Neuro4j Workflow is a light-weight workflow engine for Java with Eclipse-based development environment. Workflow allows to build reusable business code and easy integrate your application with other external systems and technologies. It's open-source and distributed under the Apache license. Inspired by Demandware
Neuro4j Workflow.
Java workflow engine with Eclipse-based development environment.
What is new
3.5.1-TBD
- Dynamic flow creation
- AmazonS3 WorkflowLoader
3.4.1 - 02/19/2017
- netflix-hystrix-adapter and [example] (https://github.com/eternita/workflow/tree/master/tutorials/HystrixExample)
Hystrix is a latency and fault tolerance library designed to isolate points of access to remote systems, services and 3rd party libraries, stop cascading failure and enable resilience in complex distributed systems where failure is inevitable.
3.3.1 - 12/05/2016
- typesafe plugin to configure WorkflowEngine from file
- netflix-governator plugin
3.2.1 - 11/26/2016
- Parallel execution inside workflow
- Removed all web plugins
3.1.1 - 11/16/2016
- Asynchronous execution
- WorkflowCache and LoaderCache based on GuavaCache
3.0.1 - 11/07/2016
- XMLFileWorkflowLoader, ClasspathWorkflowLoader, RemoteWorkflowLoader
- Aliases (ex. /myflow -> org.neuro4j.workflow.MyFlow-Start)
2.0.1 - 10/10/2016
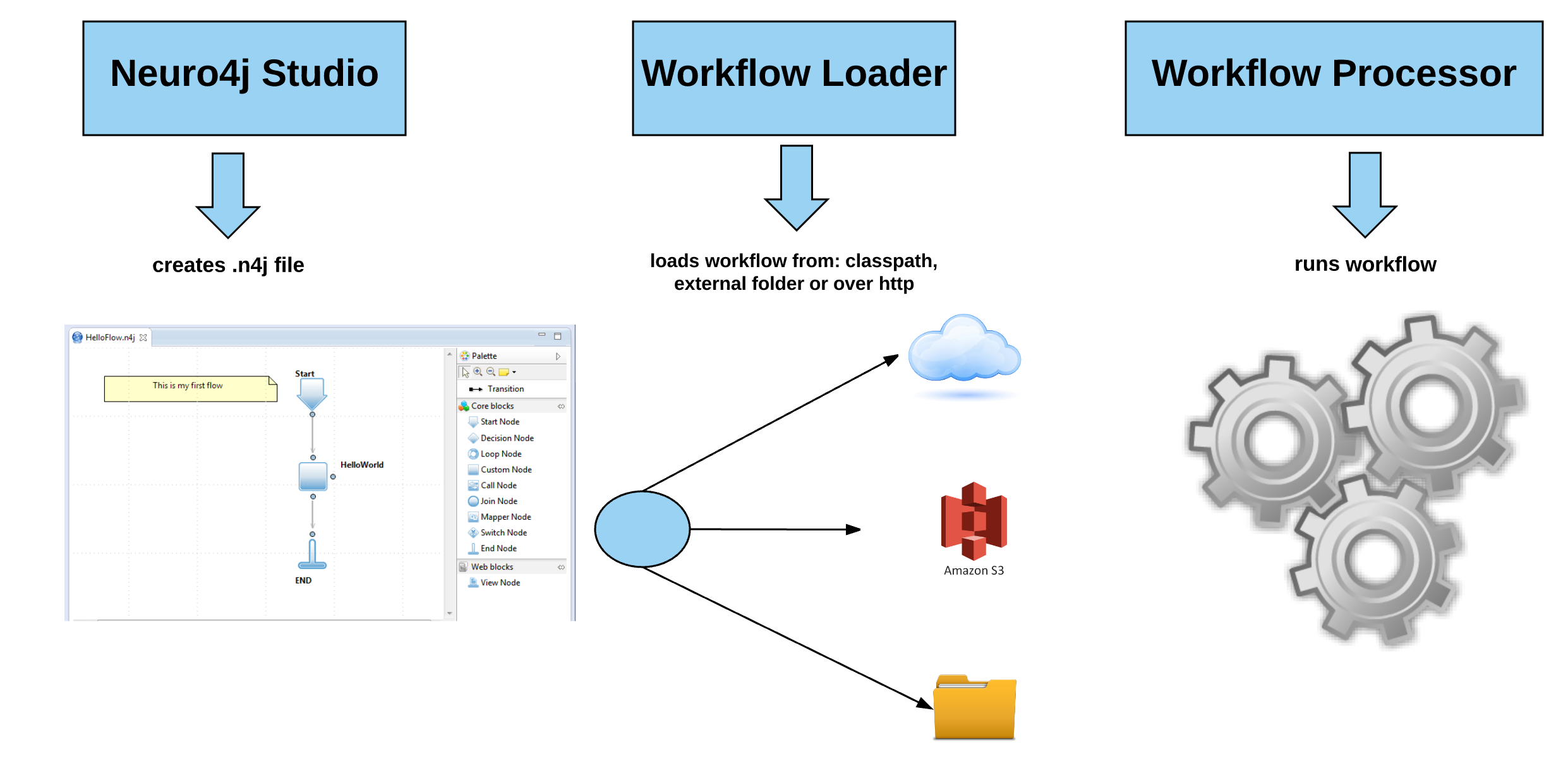
How it works
What are the advantages of Neuro4j Workflow framework?
The advantages of Workflows are as follows:
-
Asynchronous vs synchronous execution
-
Sequential or Parallel processing inside workflow
-
Neuro4j Workflow has layered architecture.
-
It will be much easier to organize, read and support your code.
-
Reusable business code, no need for duplication.
-
Module Development
-
Easy to integrate with different technologies.
-
Dependency Injection.
Developer can use Google Guice library or Spring framework to initialize code. -
