452863.924174.txt
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
Content-Type: application/json
Date: Wed, 25 Sep 2019 23:07:05 GMT
Referrer-Policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade
Server: nginx
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
X-Frame-Options: DENY
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
Content-Length: 202
Connection: keep-alive
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0"
},
"origin": "1.2.3.4, 5.6.7.8",
"url": "https://httpbin.org/get"
}
Viola!!! If you remove CA flags, encrypted data will be found in the
cached file instead of plain text.
Now use CA flags with other
plugin examples to see them work with https traffic.
Insecure TLS Interception
To intercept TLS traffic from a server using a self-signed certificate
add the --insecure-tls-interception flag to disable mandatory TLS certificate validation.
NOTE: This flag disables certificate check for all servers.
TLS Interception With Docker
Important notes about TLS Interception with Docker container:
-
Since
v2.2.0,proxy.pydocker container also ships withopenssl. This allowsproxy.py
to generate certificates on the fly for TLS Interception. -
For security reasons,
proxy.pydocker container does not ship with
CA certificates.
Here is how to start a proxy.py docker container
with TLS Interception:
-
Generate CA certificates on host computer
❯ make ca-certificates -
Copy all generated certificates into a separate directory. We’ll later mount this directory into our docker container
❯ mkdir /tmp/ca-certificates ❯ cp ca-cert.pem ca-key.pem ca-signing-key.pem /tmp/ca-certificates -
Start docker container
❯ docker run -it --rm \ -v /tmp/ca-certificates:/tmp/ca-certificates \ -p 8899:8899 \ abhinavsingh/proxy.py:latest \ --hostname 0.0.0.0 \ --plugins proxy.plugin.CacheResponsesPlugin \ --ca-key-file /tmp/ca-certificates/ca-key.pem \ --ca-cert-file /tmp/ca-certificates/ca-cert.pem \ --ca-signing-key /tmp/ca-certificates/ca-signing-key.pem-v /tmp/ca-certificates:/tmp/ca-certificatesflag mounts our CA certificate directory in container environment--plugins proxy.plugin.CacheResponsesPluginenablesCacheResponsesPluginso that we can inspect intercepted traffic--ca-*flags enable TLS Interception.
-
From another terminal, try TLS Interception using
curl. You can omit--cacertflag if CA certificate is already trusted by the system.❯ curl -v \ --cacert ca-cert.pem \ -x 127.0.0.1:8899 \ https://httpbin.org/get -
Verify
issuerfield from response headers.* Server certificate: * subject: CN=httpbin.org; C=NA; ST=Unavailable; L=Unavailable; O=Unavailable; OU=Unavailable * start date: Jun 17 09:26:57 2020 GMT * expire date: Jun 17 09:26:57 2022 GMT * subjectAltName: host "httpbin.org" matched cert's "httpbin.org" * issuer: CN=example.com * SSL certificate verify ok. -
Back on docker terminal, copy response dump path logs.
...[redacted]... [I] access_log:338 - 172.17.0.1:56498 - CONNECT httpbin.org:443 - 1031 bytes - 1216.70 ms ...[redacted]... [I] close:49 - Cached response at /tmp/httpbin.org-ae1a927d064e4ab386ea319eb38fe251.txt -
In another terminal,
catthe response dump:❯ docker exec -it $(docker ps | grep proxy.py | awk '{ print $1 }') cat /tmp/httpbin.org-ae1a927d064e4ab386ea319eb38fe251.txt HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...[redacted]... { ...[redacted]..., "url": "http://httpbin.org/get" }
GROUT (NGROK Alternative)
groutis a drop-in alternative forngrokandfrpgroutcomes packaged withinproxy.py
Grout Usage
❯ grout
NAME:
grout - securely tunnel local files, folders and services to public URLs
USAGE:
grout route [name]
DESCRIPTION:
grout exposes local networked services behinds NATs and firewalls to the
public internet over a secure tunnel. Share local folders, directories and websites,
build/test webhook consumers and self-host personal services to public URLs.
EXAMPLES:
Share Files and Folders:
grout C:\path\to\folder # Share a folder on your system
grout /path/to/folder # Share a folder on your system
grout /path/to/folder --basic-auth user:pass # Add authentication for shared folder
grout /path/to/photo.jpg # Share a specific file on your system
Expose HTTP, HTTPS and Websockets:
grout http://localhost:9090 # Expose HTTP service running on port 9090
grout https://localhost:8080 # Expose HTTPS service running on port 8080
grout https://localhost:8080 --path /worker/ # Expose only certain paths of HTTPS service on port 8080
grout https://localhost:8080 --basic-auth u:p # Add authentication for exposed HTTPS service on port 8080
Expose TCP Services:
grout tcp://:6379 # Expose Redis service running locally on port 6379
grout tcp://:22 # Expose SSH service running locally on port 22
Custom URLs:
grout https://localhost:8080 abhinavsingh # Custom URL for HTTPS service running on port 8080
grout tcp://:22 abhinavsingh # Custom URL for SSH service running locally on port 22
Custom Domains:
grout tcp://:5432 abhinavsingh.domain.tld # Custom URL for Postgres service running locally on port 5432
Self-hosted solutions:
grout tcp://:5432 abhinavsingh.my.server # Custom URL for Postgres service running locally on port 5432
(*) Wildcard Domains:
grout https://host:443 do.main --wildcard # Receive traffic on provided domain and all it's subdomains
(*) Host based routing for Wildcard Domains:
grout ... --tunnel-route-url host=https://h:p # When using wildcards, optionally route traffic by incoming host header
SUPPORT:
Write to us at [email protected]
Privacy policy and Terms & conditions
https://jaxl.com/privacy/
Created by Jaxl™
https://jaxl.io
Grout Authentication
Grout supports authentication to protect your files, folders and services from unauthorized
access. Use --basic-auth flag to enforce authentication. Example:
grout /path/to/folder --basic-auth user:pass
grout https://localhost:8080 --basic-auth u:p
Grout Paths
By default, Grout allows access to all paths on the services. Use --path flag to restrict
access to only certain paths on your web service. Example:
grout https://localhost:8080 --path /worker/
grout https://localhost:8080 --path /webhook/ --path /callback/
Grout Wildcard Domains
By default, Grout client serves incoming traffic on a dedicated subdomain.
However, some services (e.g. Kubernetes) may want to serve traffic on adhoc subdomains.
Starting a dedicated Grout client for every adhoc subdomain may not be a practical solution.
For such scenarios, Grout supports wildcard domains. Here is how to configure your own
wildcard domain for use with Grout clients.