Open source.
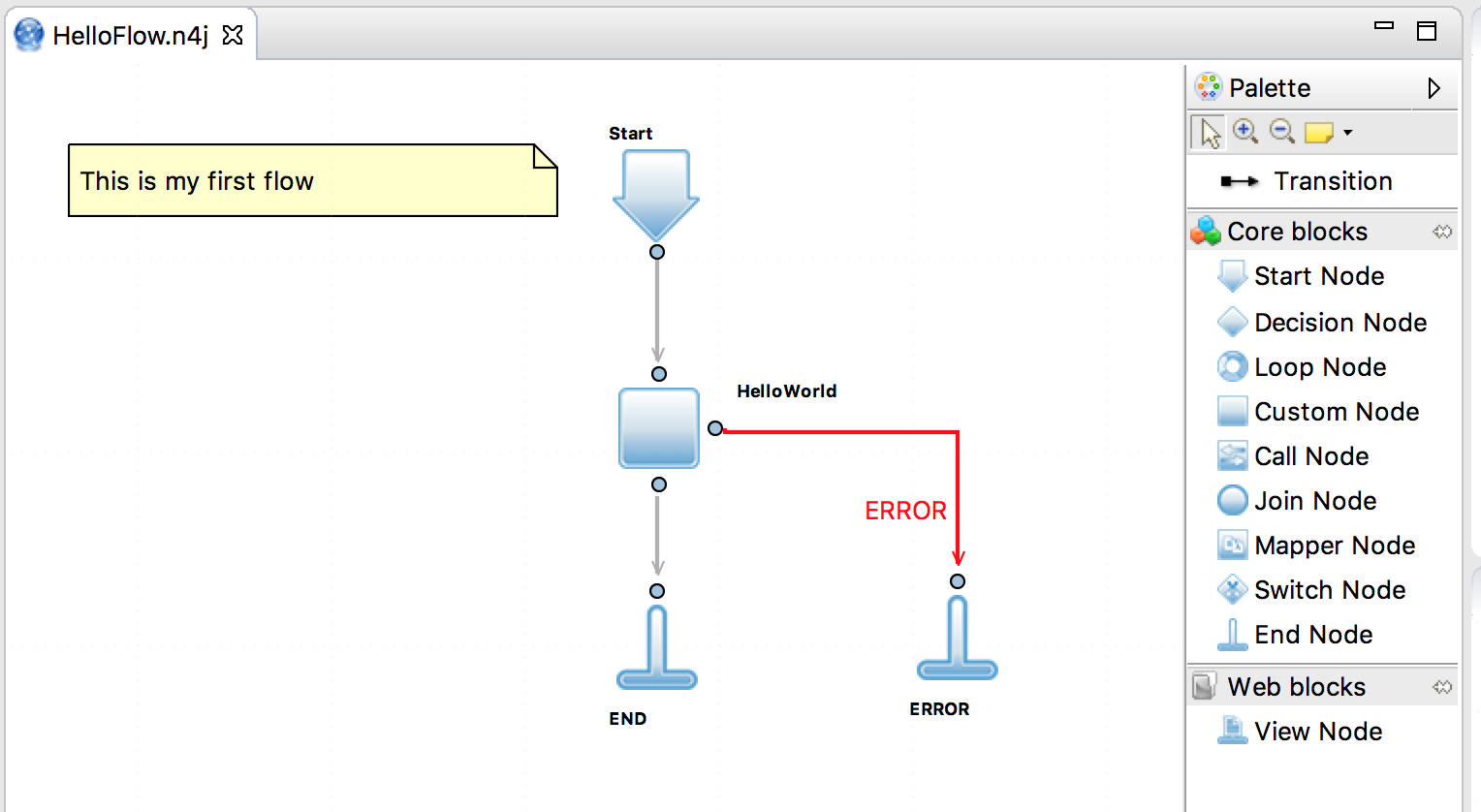
First Flow
This is HelloWorld example how to use Neuro4j Flows.
Flow file org\neuro4j\example\HelloWorld.n4j:
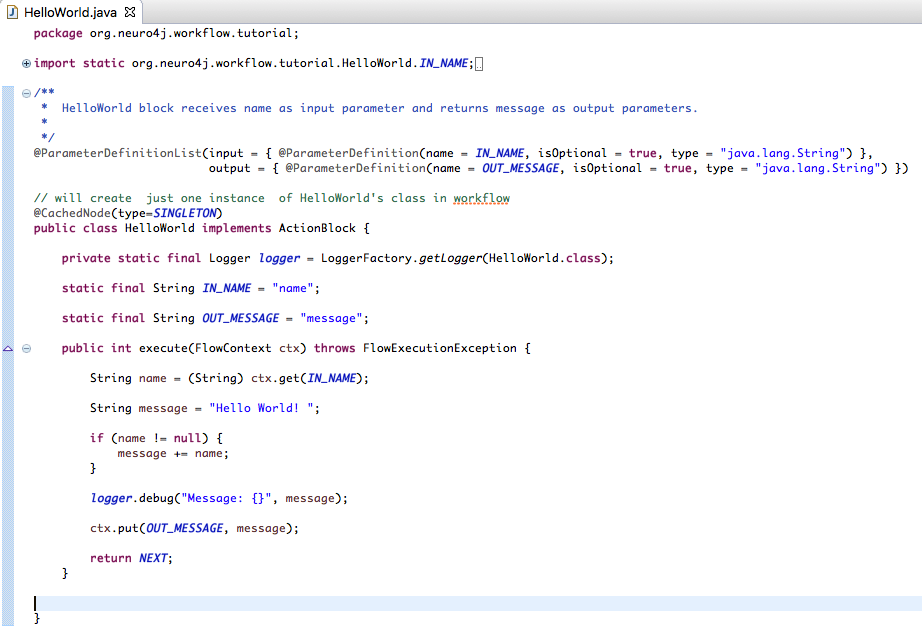
HelloWorld.java
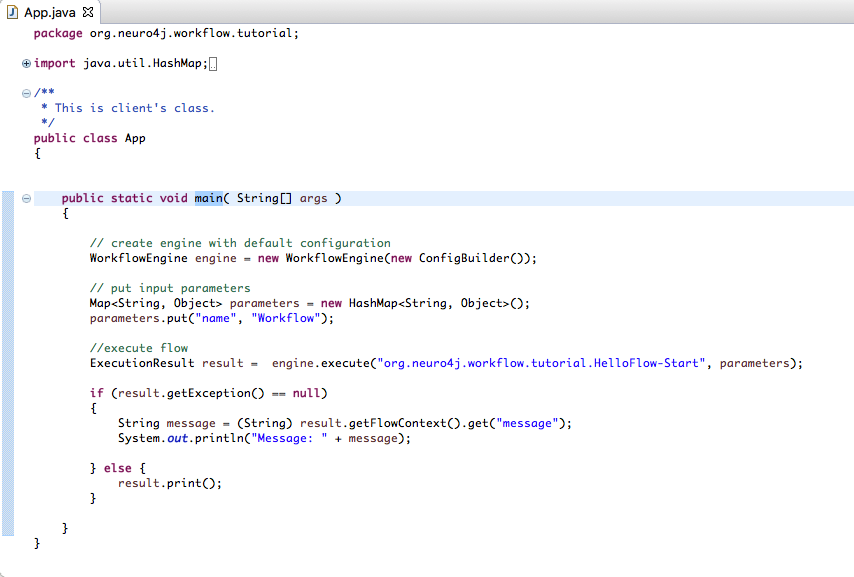
Following code execute flow:
Online documentation how to create first application based on flow available at (http://neuro4j.org/articles/tutorial_hello_world)
Creating HelloWorld workflow with java
// StartNode1 -> CustomNode(o.n.f.e.HelloWorld) -> EndNode
Workflow workflow = new WorkflowBuilder("org.neuro4j.flows.HelloWorld", "StartNode1")
.addCustomNode("org.neuro4j.flows.example.HelloWorld")
.withOnError(createEndNode()).done()
.addEndNode()
.build();
WorkflowEngine engine = new WorkflowEngine(new ConfigBuilder());
WorkflowRequest request = new WorkflowRequest();
request.addParameter("name", "Mister");
ExecutionResult result = engine.execute(workflow, "StartNode1", request);