- Choose a domain e.g.
custom.example.com - Your service wants to serve traffic for
custom.example.comand*.custom.example.com - If you plan on using
https://, you need to setup a load balancer:- Setup a HTTPS load balancer (LB)
- Configure LB with certificate generated for
custom.example.comand*.custom.example.com - Point traffic to Grout service public IP addresses
- Contact Grout team at [email protected] to whitelist
custom.example.com. Grout team will make
sure you really own the domain and you have configured a valid SSL certificate as described above
Start Grout with --wildcard flag. Example:
grout https://localhost:8080 custom.example.com --wildcard
2024-08-05 18:24:59,294 - grout - Logged in as [email protected]
2024-08-05 18:25:03,159 - setup - Grouting https://*.custom.domain.com
Grout Wildcard Domain Routing Based Upon “Host” Header
Only available with
--wildcard
Along with the default route you can also provide additional routes which takes precedence when the host field matches. Example:
grout https://localhost:8080 custom.example.com \
--wildcard \
--tunnel-route-url stream.example.com=http://localhost:7001
You can provide multiple custom routes by repeating this flag.
Grout Client Plugin
GroutClientBasePlugin allows you to dynamically route traffic to different upstreams. Below is a simple implementation with some description about how to use it.
class GroutClientPlugin(GroutClientBasePlugin):
def resolve_route(
self,
route: str,
request: HttpParser,
origin: HostPort,
server: HostPort,
) -> Tuple[Optional[str], HttpParser]:
print(request, origin, server, '->', route)
print(request.header(b'host'), request.path)
#
# Here, we send traffic to localhost:7001 irrespective
# of the original "route" value provided to the grout
# client OR any custom host:upstream mapping provided
# through the --tunnel-route-url flags (when using
# --wildcard).
#
# Optionally, you can also strip path before
# sending traffic to upstrem, like:
# request.path = b"/"
#
# To drop the request, simply return None for route
# return None, request
#
return 'http://localhost:7001', request
See grout_client.py for more information. To try this out, start by passing --plugin proxy.plugin.grout_client.GroutClientPlugin when starting the grout client.
Grout using Docker
❯ docker run --rm -it \
--entrypoint grout \
-v ~/.proxy:/root/.proxy \
abhinavsingh/proxy.py:latest \
http://host.docker.internal:29876
Above:
- We changed
--entrypointtogrout - We replaced
localhostwithhost.docker.internal, so thatgroutcan route traffic to port29876running on the host machine - (Optional) Mount host machine
~/.proxyfolder, so thatgroutcredentials can persist across container restarts
How Grout works
groutinfrastructure has 2 components: client and servergroutclient has 2 components: a thin and a thick clientgroutthin client is part of open sourceproxy.py(BSD 3-Clause License)groutthick client and servers are hosted at jaxl.io
and a copyright of Jaxl Innovations Private Limitedgroutserver has 3 components: a registry server, a reverse proxy server and a tunnel server
Self-Hosted grout
groutthick client and servers can also be hosted on your GCP, AWS, Cloud infrastructures- With a self-hosted version, your traffic flows through the network you control and trust
groutdevelopers at jaxl.io provides GCP, AWS, Docker images for self-hosted solutions- Please drop an email at [email protected] to get started.
Proxy Over SSH Tunnel
This is a WIP and may not work as documented
Requires paramiko to work. Install dependencies using pip install "proxy.py[tunnel]"
Proxy Remote Requests Locally
|
+------------+ | +----------+
| LOCAL | | | REMOTE |
| HOST | <== SSH ==== :8900 == | PROXY |
+------------+ | +----------+
:8899 proxy.py |
|
FIREWALL
(allow tcp/22)
What
Proxy HTTP(s) requests made on a remote proxy server through proxy.py server running on localhost.
How
- Requested
remoteport is forwarded over the SSH connection. proxy.pyrunning on thelocalhosthandles and responds to
remoteproxy requests.
Requirements
localhostMUST have SSH access to theremoteserverremoteserver MUST be configured to proxy HTTP(s) requests
through the forwarded port number e.g.:8900.remoteandlocalhostports CAN be same e.g.:8899.:8900is chosen in ascii art for differentiation purposes.
Try it
Start proxy.py as:
❯ # On localhost
❯ proxy --enable-ssh-tunnel \
--tunnel-username username \
--tunnel-hostname ip.address.or.domain.name \
--tunnel-port 22 \
--tunnel-remote-port 8899 \
--tunnel-ssh-key /path/to/ssh/private.key \
--tunnel-ssh-key-passphrase XXXXX
...[redacted]... [I] listener.setup:97 - Listening on 127.0.0.1:8899
...[redacted]... [I] pool.setup:106 - Started 16 acceptors in threadless (local) mode
...[redacted]... [I] transport._log:1873 - Connected (version 2.0, client OpenSSH_7.6p1)
...[redacted]... [I] transport._log:1873 - Authentication (publickey) successful!
...[redacted]... [I] listener.setup:116 - SSH connection established to ip.address.or.domain.name:22...
...[redacted]... [I] listener.start_port_forward:91 - :8899 forwarding successful...
Make a HTTP proxy request on remote server and
verify that response contains public IP address of localhost as origin:
❯ # On remote
❯ curl -x 127.0.0.1:8899 http://httpbin.org/get
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0"
},
"origin": "x.x.x.x, y.y.y.y",
"url": "https://httpbin.org/get"
}
Also, verify that proxy.py logs on localhost contains remote IP as client IP.
access_log:328 - remote:52067 - GET httpbin.org:80
Proxy Local Requests Remotely
|
+------------+ | +----------+
| LOCAL | | | REMOTE |
| HOST | === SSH =====> | SERVER |
+------------+ | +----------+
| :8899 proxy.py
|
FIREWALL
(allow tcp/22)
Not planned.
If you have a valid use case, kindly open an issue. You are always welcome to send
contributions via pull-requests to add this functionality 😃
To proxy local requests remotely, make use of Proxy Pool Plugin.
Embed proxy.py
Blocking Mode
Start proxy.py in embedded mode with default configuration
by using proxy.main method. Example:
import proxy
if __name__ == '__main__':
proxy.main()
Customize startup flags by passing them as kwargs:
import ipaddress
import proxy
if __name__ == '__main__':
proxy.main(
hostname=ipaddress.IPv6Address('::1'),
port=8899
)
Note that:
mainis equivalent to startingproxy.pyfrom command line.maindoes not accept anyargs(onlykwargs).mainwill automatically consume any availablesys.argvasargs.mainwill block untilproxy.pyshuts down.
Non-blocking Mode
Start proxy.py in non-blocking embedded mode with default configuration
by using Proxy context manager: Example:
import proxy
if __name__ == '__main__':
with proxy.Proxy() as p:
# Uncomment the line below and
# implement your app your logic here
proxy.sleep_loop()
Note that:
Proxyis similar tomain, exceptProxywill not block.- Internally,
Proxyis a context manager which will start
proxy.pywhen called and will shut it down once the scope ends. - Unlike
main, startup flags withProxycan also be customized
by usingargsandkwargs. e.g.Proxy(['--port', '8899'])or
by using passing flags as kwargs e.g.Proxy(port=8899). - Unlike
main,Proxywill not inspectsys.argv.
Ephemeral Port
Use --port=0 to bind proxy.py on a random port allocated by the kernel.