System.out.println(result.getFlowContext().get("message"));
Sync vs Asyn
Workflow can be executed synchronously:
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<String, Object>();
// add input parameters
WorkflowEngine engine = new WorkflowEngine();
ExecutionResult result = engine.execute("org.neuro4j.workflow.tutorial.HelloFlow-Start", parameters);
if (result.getException() == null)
{
....
}
or asynchronously:
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<String, Object>();
// add input parameters
WorkflowEngine engine = new WorkflowEngine();
FutureTask<ExecutionResult> result = engine.executeAsync("org.neuro4j.workflow.tutorial.HelloFlow-Start", parameters);
while (...) {
if (result.isDone()){
ExecutionResult executionResult = result.get();
}
}
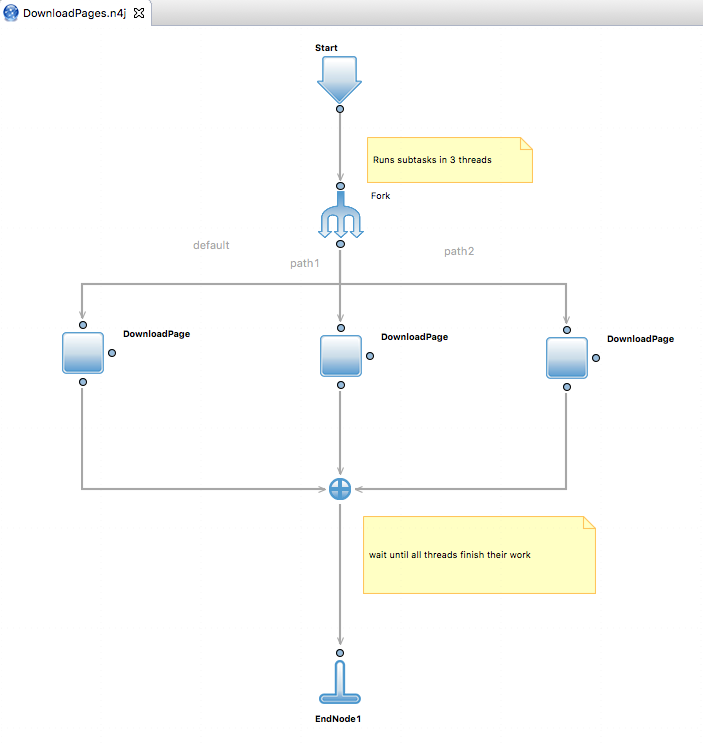
###Sequential vs Parallel (example)
Code inside workflow can be executed in sequential or parallel way.