In embedded mode, you can access this port. Example:
import proxy
if __name__ == '__main__':
with proxy.Proxy(port=0) as p:
print(p.flags.port)
proxy.sleep_loop()
flags.port will give you access to the random port allocated by the kernel.
Loading Plugins
Users can use --plugins flag multiple times to load multiple plugins.
See Unable to load plugins if you are running into issues.
When using in embedded mode, you have a few more options. Example:
- Provide a fully-qualified name of the plugin class as
bytesto theproxy.mainmethod orproxy.Proxycontext manager. - Provide
typeinstance of the plugin class. This is especially useful if you plan to define plugins at runtime.
Example, load a single plugin using --plugins flag:
import proxy
if __name__ == '__main__':
proxy.main(plugins=['proxy.plugin.CacheResponsesPlugin'])
For simplicity, you can also pass the list of plugins as a keyword argument to proxy.main or the Proxy constructor.
Example:
import proxy
from proxy.plugin import FilterByUpstreamHostPlugin
if __name__ == '__main__':
proxy.main(plugins=[
b'proxy.plugin.CacheResponsesPlugin',
FilterByUpstreamHostPlugin,
])
Unit testing with proxy.py
proxy.TestCase
To setup and tear down proxy.py for your Python unittest classes, simply use proxy.TestCase instead of unittest.TestCase.
Example:
import proxy
class TestProxyPyEmbedded(proxy.TestCase):
def test_my_application_with_proxy(self) -> None:
self.assertTrue(True)
Note that:
proxy.TestCaseoverridesunittest.TestCase.run()method to setup and tear downproxy.py.proxy.pyserver will listen on a random available port on the system.
This random port is available asself.PROXY.flags.portwithin your test cases.- Only a single acceptor and worker is started by default (
--num-workers 1 --num-acceptors 1) for faster setup and tear down. - Most importantly,
proxy.TestCasealso ensuresproxy.pyserver
is up and running before proceeding with execution of tests. By default,
proxy.TestCasewill wait for10 secondsforproxy.pyserver to start,
upon failure aTimeoutErrorexception will be raised.
Override startup flags
To override default startup flags, define a PROXY_PY_STARTUP_FLAGS variable in your test class.
Example:
class TestProxyPyEmbedded(TestCase):
PROXY_PY_STARTUP_FLAGS = [
'--num-workers', '2',
'--num-acceptors', '1',
'--enable-web-server',
]
def test_my_application_with_proxy(self) -> None:
self.assertTrue(True)
See test_embed.py for full working example.
With unittest.TestCase
If for some reasons you are unable to directly use proxy.TestCase,
then simply override unittest.TestCase.run yourself to setup and tear down proxy.py.
Example:
import unittest
import proxy
class TestProxyPyEmbedded(unittest.TestCase):
def test_my_application_with_proxy(self) -> None:
self.assertTrue(True)
def run(self, result: Optional[unittest.TestResult] = None) -> Any:
with proxy.start([
'--num-workers', '1',
'--num-acceptors', '1',
'--port', '... random port ...']):
super().run(result)
or simply setup / tear down proxy.py within
setUpClass and teardownClass class methods.
Utilities
TCP Sockets
new_socket_connection
Attempts to create an IPv4 connection, then IPv6 and
finally a dual stack connection to provided address.
>>> conn = new_socket_connection(('httpbin.org', 80))
>>> ...[ use connection ]...
>>> conn.close()
socket_connection
socket_connection is a convenient decorator + context manager
around new_socket_connection which ensures conn.close is implicit.
As a context manager:
>>> with socket_connection(('httpbin.org', 80)) as conn:
>>> ... [ use connection ] ...
As a decorator:
>>> @socket_connection(('httpbin.org', 80))
>>> def my_api_call(conn, *args, **kwargs):
>>> ... [ use connection ] ...
HTTP Client
build_http_request
-
Generate HTTP GET request
>>> build_http_request(b'GET', b'/') b'GET / HTTP/1.1\r\n\r\n' -
Generate HTTP GET request with headers
>>> build_http_request(b'GET', b'/', conn_close=True) b'GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nConnection: close\r\n\r\n' -
Generate HTTP POST request with headers and body
>>> import json >>> build_http_request(b'POST', b'/form', headers={b'Content-type': b'application/json'}, body=proxy.bytes_(json.dumps({'email': '[email protected]'}))) b'POST /form HTTP/1.1\r\nContent-type: application/json\r\n\r\n{"email": "[email protected]"}'
build_http_response
build_http_response(
status_code: int,
protocol_version: bytes = HTTP_1_1,
reason: Optional[bytes] = None,
headers: Optional[Dict[bytes, bytes]] = None,
body: Optional[bytes] = None) -> bytes
PKI
API Usage
-
gen_private_keygen_private_key( key_path: str, password: str, bits: int = 2048, timeout: int = 10) -> bool -
gen_public_keygen_public_key( public_key_path: str, private_key_path: str, private_key_password: str, subject: str, alt_subj_names: Optional[List[str]] = None, extended_key_usage: Optional[str] = None, validity_in_days: int = 365, timeout: int = 10) -> bool -
remove_passphraseremove_passphrase( key_in_path: str, password: str, key_out_path: str, timeout: int = 10) -> bool -
gen_csrgen_csr( csr_path: str, key_path: str, password: str, crt_path: str, timeout: int = 10) -> bool -
sign_csrsign_csr( csr_path: str, crt_path: str, ca_key_path: str, ca_key_password: str, ca_crt_path: str, serial: str, alt_subj_names: Optional[List[str]] = None, extended_key_usage: Optional[str] = None, validity_in_days: int = 365, timeout: int = 10) -> bool
See pki.py and
test_pki.py
for usage examples.
CLI Usage
Use proxy.common.pki module for:
- Generation of public and private keys
- Generating CSR requests
- Signing CSR requests using custom CA.
❯ python -m proxy.common.pki -h
usage: pki.py [-h] [--password PASSWORD] [--private-key-path PRIVATE_KEY_PATH] [--public-key-path PUBLIC_KEY_PATH]
[--subject SUBJECT] [--csr-path CSR_PATH] [--crt-path CRT_PATH] [--hostname HOSTNAME] [--openssl OPENSSL]
action
proxy.py v2.4.4rc2.dev12+gdc06ea4 : PKI Utility
positional arguments:
action Valid actions: remove_passphrase, gen_private_key, gen_public_key, gen_csr, sign_csr
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--password PASSWORD Password to use for encryption. Default: proxy.py
--private-key-path PRIVATE_KEY_PATH
Private key path
--public-key-path PUBLIC_KEY_PATH
Public key path
--subject SUBJECT Subject to use for public key generation. Default: /CN=localhost
--csr-path CSR_PATH CSR file path. Use with gen_csr and sign_csr action.
--crt-path CRT_PATH Signed certificate path. Use with sign_csr action.
--hostname HOSTNAME Alternative subject names to use during CSR signing.
--openssl OPENSSL Path to openssl binary. By default, we assume openssl is in your PATH
Internal Documentation
Read The Doc
- Visit proxypy.readthedocs.io
- Build locally using:
make lib-doc
pydoc
Code is well documented. Grab the source code and run:
pydoc3 proxy
pyreverse
Generate class level hierarchy UML diagrams for in-depth analysis:
make lib-pyreverse
Run Dashboard
Dashboard is currently under development and not yet bundled with pip packages.
To run dashboard, you must checkout the source.
Dashboard is written in Typescript and SCSS, so let’s build it first using:
❯ make dashboard
Also build the embedded Chrome DevTools if you plan on using it:
❯ make devtools
Now start proxy.py with dashboard plugin and by overriding root directory for static server:
❯ proxy --enable-dashboard --static-server-dir dashboard/public
...[redacted]... - Loaded plugin proxy.http.server.HttpWebServerPlugin
...[redacted]... - Loaded plugin proxy.dashboard.dashboard.ProxyDashboard
...[redacted]... - Loaded plugin proxy.dashboard.inspect_traffic.InspectTrafficPlugin
...[redacted]... - Loaded plugin proxy.http.inspector.DevtoolsProtocolPlugin
...[redacted]... - Loaded plugin proxy.http.proxy.HttpProxyPlugin
...[redacted]... - Listening on ::1:8899
...[redacted]... - Core Event enabled
Currently, enabling dashboard will also enable all the dashboard plugins.
Visit dashboard:
❯ open http://localhost:8899/dashboard/
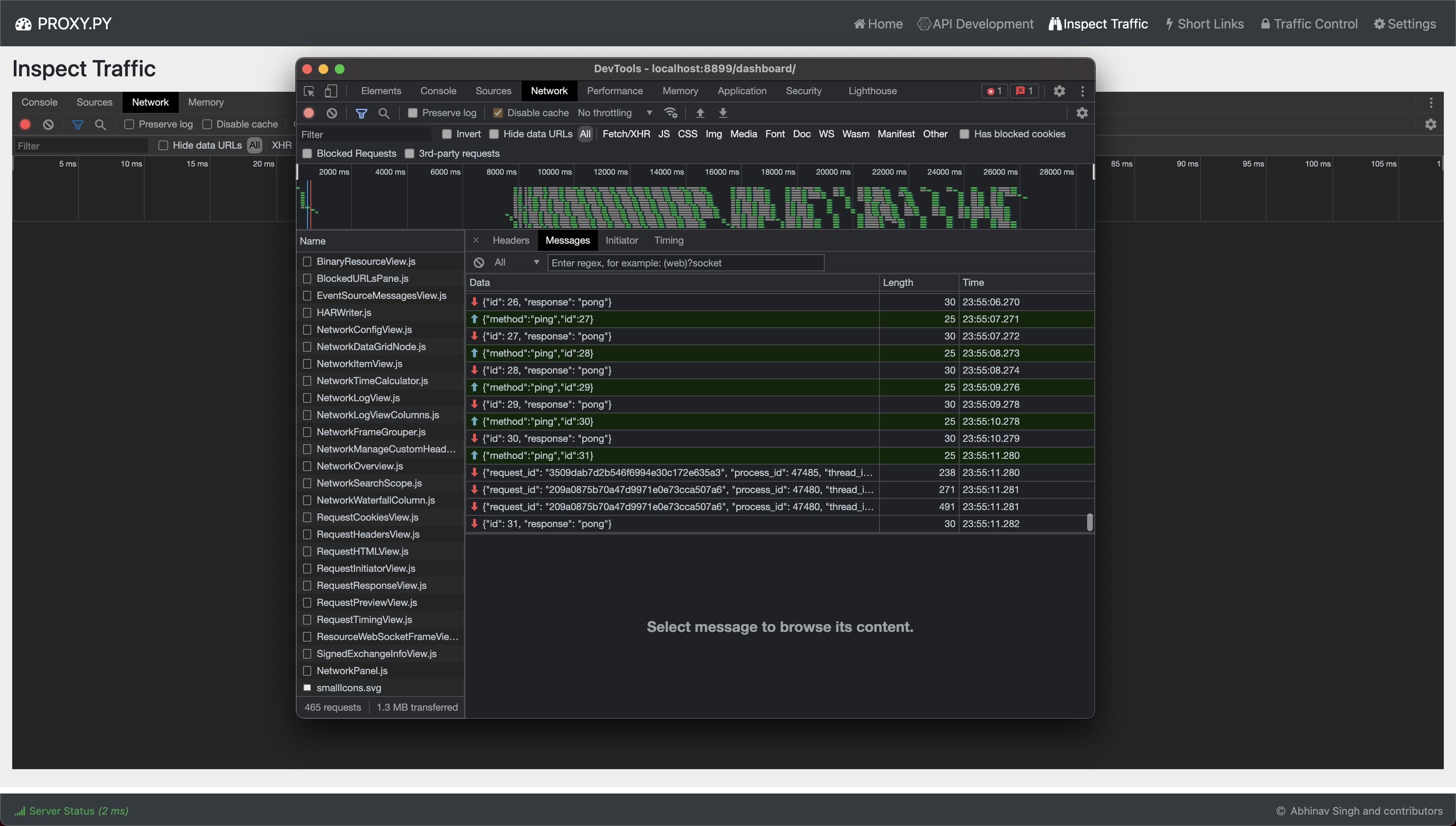
Inspect Traffic
This is a WIP and may not work as documented
Wait for embedded Chrome Dev Console to load. Currently, detail about all traffic flowing
through proxy.py is pushed to the Inspect Traffic tab. However, received payloads are not
yet integrated with the embedded developer console.
Current functionality can be verified by opening the Dev Console of dashboard and inspecting
the websocket connection that dashboard established with the proxy.py server.
Chrome DevTools Protocol
For scenarios where you want direct access to Chrome DevTools protocol websocket endpoint,
start proxy.py as:
❯ proxy --enable-devtools --enable-events
Now point your CDT instance to ws://localhost:8899/devtools.
Prometheus Metrics
- Start
proxy.pywith--enable-metricsflag to internal metrics via a prometheus endpoint - Configure your
prometheus.yamlto scrape from/metricsendpoint e.g. http://localhost:8899/metrics - Customize metrics path by using
--metrics-pathflag - NOTE that
--enable-metricsinternally also--enable-eventsand the web server plugin
Frequently Asked Questions
Deploying proxy.py in production
Listed below are a few strategies for using proxy.py in your private/production/corporate projects.
What not to do?
You MUST
avoid forkingthe repository “just” to put your plugin code inproxy/plugindirectory. Forking is recommended workflow for project contributors, NOT for project users.
- Instead, use one of the suggested approaches from below.
- Then load your plugins using
--plugin,--pluginsflags orpluginkwargs. - See skeleton app for example standalone project using
proxy.py.