By default all nodes in workflow will be processing sequentially but developers can specify parallel workflow.
- add SwitchNode to workflow
- change Fork property to “true”
- add a few subflows
- add JoinNode with property Fork=true (shows like JoinNode with blue cross) (processor waits here until all subflows finished)
Example:
Loading workflow
Workflow are loaded using the WorkflowLoader class. neuro4j-core provides three implementations of a WorkflowLoader:
- ClassPathWorkflowLoader
- FileWorkflowLoader
- RemoteWorkflowLoader
WorkflowLoader uses hierarchical delegation - if loader is not able to load workflow it delegates task to next loader
WorkflowEngine engine = new WorkflowEngine(new ConfigBuilder()
.withLoader(new RemoteWorkflowLoader(converter, new ClasspathWorkflowLoader(converter))));
or
File baseDir ...
FileWorkflowLoader loader = new FileWorkflowLoader(converter, new ClasspathWorkflowLoader(converter), baseDir);
WorkflowEngine engine = new WorkflowEngine(new ConfigBuilder()
.withLoader(loader));
ClassPathWorkflowLoader
Loads workflows from folders/jars in classpath
FileWorkflowLoader
Loads workflows from some external folder. Can be used to overwrite workflow from classpath
RemoteWorkflowLoader
Loads remote workflow over http/https.
Workflow cache
WorkflowProcessor keeps all loaded and converted workflows in cache. By default it uses ConcurrentMapWorkflowCache but during development
WorkflowEngine can be configured to use EmptyWorkflowCache.
WorkflowEngine engine = new WorkflowEngine(
new ConfigBuilder()
.withWorkflowCache(EmptyWorkflowCache.INSTANCE));
engine.execute("org.neuro4j.workflow.tutorial.HelloFlow-Start", parameters);
Aliases
WorkflowEngine can be configured to use aliases for workflows.
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("myflow", "org.mydomain.FlowForFileWorkflowLoader-StartNode1");
ConfigBuilder builder = new ConfigBuilder().withAliases(map);
WorkflowEngine engine = new WorkflowEngine(builder);
ExecutionResult result = engine.execute("myflow");
Flow org.mydomain.FlowForFileWorkflowLoader-StartNode1 will be loaded and processed.
ActionHandler
Developers can define ActionHandler to execute code before/after CustomBlock
ActionHandler handler = new ActionHandler() {
@Override
public void preExecute(NodeInfo nodeInfo, FlowContext context, ActionBlock actionBlock) {
}
@Override
public void postExecute(NodeInfo nodeInfo, FlowContext context, ActionBlock actionBlock) {
}
};
Map<Class<? extends ActionBlock>, ActionHandler> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(SystemOutBlock.class, handler);
WorkflowEngine engine = new WorkflowEngine(new ConfigBuilder().withActionRegistry(new ActionHandlersRegistry(map)));
WorkflowProcessor will call handler before/after each call SystemOutBlock.execute(....)
CustomBlock cache
Developers can define cache strategy for each custom block using @CachedNode annotation
- SINGLETON
- NODE
- NONE
SINGLETON
Just one instance of block will be created. ex. SystemOutBlock
NONE
WorkflowLoader will create new instance of block for each call.
NODE
Debuging flow
Neuro4j Studio provides plugin which allows to debug flow in visual editor.