Via Requirements
It is highly recommended that you use proxy.py via requirements.txt or similar dependency management setups. This will allow you to take advantages of regular performance updates, bug fixes, security patches and other improvements happening in the proxy.py ecosystem. Example:
-
Use
--preoption to depend upon lastpre-release❯ pip install proxy.py --prePre-releases are similar to depending upon
developbranch code, just that pre-releases may not point to theHEAD. This could happen because pre-releases are NOT made available onPyPiafter every PR merge. -
Use
TestPyPiwith--preoption to depend upondevelopbranch code❯ pip install -i https://test.pypi.org/simple/ proxy.py --preA pre-release is made available on
TestPyPiafter every PR merge. -
Use last
stablerelease codeAs usual, simply use:
❯ pip install proxy.py
Via Docker Container
If you are into deploying containers, then simply build your image from base proxy.py container images.
-
Use
GHCRto build fromdevelopbranch code:FROM ghcr.io/abhinavsingh/proxy.py:latest as basePS: I use GHCR latest for several production level projects
-
Use
DockerHubto build from laststablerelease code:FROM abhinavsingh/proxy.py:latest as base
PS: IMHO, container based strategy is the best approach and the only strategy that I use myself.
Integrate your CI/CD with proxy.py
Hey, but you keep making breaking changes in the develop branch.
I hear you. And hence, for your production grade applications, you MUST integrate application CI/CD with proxy.py. You must make sure that your application builds and passes its tests for every PR merge into the proxy.py upstream repo.
If your application repository is public, in certain scenarios, PR authors may send patch PRs for all dependents to maintain backward incompatibility and green CI/CD.
CI/CD integration ensure your app continues to build with latest proxy.py code. Depending upon where you host your code, use the strategy listed below:
-
GitHub
TBD
-
Google Cloud Build
TBD
-
AWS
TBD
-
Azure
TBD
-
Others
TBD
At some stage, we’ll deprecate
masterbranch segregation and simply maintain adevelopbranch. As dependents can maintain stability via CI/CD integrations. Currently, it’s hard for a production grade project to blindly depend upondevelopbranch.
Stable vs Develop
-
masterbranch contains lateststablecode and is available viaPyPirepository andDockercontainers viadocker.ioandghcr.ioregistries.Issues reported for
stablereleases are considered with top-priority. However, currently we don’t back port fixes into older releases. Example, if you reported an issue inv2.3.1, but currentmasterbranch now containsv2.4.0rc1. Then, the fix will land inv2.4.0rc2. -
developbranch contains cutting edge changesDevelopment branch is kept stable (most of the times). But, if you want 100% reliability and serving users in production environment, ALWAYS use the stable version.
Release Schedule
A vX.Y.ZrcN pull request is created once a month which merges develop → master. Find below how code flows from a pull request to the next stable release.
-
Development release is deployed from
develop→test.pypi.orgafter every pull request merge -
Alpha release is deployed from
develop→pypi.orgbefore merging thevX.Y.Z.rcNpull request fromdevelop→masterbranch. There can be multiple alpha releases made before merging thercpull request -
Beta release is deployed from
master→pypi.org. Beta releases are made in preparation ofrcreleases and can be skipped if unnecessary -
Release candidate is deployed from
master→pypi.org. Release candidates are always made available before final stable release -
Stable release is deployed from
master→pypi.org
Threads vs Threadless
v1.x
proxy.py used to spawn new threads for handling client requests.
v2.0+
proxy.py added support for threadless execution of client requests using asyncio.
v2.4.0+
Threadless execution was turned ON by default for Python 3.8+ on mac and linux environments.
proxy.py threadless execution has been reported safe on these environments by our users. If you are running into trouble, fallback to threaded mode using --threaded flag.
For windows and Python < 3.8, you can still try out threadless mode by starting proxy.py with --threadless flag.
If threadless works for you, consider sending a PR by editing _env_threadless_compliant method in the proxy/common/constants.py file.
Threadless Remote vs Local execution mode
Original threadless implementation used remote execution mode. This is also depicted under High level architecture as ASCII art.
Under remote execution mode, acceptors delegate incoming client connection processing to a remote worker process. By default, acceptors delegate connections in round-robin fashion. Worker processing the request may or may not be running on the same CPU core as the acceptor. This architecture scales well for high throughput, but results in spawning two process per CPU core.
Example, if there are N-CPUs on the machine, by default, N acceptors and N worker processes are started. You can tune number of processes using --num-acceptors and --num-workers flag. You might want more workers than acceptors or vice versa depending upon your use case.
In v2.4.x, local execution mode was added, mainly to reduce number of processes spawned by default. This model serves well for day-to-day single user use cases and for developer testing scenarios. Under local execution mode, acceptors delegate client connections to a companion thread, instead of a remote process. local execution mode ensure CPU affinity, unlike in the remote mode where acceptor and worker might be running on different CPU cores.
--local-executor 1 was made default in v2.4.x series. Under local execution mode, --num-workers flag has no effect, as no remote workers are started.
To use remote execution mode, use --local-executor 0 flag. Then use --num-workers to tune number of worker processes.
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
proxy.py is strictly typed and uses Python typing annotations. Example:
>>> my_strings : List[str] = []
>>> #############^^^^^^^^^#####
Hence a Python version that understands typing annotations is required.
Make sure you are using Python 3.6+.
Verify the version before running proxy.py:
❯ python --version
All typing annotations can be replaced with comment-only annotations. Example:
>>> my_strings = [] # List[str]
>>> ################^^^^^^^^^^^
It will enable proxy.py to run on Python pre-3.6, even on 2.7.
However, as all future versions of Python will support typing annotations,
this has not been considered.
Unable to load plugins
Make sure plugin modules are discoverable by adding them to PYTHONPATH. Example:
PYTHONPATH=/path/to/my/app proxy --plugins my_app.proxyPlugin
...[redacted]... - Loaded plugin proxy.HttpProxyPlugin
...[redacted]... - Loaded plugin my_app.proxyPlugin
OR, simply pass fully-qualified path as parameter, e.g.
proxy --plugins /path/to/my/app/my_app.proxyPlugin
Here is a quick working example:
- Contents of
/tmp/plugfolder
╰─ ls -1 /tmp/plug ─╯
my_plugin.py
- Custom
MyPluginclass
╰─ cat /tmp/plug/my_plugin.py ─╯
from proxy.http.proxy import HttpProxyBasePlugin
class MyPlugin(HttpProxyBasePlugin):
pass
This is an empty plugin for demonstrating external plugin usage. You must implement necessary methods to make your plugins work for real traffic
- Start
proxy.pywithMyPlugin
╰─ PYTHONPATH=/tmp/plug proxy --plugin my_plugin.MyPlugin ─╯
...[redacted]... - Loaded plugin proxy.http.proxy.HttpProxyPlugin
...[redacted]... - Loaded plugin my_plugin.MyPlugin
...[redacted]... - Listening on ::1:8899
Unable to connect with proxy.py from remote host
Make sure proxy.py is listening on correct network interface.
Try following flags:
- For IPv6
--hostname :: - For IPv4
--hostname 0.0.0.0
Basic auth not working with a browser
Most likely it’s a browser integration issue with system keychain.
-
First verify that basic auth is working using
curlcurl -v -x username:password@localhost:8899 https://httpbin.org/get -
See this thread
for further details.
Docker image not working on macOS
It’s a compatibility issue with vpnkit.
See moby/vpnkit exhausts docker resources
and Connection refused: The proxy could not connect
for some background.
GCE log viewer integration for proxy.py
A starter fluentd.conf
template is available.
-
Copy this configuration file as
proxy.py.confunder
/etc/google-fluentd/config.d/ -
Update
pathfield to log file path as used with--log-fileflag.
By default/tmp/proxy.logpath is tailed. -
Reload
google-fluentd:sudo service google-fluentd restart
Now proxy.py logs can be browsed using
GCE log viewer.
ValueError: filedescriptor out of range in select
proxy.py is made to handle thousands of connections per second
without any socket leaks.
- Make use of
--open-file-limitflag to customizeulimit -n. - Make sure to adjust
--backlogflag for higher concurrency.
If nothing helps, open an issue
with requests per second sent and output of following debug script:
❯ ./helper/monitor_open_files.sh <proxy-py-pid>
None:None in access logs
Sometimes you may see None:None in access logs. It simply means
that an upstream server connection was never established i.e.
upstream_host=None, upstream_port=None.
There can be several reasons for no upstream connection,
few obvious ones include:
- Client established a connection but never completed the request.
- A plugin returned a response prematurely, avoiding connection to upstream server.
OSError when wrapping client for TLS Interception
With TLS Interception on, you might occasionally see following exceptions:
2021-11-06 23:33:34,540 - pid:91032 [E] server.intercept:678 - OSError when wrapping client
Traceback (most recent call last):
...[redacted]...
...[redacted]...
...[redacted]...
ssl.SSLError: [SSL: TLSV1_ALERT_UNKNOWN_CA] tlsv1 alert unknown ca (_ssl.c:997)
...[redacted]... - CONNECT oauth2.googleapis.com:443 - 0 bytes - 272.08 ms
Some clients can throw TLSV1_ALERT_UNKNOWN_CA if they cannot verify the certificate of the server
because it is signed by an unknown issuer CA. Which is the case when we are doing TLS interception.
This can be for a variety of reasons e.g. certificate pinning etc.
Another exception you might see is CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED:
2021-11-06 23:36:02,002 - pid:91033 [E] handler.handle_readables:293 - Exception while receiving from client connection <socket.socket fd=28, family=AddressFamily.AF_INET, type=SocketKind.SOCK_STREAM, proto=0, laddr=('127.0.0.1', 8899), raddr=('127.0.0.1', 51961)> with reason SSLCertVerificationError(1, '[SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED] certificate verify failed: self signed certificate in certificate chain (_ssl.c:997)')
Traceback (most recent call last):
...[redacted]...
...[redacted]...
...[redacted]...
ssl.SSLCertVerificationError: [SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED] certificate verify failed: self signed certificate in certificate chain (_ssl.c:997)
...[redacted]... - CONNECT init.push.apple.com:443 - 0 bytes - 892.99 ms
In future, we might support serving original HTTPS content for such clients while still
performing TLS interception in the background. This will keep the clients happy without
impacting our ability to TLS intercept. Unfortunately, this feature is currently not available.
Another example with SSLEOFError exception:
2021-11-06 23:46:40,446 - pid:91034 [E] server.intercept:678 - OSError when wrapping client
Traceback (most recent call last):
...[redacted]...
...[redacted]...
...[redacted]...
ssl.SSLEOFError: EOF occurred in violation of protocol (_ssl.c:997)
...[redacted]... - CONNECT stock.adobe.io:443 - 0 bytes - 685.32 ms
Plugin Developer and Contributor Guide
High level architecture
+-------------+
| |
| Proxy([]) |
| |
+------+------+
|
|
+-----------v--------------+
| |
| AcceptorPool(...) |
| |
+------------+-------------+
|
+-----------------+ | +-----------------+
| | | | |
| Acceptor(..) <-------------+-----------> Acceptor(..) |
| | | |
+---+-------------+ +---------+-------+
| |
| |
| +------++------++------++------++------+ |
| | || || || || | |
+----> || || || || <-----+
| || || || || |
+------++------++------++------++------+
Threadless Worker Processes
proxy.py is made with performance in mind. By default, proxy.py
will try to utilize all available CPU cores to it for accepting new
client connections. This is achieved by starting AcceptorPool which
listens on configured server port. Then, AcceptorPool starts Acceptor
processes (--num-acceptors) to accept incoming client connections.
Alongside, if --threadless is enabled, ThreadlessPool is setup
which starts Threadless processes (--num-workers) to handle
the incoming client connections.
Each Acceptor process delegates the accepted client connection
to a threadless process via Work class. Currently, HttpProtocolHandler
is the default work class.
HttpProtocolHandler simply assumes that incoming clients will follow
HTTP specification. Specific HTTP proxy and HTTP server implementations
are written as plugins of HttpProtocolHandler.
See documentation of HttpProtocolHandlerPlugin for available lifecycle hooks.
Use HttpProtocolHandlerPlugin to add new features for http(s) clients. Example,
See HttpWebServerPlugin.
Everything is a plugin
Within proxy.py everything is a plugin.
-
We enabled
proxy serverplugins using--pluginsflag.
Proxy serverHttpProxyPluginis a plugin ofHttpProtocolHandler.
Further, Proxy server allows plugin throughHttpProxyBasePluginspecification. -
All the proxy server plugin examples were implementing
HttpProxyBasePlugin. See documentation ofHttpProxyBasePluginfor available
lifecycle hooks. UseHttpProxyBasePluginto modify behavior of http(s) proxy protocol
between client and upstream server. Example,
FilterByUpstreamHostPlugin. -
We also enabled inbuilt
web serverusing--enable-web-server.
Web serverHttpWebServerPluginis a plugin ofHttpProtocolHandler
and implementsHttpProtocolHandlerPluginspecification. -
There also is a
--disable-http-proxyflag. It disables inbuilt proxy server.
Use this flag with--enable-web-serverflag to runproxy.pyas a programmable
http(s) server.
Managing states for your stateless plugins
Plugin class instances are created per-request. Most importantly,
plugin instances are created within CPU core context where the request
was received.
For above reason, global variables in your plugins may not work as expected.
Your plugin code by design must be stateless.
To manage global states, you have a couple of options:
- Make use of Python’s multiprocessing safe data structures
- Make use of
proxy.pyin-built eventing mechanism
Passing processing context between plugins
Sometimes, a plugin may need to pass additional context to other plugins after them in the processing chain. Example, this additional
context can also be dumped as part of access logs.
To pass processing context, make use of plugin’s on_access_log method. See how Program Name plugin modifies default client_ip key in the context and updates it to detected program name.