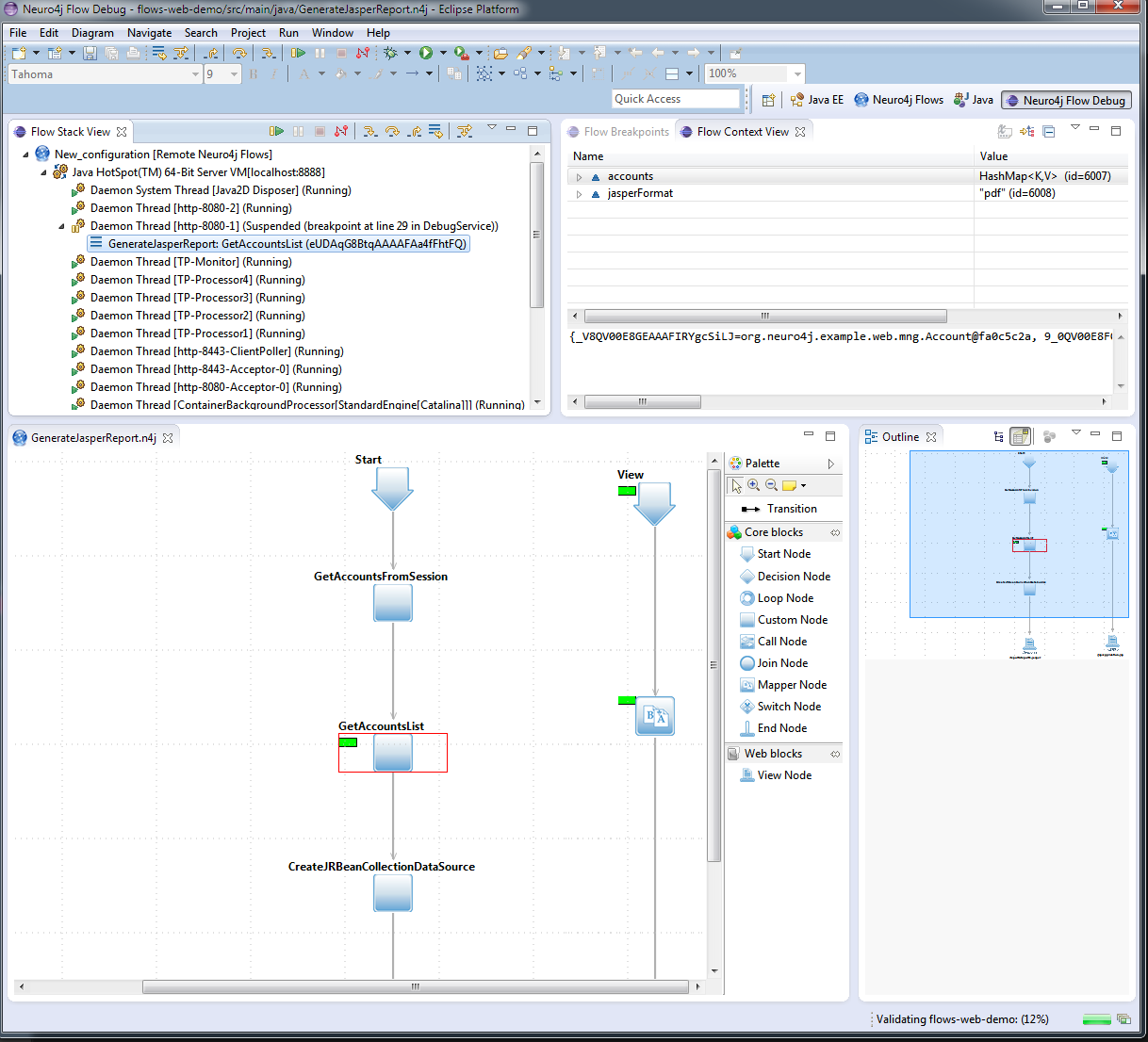
More information about debug plugin avaliable at http://neuro4j.org/docs/wf/flowdebugtool