As a result, when we enable Program Name Plugin, we see local client program name instead of IP address in the access logs.
Development Guide
Setup Local Environment
Contributors must start proxy.py from source to verify and develop new features / fixes.
See Run proxy.py from command line using repo source for details.

macOS
you must install Python using pyenv, as Python installed via homebrew tends
to be problematic. See linked thread for more details.
Setup Git Hooks
Pre-commit hook ensures tests are passing.
cd /path/to/proxy.pyln -s $(PWD)/git-pre-commit .git/hooks/pre-commit
Pre-push hook ensures lint and tests are passing.
cd /path/to/proxy.pyln -s $(PWD)/git-pre-push .git/hooks/pre-push
Sending a Pull Request
Every pull request is tested using GitHub actions.
See GitHub workflow
for list of tests.
Projects Using Proxy.Py
Some popular projects using proxy.py
- pip
- ray-project
- aio-libs
- Selenium Base
- wifipumpkin3
- MerossIot
- pyshorteners
- Slack API
- ibeam
- PyPaperBot
For full list see used by
Benchmarks
See Benchmark directory on how to run benchmark comparisons with other OSS web servers.
To run standalone benchmark for proxy.py, use the following command from repo root:
❯ ./benchmark/compare.sh
Flags
❯ proxy -h
usage: -m [-h] [--tunnel-hostname TUNNEL_HOSTNAME] [--tunnel-port TUNNEL_PORT]
[--tunnel-username TUNNEL_USERNAME]
[--tunnel-ssh-key TUNNEL_SSH_KEY]
[--tunnel-ssh-key-passphrase TUNNEL_SSH_KEY_PASSPHRASE]
[--tunnel-remote-port TUNNEL_REMOTE_PORT] [--threadless]
[--threaded] [--num-workers NUM_WORKERS] [--enable-events]
[--inactive-conn-cleanup-timeout INACTIVE_CONN_CLEANUP_TIMEOUT]
[--enable-proxy-protocol] [--enable-conn-pool] [--key-file KEY_FILE]
[--cert-file CERT_FILE] [--client-recvbuf-size CLIENT_RECVBUF_SIZE]
[--server-recvbuf-size SERVER_RECVBUF_SIZE]
[--max-sendbuf-size MAX_SENDBUF_SIZE] [--timeout TIMEOUT]
[--local-executor LOCAL_EXECUTOR] [--backlog BACKLOG]
[--hostname HOSTNAME] [--hostnames HOSTNAMES [HOSTNAMES ...]]
[--port PORT] [--ports PORTS [PORTS ...]] [--port-file PORT_FILE]
[--unix-socket-path UNIX_SOCKET_PATH]
[--num-acceptors NUM_ACCEPTORS] [--version] [--log-level LOG_LEVEL]
[--log-file LOG_FILE] [--log-format LOG_FORMAT]
[--open-file-limit OPEN_FILE_LIMIT]
[--plugins PLUGINS [PLUGINS ...]] [--enable-dashboard]
[--basic-auth BASIC_AUTH] [--enable-ssh-tunnel]
[--work-klass WORK_KLASS] [--pid-file PID_FILE] [--openssl OPENSSL]
[--data-dir DATA_DIR] [--ssh-listener-klass SSH_LISTENER_KLASS]
[--disable-http-proxy] [--disable-headers DISABLE_HEADERS]
[--ca-key-file CA_KEY_FILE] [--insecure-tls-interception]
[--ca-cert-dir CA_CERT_DIR] [--ca-cert-file CA_CERT_FILE]
[--ca-file CA_FILE] [--ca-signing-key-file CA_SIGNING_KEY_FILE]
[--auth-plugin AUTH_PLUGIN] [--cache-requests]
[--cache-by-content-type] [--cache-dir CACHE_DIR]
[--proxy-pool PROXY_POOL] [--enable-web-server]
[--enable-static-server] [--static-server-dir STATIC_SERVER_DIR]
[--min-compression-length MIN_COMPRESSION_LENGTH]
[--enable-reverse-proxy] [--rewrite-host-header] [--enable-metrics]
[--metrics-path METRICS_PATH] [--pac-file PAC_FILE]
[--pac-file-url-path PAC_FILE_URL_PATH]
[--cloudflare-dns-mode CLOUDFLARE_DNS_MODE]
[--filtered-upstream-hosts FILTERED_UPSTREAM_HOSTS]
[--filtered-client-ips-mode FILTERED_CLIENT_IPS_MODE]
[--filtered-client-ips FILTERED_CLIENT_IPS]
[--filtered-url-regex-config FILTERED_URL_REGEX_CONFIG]
proxy.py v2.4.8.dev8+gc703edac.d20241013
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--tunnel-hostname TUNNEL_HOSTNAME
Default: None. Remote hostname or IP address to which
SSH tunnel will be established.
--tunnel-port TUNNEL_PORT
Default: 22. SSH port of the remote host.
--tunnel-username TUNNEL_USERNAME
Default: None. Username to use for establishing SSH
tunnel.
--tunnel-ssh-key TUNNEL_SSH_KEY
Default: None. Private key path in pem format
--tunnel-ssh-key-passphrase TUNNEL_SSH_KEY_PASSPHRASE
Default: None. Private key passphrase
--tunnel-remote-port TUNNEL_REMOTE_PORT
Default: 8899. Remote port which will be forwarded
locally for proxy.
--threadless Default: True. Enabled by default on Python 3.8+ (mac,
linux). When disabled a new thread is spawned to
handle each client connection.
--threaded Default: False. Disabled by default on Python < 3.8
and windows. When enabled a new thread is spawned to
handle each client connection.
--num-workers NUM_WORKERS
Defaults to number of CPU cores.
--enable-events Default: False. Enables core to dispatch lifecycle
events. Plugins can be used to subscribe for core
events.
--inactive-conn-cleanup-timeout INACTIVE_CONN_CLEANUP_TIMEOUT
Time after which inactive works must be cleaned up.
Increase this value if your backend services are slow
to response or when proxy.py is handling a high
volume. When running proxy.py on Google Cloud (GCP)
you may see 'backend_connection_closed_before_data_sen
t_to_client', with curl clients you may see 'Empty
reply from server' error when '--inactive-conn-
cleanup-timeout' value is low for your use-case.
Default 1 seconds
--enable-proxy-protocol
Default: False. If used, will enable proxy protocol.
Only version 1 is currently supported.
--enable-conn-pool Default: False. (WIP) Enable upstream connection
pooling.
--key-file KEY_FILE Default: None. Server key file to enable end-to-end
TLS encryption with clients. If used, must also pass
--cert-file.
--cert-file CERT_FILE
Default: None. Server certificate to enable end-to-end
TLS encryption with clients. If used, must also pass
--key-file.
--client-recvbuf-size CLIENT_RECVBUF_SIZE
Default: 128 KB. Maximum amount of data received from
the client in a single recv() operation.
--server-recvbuf-size SERVER_RECVBUF_SIZE
Default: 128 KB. Maximum amount of data received from
the server in a single recv() operation.
--max-sendbuf-size MAX_SENDBUF_SIZE
Default: 64 KB. Maximum amount of data to flush in a
single send() operation.
--timeout TIMEOUT Default: 10.0. Number of seconds after which an
inactive connection must be dropped. Inactivity is
defined by no data sent or received by the client.
--local-executor LOCAL_EXECUTOR
Default: 1. Enabled by default. Use 0 to disable. When
enabled acceptors will make use of local (same
process) executor instead of distributing load across
remote (other process) executors. Enable this option
to achieve CPU affinity between acceptors and
executors, instead of using underlying OS kernel
scheduling algorithm.
--backlog BACKLOG Default: 100. Maximum number of pending connections to
proxy server.
--hostname HOSTNAME Default: 127.0.0.1. Server IP address.
--hostnames HOSTNAMES [HOSTNAMES ...]
Default: None. Additional IP addresses to listen on.
--port PORT Default: 8899. Server port. To listen on more ports,
pass them using --ports flag.
--ports PORTS [PORTS ...]
Default: None. Additional ports to listen on.
--port-file PORT_FILE
Default: None. Save server port numbers. Useful when
using --port=0 ephemeral mode.
--unix-socket-path UNIX_SOCKET_PATH
Default: None. Unix socket path to use. When provided
--host and --port flags are ignored
--num-acceptors NUM_ACCEPTORS
Defaults to number of CPU cores.
--version, -v Prints proxy.py version.
--log-level LOG_LEVEL
Valid options: DEBUG, INFO (default), WARNING, ERROR,
CRITICAL. Both upper and lowercase values are allowed.
You may also simply use the leading character e.g.
--log-level d
--log-file LOG_FILE Default: sys.stdout. Log file destination.
--log-format LOG_FORMAT
Log format for Python logger.
--open-file-limit OPEN_FILE_LIMIT
Default: 1024. Maximum number of files (TCP
connections) that proxy.py can open concurrently.
--plugins PLUGINS [PLUGINS ...]
Comma separated plugins. You may use --plugins flag
multiple times.
--enable-dashboard Default: False. Enables proxy.py dashboard.
--basic-auth BASIC_AUTH
Default: No authentication. Specify colon separated
user:password to enable basic authentication.
--enable-ssh-tunnel Default: False. Enable SSH tunnel.
--work-klass WORK_KLASS
Default: proxy.http.HttpProtocolHandler. Work klass to
use for work execution.
--pid-file PID_FILE Default: None. Save "parent" process ID to a file.
--openssl OPENSSL Default: openssl. Path to openssl binary. By default,
assumption is that openssl is in your PATH.
--data-dir DATA_DIR Default: ~/.proxypy. Path to proxypy data directory.
--ssh-listener-klass SSH_LISTENER_KLASS
Default: proxy.core.ssh.listener.SshTunnelListener. An
implementation of BaseSshTunnelListener
--disable-http-proxy Default: False. Whether to disable
proxy.HttpProxyPlugin.
--disable-headers DISABLE_HEADERS
Default: None. Comma separated list of headers to
remove before dispatching client request to upstream
server.
--ca-key-file CA_KEY_FILE
Default: None. CA key to use for signing dynamically
generated HTTPS certificates. If used, must also pass
--ca-cert-file and --ca-signing-key-file
--insecure-tls-interception
Default: False. Disables certificate verification
--ca-cert-dir CA_CERT_DIR
Default: ~/.proxy/certificates. Directory to store
dynamically generated certificates. Also see --ca-key-
file, --ca-cert-file and --ca-signing-key-file
--ca-cert-file CA_CERT_FILE
Default: None. Signing certificate to use for signing
dynamically generated HTTPS certificates. If used,
must also pass --ca-key-file and --ca-signing-key-file
--ca-file CA_FILE Default: /Users/abhinavsingh/Dev/proxy.py/.venv3122/li
b/python3.12/site-packages/certifi/cacert.pem. Provide
path to custom CA bundle for peer certificate
verification
--ca-signing-key-file CA_SIGNING_KEY_FILE
Default: None. CA signing key to use for dynamic
generation of HTTPS certificates. If used, must also
pass --ca-key-file and --ca-cert-file
--auth-plugin AUTH_PLUGIN
Default: proxy.http.proxy.auth.AuthPlugin. Auth plugin
to use instead of default basic auth plugin.
--cache-requests Default: False. Whether to also write request packets
in the cache file.
--cache-by-content-type
Default: False. Whether to extract content by type
from responses. Extracted content type is written to
the cache directory e.g. video.mp4.
--cache-dir CACHE_DIR
Default: /Users/abhinavsingh/.proxy/cache. Flag only
applicable when cache plugin is used with on-disk
storage.
--proxy-pool PROXY_POOL
List of upstream proxies to use in the pool
--enable-web-server Default: False. Whether to enable
proxy.HttpWebServerPlugin.
--enable-static-server
Default: False. Enable inbuilt static file server.
Optionally, also use --static-server-dir to serve
static content from custom directory. By default,
static file server serves out of installed proxy.py
python module folder.
--static-server-dir STATIC_SERVER_DIR
Default: "public" folder in directory where proxy.py
is placed. This option is only applicable when static
server is also enabled. See --enable-static-server.
--min-compression-length MIN_COMPRESSION_LENGTH
Default: 20 bytes. Sets the minimum length of a
response that will be compressed (gzipped).
--enable-reverse-proxy
Default: False. Whether to enable reverse proxy core.
--rewrite-host-header
Default: False. If used, reverse proxy server will
rewrite Host header field before sending to upstream.
--enable-metrics Default: False. Enables metrics.
--metrics-path METRICS_PATH
Default: /metrics. Web server path to serve proxy.py
metrics.
--pac-file PAC_FILE A file (Proxy Auto Configuration) or string to serve
when the server receives a direct file request. Using
this option enables proxy.HttpWebServerPlugin.
--pac-file-url-path PAC_FILE_URL_PATH
Default: /. Web server path to serve the PAC file.
--cloudflare-dns-mode CLOUDFLARE_DNS_MODE
Default: security. Either "security" (for malware
protection) or "family" (for malware and adult content
protection)
--filtered-upstream-hosts FILTERED_UPSTREAM_HOSTS
Default: Blocks Facebook. Comma separated list of IPv4
and IPv6 addresses.
--filtered-client-ips-mode FILTERED_CLIENT_IPS_MODE
Default: blacklist. Can be either "whitelist"
(restrict access to specific IPs)or "blacklist" (allow
everything except specific IPs).
--filtered-client-ips FILTERED_CLIENT_IPS
Default: 127.0.0.1,::1. Comma separated list of IPv4
and IPv6 addresses.
--filtered-url-regex-config FILTERED_URL_REGEX_CONFIG
Default: No config. Comma separated list of IPv4 and
IPv6 addresses.
Proxy.py not working? Report at:
https://github.com/abhinavsingh/proxy.py/issues/new